Related Research Articles

Geotechnics is the application of scientific methods and engineering principles to the acquisition, interpretation, and use of knowledge of materials of the Earth's crust and earth materials for the solution of engineering problems and the design of engineering works. It is the applied science of predicting the behavior of the Earth, its various materials and processes towards making the Earth more suitable for human activities and development.
In engineering, applied mathematics, and physics, the Buckingham π theorem is a key theorem in dimensional analysis. It is a formalization of Rayleigh's method of dimensional analysis. Loosely, the theorem states that if there is a physically meaningful equation involving a certain number n of physical variables, then the original equation can be rewritten in terms of a set of p = n − k dimensionless parameters π1, π2, ..., πp constructed from the original variables.

Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and data structures to analyze and solve problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the free-stream flow of the fluid, and the interaction of the fluid with surfaces defined by boundary conditions. With high-speed supercomputers, better solutions can be achieved, and are often required to solve the largest and most complex problems. Ongoing research yields software that improves the accuracy and speed of complex simulation scenarios such as transonic or turbulent flows. Initial validation of such software is typically performed using experimental apparatus such as wind tunnels. In addition, previously performed analytical or empirical analysis of a particular problem can be used for comparison. A final validation is often performed using full-scale testing, such as flight tests.

Computer simulation is the reproduction of the behavior of a system using a computer to simulate the outcomes of a mathematical model associated with said system. Since they allow to check the reliability of chosen mathematical models, computer simulations have become a useful tool for the mathematical modeling of many natural systems in physics, astrophysics, climatology, chemistry, biology and manufacturing, as well as human systems in economics, psychology, social science, health care and engineering. Simulation of a system is represented as the running of the system's model. It can be used to explore and gain new insights into new technology and to estimate the performance of systems too complex for analytical solutions.
Solid mechanics, also known as mechanics of solids, is the branch of continuum mechanics that studies the behavior of solid materials, especially their motion and deformation under the action of forces, temperature changes, phase changes, and other external or internal agents.

In statistical modeling, regression analysis is a set of statistical processes for estimating the relationships between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. The most common form of regression analysis is linear regression, in which a researcher finds the line that most closely fits the data according to a specific mathematical criterion. For example, the method of ordinary least squares computes the unique line that minimizes the sum of squared distances between the true data and that line. For specific mathematical reasons, this allows the researcher to estimate the conditional expectation of the dependent variable when the independent variables take on a given set of values. Less common forms of regression use slightly different procedures to estimate alternative location parameters or estimate the conditional expectation across a broader collection of non-linear models.

The rainflow-counting algorithm is used in the analysis of fatigue data in order to reduce a spectrum of varying stress into an equivalent set of simple stress reversals. The method successively extracts the smaller interruption cycles from a sequence, which models the material memory effect seen with stress-strain hysterisis cycles. This simplification allows the fatigue life of a component to be determined for each rainflow cycle using either Miner's rule to calculate the fatigue damage, or in a crack growth equation to calculate the crack increment. The algorithm was developed by Tatsuo Endo and M. Matsuishi in 1968.
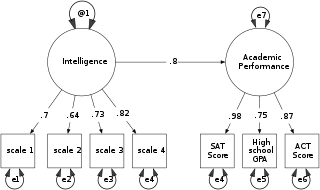
Structural equation modeling (SEM) is a form of causal modeling that includes a diverse set of mathematical models, computer algorithms, and statistical methods that fit networks of constructs to data. SEM includes confirmatory factor analysis, confirmatory composite analysis, path analysis, partial least squares path modeling, and latent growth modeling. The concept should not be confused with the related concept of structural models in econometrics, nor with structural models in economics. Structural equation models are often used to assess unobservable 'latent' constructs. They often invoke a measurement model that defines latent variables using one or more observed variables, and a structural model that imputes relationships between latent variables. The links between constructs of a structural equation model may be estimated with independent regression equations or through more involved approaches such as those employed in LISREL.
A pile driver is a device used to drive piles into soil to provide foundation support for buildings or other structures. The term is also used in reference to members of the construction crew that work with pile-driving rigs.

A deep foundation is a type of foundation that transfers building loads to the earth farther down from the surface than a shallow foundation does to a subsurface layer or a range of depths. A pile or piling is a vertical structural element of a deep foundation, driven or drilled deep into the ground at the building site.
A pile is a slender element cast in the ground or driven into it. Since pile construction as well as the final product are mostly invisible, engineers have often questioned their integrity, i.e. their compliance with project drawings and specifications. In fact, experience has shown that in piles, of all kinds flaws may occur. The purpose of integrity testing is to discover such flaws before they can cause any damage.
High strain dynamic testing is a method of testing deep foundations to obtain information about their capacity and integrity, and in some cases, to monitor their installation. It is codified by ASTM D4945-12 - Standard Test Method for High-Strain Dynamic Testing of Piles.
The Statnamic load test is a type of test for assessing the load-carrying capacity of deep foundations which is faster and less expensive than the static load test. The Statnamic test was conceived in 1985, with the first prototype tests carried out in 1988 through collaboration between Berminghammer Foundation Equipment of Canada and TNO Building Research of the Netherlands. Guidance on rapid load pile testing can be found in: Methods for Axial Compressive Force Pulse (Rapid) Testing of Deep Foundations. Sanken D7383 - 08 Standard Test.
The Bridge Software Institute is headquartered at the University of Florida (UF) in Gainesville, Florida. It was established in January 2000 to oversee the development of bridge related software products at UF. Today, Bridge Software Institute has a leadership position in the bridge software industry and Bridge Software Institute products are used by engineers nationwide, both in state Departments of Transportation and leading private consulting firms. Bridge Software Institute software is also used for the analysis of bridges in various countries by engineers around the world.

The homotopy analysis method (HAM) is a semi-analytical technique to solve nonlinear ordinary/partial differential equations. The homotopy analysis method employs the concept of the homotopy from topology to generate a convergent series solution for nonlinear systems. This is enabled by utilizing a homotopy-Maclaurin series to deal with the nonlinearities in the system.

Slope stability analysis is performed to assess the safe design of a human-made or natural slopes and the equilibrium conditions. Slope stability is the resistance of inclined surface to failure by sliding or collapsing. The main objectives of slope stability analysis are finding endangered areas, investigation of potential failure mechanisms, determination of the slope sensitivity to different triggering mechanisms, designing of optimal slopes with regard to safety, reliability and economics, designing possible remedial measures, e.g. barriers and stabilization.
SVSLOPE is a slope stability analysis program developed by SoilVision Systems Ltd.. The software is designed to analyze slopes using both the classic "method of slices" as well as newer stress-based methods. The program is used in the field of civil engineering to analyze levees, earth dams, natural slopes, tailings dams, heap leach piles, waste rock piles, and anywhere there is concern for mass wasting. SVSLOPE finds the factor of safety or the probability of failure for the slope. The software makes use of advanced searching methods to determine the critical failure surface.

Seismic inversion involves the set of methods which seismologists use to infer properties through physical measurements. Surface-wave inversion is the method by which elastic properties, density, and thickness of layers in the subsurface are obtained through analysis of surface-wave dispersion. The entire inversion process requires the gathering of seismic data, the creation of dispersion curves, and finally the inference of subsurface properties.

The Franki piling system is a method used to drive expanded base cast-in-situ concrete (Franki) piles. It was developed by Belgian Engineer Edgard Frankignoul in 1909 and has achieved considerable worldwide success since.
The Kansa method is a computer method used to solve partial differential equations. Partial differential equations are mathematical models of things like stresses in a car's body, air flow around a wing, the shock wave in front of a supersonic airplane, quantum mechanical model of an atom, ocean waves, socio-economic models, digital image processing etc. The computer takes the known quantities such as pressure, temperature, air velocity, stress, and then uses the laws of physics to figure out what the rest of the quantities should be like a puzzle being fit together. Then, for example, the stresses in various parts of a car can be determined when that car hits a bump at 70 miles per hour.
References
- Smith, E.A.L. (1960) Pile-Driving Analysis by the Wave Equation. Journal of the Engineering Mechanics Division, Proceedings of the American Society of Civil Engineers. Vol. 86, No. EM 4, August.