
Branford is a shoreline town located on Long Island Sound in New Haven County, Connecticut, United States, about 6 miles (10 km) east of downtown New Haven. The town is part of the South Central Connecticut Planning Region. Branford borders East Haven to the west, Guilford to the east, and North Branford to the north. The population was 28,273 in the 2020 census.

Miller Place is a hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) in the Town of Brookhaven, Suffolk County, New York, United States. Despite preserving much of its historic identity, changes in the 20th century have transitioned the hamlet into a desirable and densely populated suburban area. The population was 11,723 at the 2020 census.

Stony Brook is a hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) in the Town of Brookhaven in Suffolk County, New York, United States, on the North Shore of Long Island. Begun in the colonial era as an agricultural enclave, the hamlet experienced growth first as a resort town and then to its current state as one of Long Island's major tourist towns and centers of education. Despite being referred to as a village by residents and tourists alike, Stony Brook has never been legally incorporated by the state. The population was 13,740 at the 2010 census.
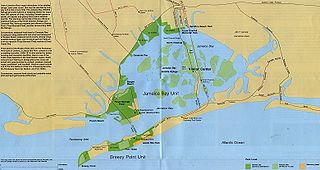
Jamaica Bay is an estuary on the southern portion of the western tip of Long Island, in the U.S. state of New York. The estuary is partially man-made, and partially natural. The bay connects with Lower New York Bay to the west, through Rockaway Inlet, and is the westernmost of the coastal lagoons on the south shore of Long Island. Politically, it is primarily divided between the boroughs of Brooklyn and Queens in New York City, with a small part touching Nassau County.

Jamaica Bay Wildlife Refuge is a wildlife refuge in New York City managed by the National Park Service as part of Gateway National Recreation Area. It is composed of the open water and intertidal salt marshes and wetlands of Jamaica Bay. It lies entirely within the boundaries of New York City, divided between the boroughs of Brooklyn to the west and Queens to the east.

Brookhaven is a large suburban town in Suffolk County, Long Island, New York. With a population of 488,497 as of 2022, it is the second most populous town in the United States and in New York and the third most populous community in the state.

Cove Island Park is an 83-acre park, beach and recreation area in the Cove section of Stamford, Connecticut, located on Long Island Sound.

Assateague Island National Seashore is a unit of the National Park Service system of the U.S. Department of the Interior. Located on the East Coast along the Atlantic Ocean in Maryland and Virginia, Assateague Island is the largest natural barrier island ecosystem in the Middle Atlantic states region that remains predominantly unaffected by human development. Located within a three-hour drive to the east and south of Richmond, Washington, Baltimore, Wilmington, Philadelphia major metropolitan areas plus north of the several clustered smaller cities around Hampton Roads harbor of Virginia with Newport News, Hampton, Norfolk, Portsmouth, Chesapeake and Virginia Beach. The National Seashore offers a setting in which to experience a dynamic barrier island and to pursue a multitude of recreational opportunities. The stated mission of the park is to preserve and protect “unique coastal resources and the natural ecosystem conditions and processes upon which they depend, provide high-quality resource-based recreational opportunities compatible with resource protection and educate the public as to the values and significance of the area”.
The Stewart B. McKinney National Wildlife Refuge is a 950-acre (384.5 ha) National Wildlife Refuge in ten units across the U.S. state of Connecticut. Located in the Atlantic Flyway, the refuge spans 70 miles (110 km) of Connecticut coastline and provides important resting, feeding, and nesting habitat for many species of wading birds, shorebirds, songbirds and terns, including the endangered roseate tern. Adjacent waters serve as wintering habitat for brant, scoters, American black duck, and other waterfowl. Overall, the refuge encompasses over 900 acres (364.2 ha) of barrier beach, intertidal wetland and fragile island habitats.

Iona Island is a 556-acre (2.25 km2) island of the Hudson River in the town of Stony Point, New York, on its west bank. The island is located approximately one mile (1.6 km) south of the Bear Mountain Bridge and is separated from the Hudson's western shore by mudflats and freshwater tidal marshes. It is part of Bear Mountain State Park, although it is occasionally listed separately as Iona Island State Park. From 1899 to 1947 the island was used as the Naval Ammunition Depot Iona Island.

The Boston Post Road Historic District is a 286-acre (116 ha) National Historic Landmark District in Rye, New York, and is composed of five distinct and adjacent properties. Within this landmarked area are three architecturally significant, pre-Civil War mansions and their grounds; a 10,000-year-old Indigenous peoples site and viewshed; a private cemetery, and a nature preserve. It is one of only 11 National Historic Landmark Districts in New York State and the only National Historic Landmark District in Westchester County. It touches on the south side of the nation's oldest road, the Boston Post Road, which extends through Rye. A sandstone Westchester Turnpike marker "24", inspired by Benjamin Franklin's original mile marker system, is set into a wall that denotes the perimeter of three of the contributing properties. The district reaches to Milton Harbor of Long Island Sound. Two of the properties included in the National Park Service designation are anchored by Greek Revival buildings; the third property is dominated by a Gothic Revival structure that was designed by Alexander Jackson Davis.

The Chincoteague National Wildlife Refuge is a 14,000-acre (57 km2) wildlife preserve operated by the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service. It is primarily located on the Virginia half of Assateague Island with portions located on the Maryland side of the island, as well as Morris Island and Wildcat Marsh. Mostly composed of beach, dunes, marsh, and maritime forest, the refuge contains a large variety of wildlife, including the Chincoteague pony. The purpose of the refuge is to maintain, regulate, and preserve animal and plant species as well as their habitats for present and future generations.

Flax Pond is a tidal estuary located in Old Field, New York, on the north shore of Long Island. As a 146-acre (0.59 km2) salt marsh, Flax Pond is a natural site of great biodiversity and natural beauty. Flax Pond is owned by the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation (NYSDEC) and is accessed by researchers at Stony Brook University as a Marine Lab for the state

New York State Wildlife Management Areas (WMAs) are conservation areas managed by the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation (NYSDEC) primarily for the benefit of wildlife, and used extensively by the public for hunting, fishing, and trapping. As of 2016, the NYSDEC owns and maintains 113 WMAs, with a total area of approximately 197,000 acres. The Wildlife Management Areas program is administered by the Division of Fish, Wildlife and Marine Resources of the NYSDEC.

The Albany Bulb is a former landfill largely owned by the City of Albany, in California. The Bulb is the west end of a landfill peninsula jutting west from the east shore of San Francisco Bay. The term "Bulb" is often used to refer to the entire peninsula, which includes the Albany Plateau, north of Buchanan Street at its base; the high narrow "Neck," and the round "Bulb." The Bulb is part of the City of Albany, and can be reached via Buchanan Street or the Bay Trail along the east side of San Francisco Bay. Landmarks include, Mary's Mask, Gritchell's Bay, and Mad Marc's Castle. The Geotag for Gritchell's Bay is 37.8908083, -122.3257826.
Jackfish Lake is a lake in Parkland County, Alberta.

Gamecock Cottage is an historic building located at Stony Brook in Brookhaven Town, in Suffolk County, New York on Long Island. It was built in 1876 for storage of oars and sliding-seat rowboats and is the only remaining wooden beach cottage that was part of West Meadow Beach. It is located at the southernmost point of a peninsula within what is now part of the West Meadow Wetlands Reserve, as the official public beach is now restricted to the north. The Gamecock Cottage sits at the southern endpoint of West Meadow Lane, which was once called Trustees Road.

Cedar Beach is a public beach on the North Shore of Long Island, located within the Town of Brookhaven in Suffolk County, New York. The beach itself spans 3,450 feet on a peninsula that divides Mount Sinai Harbor from the Long Island Sound. Cedar Beach is located in the hamlet of Mount Sinai, while the peninsula on which it sits is accessed most directly from the adjacent hamlet of Miller Place.




















