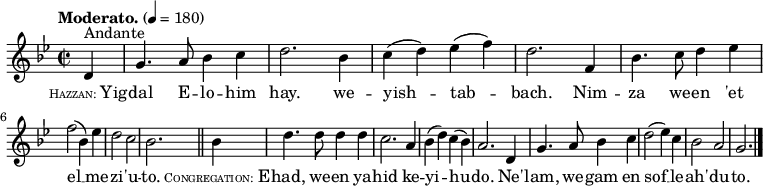Sephardic tunes
Yigdal far surpasses Adon Olam in the number of its traditional tunes and the length of time during which they have been traditional. In the Spanish ritual, in its Dutch-and English-speaking tradition, the hymn is often sung, according to the general Sephardic custom (compare e.g., Yah Shimkha ), to some "representative" melody of the particular day. Thus, for example, it is chanted at the close of evening service on Rosh Hashana to the tune of 'Et Sha'are Raẓon . On Friday evening the Sabbath Yigdal is customarily sung to the same melody as are Adon Olam and Ein Keloheinu. On the three pilgrimage festivals, the melody shown here is the tune favored. Its old Spanish character is evident.
Ashkenazic tunes
In the Eastern Ashkenazic rite Yigdal commences the morning prayer. In some communities, it is sung at the close of the evening service on Sabbaths and festivals, but in other communities is replaced by Adon Olam or simply omitted; in some communities, it is recited only on Festivals and not on the Sabbath. In London for fully two centuries there has been allotted to the hymn, according to the occasion, a definite tradition of tunes, all of which are antiphonal between chazzan and congregation. The most familiar of these tunes is the Friday evening Yigdal. It is utilized also in Germany and in some parts of Poland and Bohemia as a festival Yigdal. The melody may date from the 17th century or perhaps earlier. The tune was also used by the hazzan Myer Lyon (who also sang on the London opera stage as 'Michael Leoni') at the Great Synagogue of London, where it was heard by the Methodist Thomas Olivers; he adapted the tune for the English hymn The God of Abraham Praise (see below).
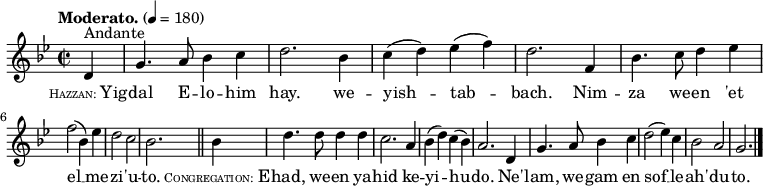
Next in importance comes the melody reserved for the solemn evenings of Rosh Hashana and Yom Kippur, and introduced, in the spirit of Psalm 137:6, into the service of Simhat Torah. This melody is constructed in the harmonic major scale (EFG # ABCD # E) with its two augmented seconds (see synagogue music), and is the inspiration of some Polish precentor, dating perhaps from the early 17th century, and certainly having spread westward from the Slavic region.
In the German use of Bavaria and the Rhineland, the old tradition has preserved a contrasting "Yigdal" for Rosh Hashana and Yom Kippur that is equally antique, but built on a diatonic scale and reminiscent of the morning service of the day.
For the evenings of the Three Pilgrimage Festivals, the old London tradition has preserved three characteristic melodies from at least the early 18th century, probably brought from north Germany or Bohemia. That for Passover illustrates the old custom according to which the precentor solemnly dwells on the last creed, that on the resurrection of the dead (in this case to a "representative" theme common to Passover and to Purim), and is answered by the choristers with an expression of confident assurance. The choral response here given received its final shaping from David Mombach. Yigdal for Shavu`oth has a solemn tone, strikingly contrasting with those for the other festivals.
The tune for Sukkot displays a gaiety quite rare in synagogal melody. It was employed by Isaac Nathan, in 1815, as the air for one of Lord Byron's " Hebrew Melodies ", being set by him to the verses "The Wild Gazelle" in such a manner as to utilize the contrasting theme then chanted by the hazzan to the last line as in the Passover "Yigdal".
Other old tunes for the hymn, such as the melody of Alsatian origin used on "Shabbat Hagadol" before Passover, are preserved in local or family tradition (cf. Zemirot ).
Opposition to its addition to the liturgy
Most Hasidic Jews do not recite Yigdal as part of their liturgy, as Isaac Luria reportedly omitted it from his siddur. Luria rejected any poem which he dated after the Talmudic era as insufficiently Kabbalistic. [5] However, based on the teachings of Isaiah Horowitz, most do consider Yigdal to be a sacred hymn, even if they do not sing it.
For similar reasons, Syrian Jews omit both Adon Olam and Yigdal at the end of the morning and evening services, but sing them on other occasions (Adon Olam at the end of the Baqashot and Yigdal before Kiddush on Friday night).
Rabbi Joseph B. Soloveitchik opposed the recitation of Yigdal at the end of prayers, as he saw it as an improper imitation of the Christian custom to recite a catechism at the end of prayers. [6]