
A diacritic is a glyph added to a letter or to a basic glyph. The term derives from the Ancient Greek διακριτικός, from διακρίνω. The word diacritic is a noun, though it is sometimes used in an attributive sense, whereas diacritical is only an adjective. Some diacritics, such as the acute ⟨ó⟩, grave ⟨ò⟩, and circumflex ⟨ô⟩, are often called accents. Diacritics may appear above or below a letter or in some other position such as within the letter or between two letters.

A breve is the diacritic mark ◌̆, shaped like the bottom half of a circle. As used in Ancient Greek, it is also called brachy, βραχύ. It resembles the caron but is rounded, in contrast to the angular tip of the caron. In many forms of Latin, ◌̆ is used for a shorter, softer variant of a vowel, such as "Ĭ", where the sound is nearly identical to the English /i/.

Ü is a Latin script character composed of the letter U and the diaeresis diacritical mark. In some alphabets such as those of a number of Romance languages or Guarani it denotes an instance of regular U to be construed in isolation from adjacent characters with which it would usually form a larger unit; other alphabets like the Azerbaijani, Estonian, German, Hungarian and Turkish ones treat it as a letter in its own right. In those cases it typically represents a close front rounded vowel.
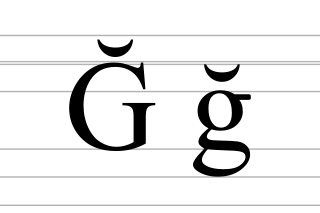
Ğ is a Latin letter found in the Turkish and Azerbaijani alphabets as well as the Latin alphabets of Zazaki, Laz, Crimean Tatar, Tatar, and Kazakh. It traditionally represented the voiced velar fricative or the voiced uvular fricative. However, in Turkish, the phoneme has in most cases been reduced to a silent letter, serving as a vowel-lengthener. In Dobrujan Tatar it represents the voiced palato-alveolar affricate.

The Cyrillic I is a letter used in almost all modern Cyrillic alphabets with the exception of Belarusian.
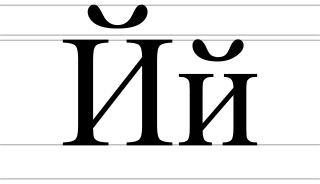
Short I or Yot/Jot or I with breve, Russian: и с бреве) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. It is made of the Cyrillic letter И with a breve.

Yeru or Eru, usually called Y in modern Russian or Yery or Ery historically and in modern Church Slavonic, is a letter in the Cyrillic script. It represents the close central unrounded vowel after non-palatalised (hard) consonants in the Belarusian and Russian alphabets.
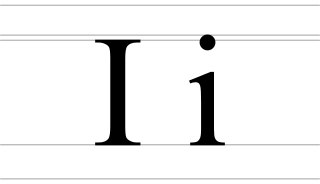
The dotted i, also called Ukrainian I, decimal i or soft-dotted i, is a letter of the Cyrillic script. It commonly represents the close front unrounded vowel, like the pronunciation of ⟨i⟩ in English "machine". It is used in the orthographies of Belarusian, Kazakh, Khakas, Komi, Carpathian Rusyn and Ukrainian and quite often, but not always, is the equivalent of the Cyrillic letter i (И и) as used in Russian and other languages. However, the letter І was also used in Russian before the Bolshevik reform of 1918.

The Latin-derived letters dotted İ i and dotless I ı, which are distinct letters in the alphabets of a number of Turkic languages, unlike in English and most languages using the Latin script, have caused some issues in computing.

The letter Ƣ has been used in the Latin orthographies of various, mostly Turkic languages, such as Azeri or the Jaꞑalif orthography for Tatar. It is also included in pinyin alphabets for Kazakh and Uyghur; and in the 1928 Soviet Kurdish Latin alphabet. It usually represents a voiced velar fricative but is sometimes used for a voiced uvular fricative. All orthographies that used the letter have been phased out and so it is not well-supported in fonts. It can still be seen in pre-1983 books published in the People’s Republic of China.
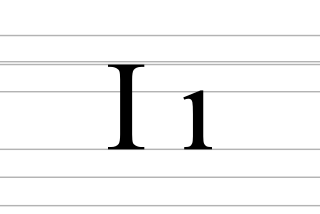
I, or ı, called dotless i, is a letter used in the Latin-script alphabets of Azerbaijani, Crimean Tatar, Gagauz, Kazakh, Tatar and Turkish. It commonly represents the close back unrounded vowel, except in Kazakh where it represents the near-close front unrounded vowel. All of the languages it is used in also use its dotted counterpart İ while not using the basic Latin letter I.

The Kazakh language is written in three scripts – Cyrillic, Latin, and Arabic – each having a distinct alphabet. The Arabic script is used in Iran, Afghanistan, and China, while the Cyrillic script is used in Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Mongolia. In October 2017, a presidential decree in Kazakhstan ordered a transition from the Cyrillic to Latin script to be phased in from 2023 to 2031.
Diacritical marks of two dots¨, placed side-by-side over or under a letter, are used in several languages for several different purposes. The most familiar to English-language speakers are the diaeresis and the umlaut, though there are numerous others. For example, in Albanian, ë represents a schwa. Such diacritics are also sometimes used for stylistic reasons.

J, or j, is the tenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its usual name in English is jay, with a now-uncommon variant jy.

The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Greek alphabet was altered by the Etruscans, and subsequently their alphabet was altered by the Ancient Romans. Several Latin-script alphabets exist, which differ in graphemes, collation and phonetic values from the classical Latin alphabet.

Yery with diaeresis is a letter of the Cyrillic script. Its form is derived from the Cyrillic letter Yery. In Unicode, this letter is known as "Yeru with Diaeresis".
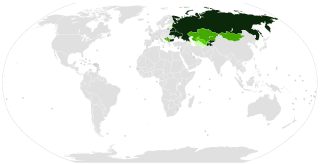
Numerous Cyrillic alphabets are based on the Cyrillic script. The early Cyrillic alphabet was developed in the 9th century AD and replaced the earlier Glagolitic script developed by the theologians Cyril and Methodius. It is the basis of alphabets used in various languages, past and present, Slavic origin, and non-Slavic languages influenced by Russian. As of 2011, around 252 million people in Eurasia use it as the official alphabet for their national languages. About half of them are in Russia. Cyrillic is one of the most-used writing systems in the world. The creator is Saint Clement of Ohrid from the Preslav literary school in the First Bulgarian Empire.
JCUKEN is the main Cyrillic keyboard layout for the Russian language in computers and typewriters.
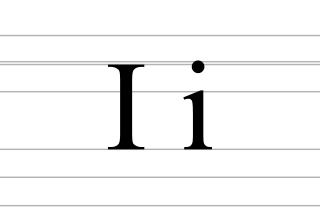
I, or i, is the ninth letter and the third vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is i, plural ies.

Dania is the traditional linguistic transcription system used in Denmark to describe the Danish language. It was invented by Danish linguist Otto Jespersen and published in 1890 in the Dania, Tidsskrift for folkemål og folkeminder magazine from which the system was named.


















