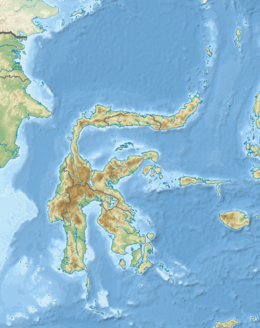
The Banggai Regency is a regency located at the eastern end of Central Sulawesi Province of Indonesia. It makes up a re-established regency (kabupaten), created on 4 October 1999 by splitting the existing Banggai Regency into this smaller Banggai Regency situated on the mainland of Sulawesi and a new Banggai Islands Regency comprising the offshore islands to the southeast which are separated from mainland Sulawesi by the Peleng Straits. The residual Banggai Regency covers an area of 9,672.70 km2 and had a population of 323,626 at the 2010 census and 362,275 at the 2020 census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 373,693.

The 2007 Bengkulu earthquakes were a series of megathrust earthquakes that struck the Sunda Trench off the coast of Sumatra, Indonesia, with three of magnitude 7 or greater. A series of tsunami bulletins was issued for the area. The most powerful of the series had a magnitude of 8.4, which makes it in the top 20 of the largest earthquakes ever recorded on a seismograph.
The 1992 Flores earthquake and tsunami occurred on 12 December on the island of Flores in Indonesia. With a magnitude of 7.8 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe), it was the largest and also the deadliest earthquake in 1992 and in the Lesser Sunda Islands region. The earthquake was caused by slip on the Flores Thrust fault. This fault dips to the south underneath Flores Island. The epicenters of most earthquakes on the Flores Thrust are on Flores Island.

On 4 June 2000, at 23:28 WIB, southern Sumatra in Indonesia was struck by an earthquake of 7.9 with a maximum Mercalli intensity of VI (Strong). The event occurred off the coast near Enggano Island. There were more than 100 fatalities and up to 2,585 injuries. Over 340 aftershocks shook the area throughout the rest of 2000, one just eleven minutes after the mainshock.
Three powerful earthquakes struck the islands of New Britain and New Ireland, Papua New Guinea on 16-17 November 2000, starting with a Mw 8.0–8.2 strike-slip event that occurred on November 16 at 04:54:56 UTC. A Mw 7.3–7.8 thrust earthquake followed at 07:42:16 UTC with its epicenter 170 km (110 mi) southeast of the first event at the southern end of its rupture zone south of New Ireland. Another Mw 7.3–7.8 thrust event occurred on November 17 at 21:01:56 UTC, occurring 174 km (108 mi) southwest of the first event with an inland epicenter at Pomio District, East New Britain Province.

The Banggai Archipelago is a group of islands located at the far eastern end of Central Sulawesi, Indonesia. It makes up a regency (kabupaten) of Central Sulawesi Province of Indonesia, created on 4 October 1999 by splitting the existing Banggai Regency into a residual Banggai Regency situated on the mainland of Sulawesi and a new Banggai Islands Regency then comprising the entire archipelago. On 14 December 2012 a splitting of the Banggai Islands archipelago took place with the removal of the more southerly seven districts from the 13-year-old regency to form a separate Banggai Laut Regency.
The 2013 Balochistan earthquakes were the deadliest to affect Pakistan since 2005. The mainshock, occurring on 24 September, had a moment magnitude of 7.8 and maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent). It had an epicenter located in Awaran District, 113 km (70 mi) northwest of Bela. The mainshock killed over 820 people, injured hundreds of others, and left 100,000 people homeless. The Awaran District was among the worst affected with 80 percent of its housing stock damaged or destroyed. On 28 September, the region was affected by a Mw 6.8 aftershock, killing an additional 15 people. Rescue and recovery efforts were severely hampered by insurgents who attacked military troops sent to distribute aid. These attacks also prompted the Pakistan government to close its doors to international aid.

On May 4, 2018, an earthquake with a magnitude of 6.9 struck Hawaii island in the Hawaii archipelago at around 12:33 p.m. local time. The earthquake's epicenter was near the south flank of Kīlauea, which has been the site of seismic and volcanic activity since late April of that year. According to the United States Geological Survey the quake was related to the new lava outbreaks at the volcano, and it resulted in the Hilina Slump moving about two feet. It was the largest earthquake to affect Hawaii since the 1975 earthquake, which affected the same region, killing two people and injuring another 28.
The Palu-Koro Fault or Palu-Koro Fault System is a major active NNW-SSE trending left-lateral strike-slip fault zone on the island of Sulawesi in Indonesia. It caused the 2018 Sulawesi earthquake and tsunami.

On 11 October 2018, an earthquake struck off the coast of East Java, Indonesia, with the epicentre located off the coast of Situbondo Regency. The earthquake, which struck at dawn, killed four people in addition to destroying or damaging hundreds of houses, mostly on the small island of Sapudi.
The first and most destructive of the 2020 Iran–Turkey earthquakes occurred on 23 February, near Khoy in north-west Iran, close to the border with Turkey, killing 9 people in Başkale, Van. It hit at 9:23 a.m. local time with a magnitude of 5.8 at a depth of 6 kilometres and the epicenter was Qotur district, according to the Iranian Seismological Center (IRSC). About 10 hours later the same area was hit by another major earthquake of 6.0 Mw .
On January 1, 1996, at 4:05 p.m. Central Indonesia Time, an earthquake with an epicenter in the Makassar Strait struck north of Minahasa on the island of Sulawesi, Indonesia. The earthquake measured 7.9 on the moment magnitude scale and was centered off Tolitoli Regency in Central Sulawesi, or 25 km from the Tonggolobibi village. A tsunami of 2–4 m (6.6–13.1 ft) was triggered by this earthquake as a result. At least 350 buildings were badly damaged, nine people died and 63 people were injured.

The 2013 Craig, Alaska earthquake struck on January 5, at 12:58 am (UTC–7) near the city of Craig and Hydaburg, on Prince of Wales Island. The Mw 7.5 earthquake came nearly three months after an Mw 7.8 quake struck Haida Gwaii on October 28, in 2012. The quake prompted a regional tsunami warning to British Columbia and Alaska, but it was later cancelled. Due to the remote location of the quake, there were no reports of casualties or damage.
A moment magnitude 6.2 earthquake struck Majene Regency in West Sulawesi, Indonesia, on 15 January 2021, at 02:28 WITA. The reverse faulting shock initiated at 18.0 km (11.2 mi) depth with an epicenter inland, located 32 km (20 mi) south of Mamuju. It was preceded by a Mw 5.7 foreshock several hours prior. Shaking from the mainshock was assigned a maximum Modified Mercalli intensity of VI (Strong) in Majene and Mamuju. Four of the five regencies in West Sulawesi were affected. More than 6,000 structures were damaged or destroyed; damage was estimated at Rp829.1 billion rupiah. At least 105 people were confirmed dead; nearly 6,500 were injured and thousands were displaced.
The western coast of West Sulawesi was struck by a major earthquake on 23 February 1969 at 00:36 UTC. It had a magnitude of 7.0 and a maximum felt intensity of VIII on the Modified Mercalli intensity scale. It triggered a major tsunami that caused significant damage along the coast of the Makassar Strait. At least 64 people were killed, with possibly a further 600 deaths caused by the tsunami.

An earthquake occurred off the coast of the Alaska Peninsula on July 28, 2021, at 10:15 p.m. local time. The large megathrust earthquake had a moment magnitude of 8.2 according to the United States Geological Survey (USGS). A tsunami warning was issued by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) but later cancelled. The mainshock was followed by a number of aftershocks, including three that were of magnitude 5.9, 6.1 and 6.9 respectively.

An earthquake occurred 112 km, offshore, north of Maumere in the Flores Sea on 14 December. The quake had a moment magnitude of 7.3 according to the United States Geological Survey (USGS). One person was killed and 173 others suffered injuries.
On 29 November, at 14:10 UTC, a magnitude 7.7 earthquake struck off the southern coast of Taliabu Island Regency in North Maluku, Indonesia. At least 41 people were killed on the nearby islands and a tsunami was triggered. Several hundred homes, buildings and offices were damaged or destroyed.
The 1979 Saint Elias earthquake affected Alaska at 12:27 AKST on 28 February. The thrust-faulting 7.5 earthquake had an epicenter in the Chugach Range. Though the maximum recorded Modified Mercalli intensity was VII, damage was minimal and there were no casualties due to the remoteness of the faulting. Damage also extended across the border in parts of Yukon, Canada.
On 18 August 2012, at 17:41:52 WITA, a 6.3 earthquake struck Sigi Regency in Central Sulawesi, Indonesia, 51 km (32 mi) south-southeast of Palu.