
A planetary nebula is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.

The Helix Nebula is a planetary nebula (PN) located in the constellation Aquarius. Discovered by Karl Ludwig Harding, most likely before 1824, this object is one of the closest of all the bright planetary nebulae to Earth. The distance, measured by the Gaia mission, is 655±13 light-years. It is similar in appearance to the Cat's Eye Nebula and the Ring Nebula, whose size, age, and physical characteristics are similar to the Dumbbell Nebula, varying only in its relative proximity and the appearance from the equatorial viewing angle. The Helix Nebula has sometimes been referred to as the "Eye of God" in pop culture, as well as the "Eye of Sauron".

Wolf–Rayet stars, often abbreviated as WR stars, are a rare heterogeneous set of stars with unusual spectra showing prominent broad emission lines of ionised helium and highly ionised nitrogen or carbon. The spectra indicate very high surface enhancement of heavy elements, depletion of hydrogen, and strong stellar winds. The surface temperatures of known Wolf–Rayet stars range from 20,000 K to around 210,000 K, hotter than almost all other kinds of stars. They were previously called W-type stars referring to their spectral classification.

The Cat's Eye Nebula is a planetary nebula in the northern constellation of Draco, discovered by William Herschel on February 15, 1786. It was the first planetary nebula whose spectrum was investigated by the English amateur astronomer William Huggins, demonstrating that planetary nebulae were gaseous and not stellar in nature. Structurally, the object has had high-resolution images by the Hubble Space Telescope revealing knots, jets, bubbles and complex arcs, being illuminated by the central hot planetary nebula nucleus (PNN). It is a well-studied object that has been observed from radio to X-ray wavelengths. At the centre of the Cat's Eye Nebula is a dying Wolf Rayet star, the sort of which can be seen in the Webb Telescope's image of WR 124. The Cat's Eye Nebula's central star shines at magnitude +11.4. Hubble Space Telescope images show a sort of dart board pattern of concentric rings emanating outwards from the centre.

The Eskimo Nebula, also known as the Clown Face Nebula, Lion Nebula, or Caldwell 39, is a bipolar double-shell planetary nebula (PN). It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel in 1787. The formation resembles a person's head surrounded by a parka hood. It is surrounded by gas that composed the outer layers of a Sun-like star. The visible inner filaments are ejected by a strong wind of particles from the central star. The outer disk contains unusual, light-year-long filaments.

The Stingray Nebula is the youngest-known planetary nebula, having appeared in the 1980s. The nebula is located in the direction of the southern constellation Ara, and is located 18,000 light-years away. Although it is some 130 times the size of the Solar System, the Stingray Nebula is only about one tenth the size of most other known planetary nebulae. The central star of the nebula is the fast-evolving star SAO 244567. Until the early 1970s, it was observed on Earth as a preplanetary nebula in which the gas had not yet become hot and ionized.

IC 418, also known as the Spirograph Nebula, is a planetary nebula located in the constellation of Lepus about 3,600 ly away from Earth. It spans 0.3 light-years across. The central star of the planetary nebula, HD 35914, is an O-type star with a spectral type of O7fp. The nebula formed a few thousand years ago during the stars last stages of its red giant phase. Material from the star’s outer layers was ejected from the star into the surrounding space. The nebula’s glow is caused by the central star’s ultraviolet radiation interacting with the gas.

NGC 5189 is a planetary nebula in the constellation Musca. It was discovered by James Dunlop on 1 July 1826, who catalogued it as Δ252. For many years, well into the 1960s, it was thought to be a bright emission nebula. It was Karl Gordon Henize in 1967 who first described NGC 5189 as quasi-planetary based on its spectral emissions.

The asymptotic giant branch (AGB) is a region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram populated by evolved cool luminous stars. This is a period of stellar evolution undertaken by all low- to intermediate-mass stars (about 0.5 to 8 solar masses) late in their lives.

NGC 7027, also known as the Jewel Bug Nebula or the Magic Carpet Nebula, is a very young and dense planetary nebula located around 3,000 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cygnus. Discovered in 1878 by Édouard Stephan using the 800 mm (31 in) reflector at Marseille Observatory, it is one of the smallest planetary nebulae and by far the most extensively studied.

NGC 6751, also known as the Glowing Eye Nebula, is a planetary nebula in the constellation Aquila. It is estimated to be about 6,500 light-years away.

The Medusa Nebula is a planetary nebula in the constellation of Gemini. It is also known as Abell 21 and Sharpless 2-274. It was originally discovered in 1955 by University of California, Los Angeles astronomer George O. Abell, who classified it as an old planetary nebula. With the computation of expansion velocities and the thermal character of the radio emission, Soviet astronomers in 1971 concluded that it was most likely a planetary nebula. As the nebula is so large, its surface brightness is very low, with surface magnitudes of between +15.99 and +25 reported.

Abell 39 is a low surface brightness planetary nebula in the constellation of Hercules. It is the 39th entry in George Abell's 1966 Abell Catalog of Planetary Nebulae of 86 old planetary nebulae which either Abell or Albert George Wilson discovered before August 1955 as part of the National Geographic Society - Palomar Observatory Sky Survey. It is estimated to be about 3,800 light-years from earth and thus 2,600 light-years above the Galactic plane. It is almost perfectly spherical and also one of the largest known spheres with a radius of about 1.4 light-years.
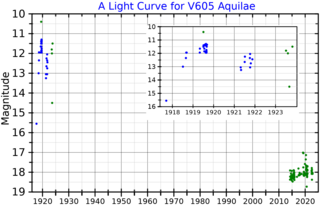
V605 Aquilae, in the constellation Aquila, is the variable central star of the planetary nebula Abell 58. It is a highly unusual hydrogen-deficient carbon-rich star.

Little Ghost Nebula, also known as NGC 6369, is a planetary nebula in the constellation Ophiuchus. It was discovered by William Herschel in 1784.

Fleming 1 is an unusual planetary nebula situated in the Centaurus constellation. It has a pair of symmetrical jets spanning more than 2.8 pc and delineated with a number of knots. The jets and knots are moving away from the center of the nebula and were probably ejected 10,000 to 16,000 years ago. The innermost part of the nebula has a butterfly shape and is immersed into a faint halo. The butterfly's wings point in the direction of jets with their axis titled by 50° to the line of sight. The waist of the "butterfly" is surrounded by a torus of expanding hot gas forming the inner bright ellipse. Fleming 1 is probably 5,000 years old.

Abell 31 is an ancient planetary nebula in the constellation of Cancer. It is estimated to be about 2,000 light years away. Although it is one of the largest planetary nebulae in the sky, it is not very bright. The central star of the planetary nebula is a white dwarf with a spectral type of DAO. The white dwarf is the dead remains of a star that existed but had died leaving behind Abell 31 and the white dwarf.

Abell 70 is a slightly elongated planetary nebula located 13,500-17,500 light years away in the constellation of Aquila. It is approaching the earth at 79 kilometers per second and expanding 38 kilometers per second. There is a galaxy named PMN J2033-0656 behind Abell 70, giving it a "diamond ring" effect.

Abell 36 is a faint barrel shaped planetary nebula located 780 light years from Earth in the constellation of Virgo. It was discovered by the American astronomer George Ogden Abell in 1955.

Cometary knots, also referred as globules, are structures observed in several nearby planetary nebulae (PNe), including the Helix Nebula, the Ring Nebula, the Dumbbell Nebula, the Eskimo Nebula, and the Retina Nebula. They are believed to be a common feature of the evolution of planetary nebulae, but can only be resolved in the nearest examples. They are generally larger than the size of the Solar System, with masses of around 0.00001 times the mass of the Sun, which is comparable to the mass of the Earth. There are about 40,000 cometary knots in the Helix Nebula.





















