
North Hertfordshire is one of ten local government districts in the county of Hertfordshire, England. Its council is based in Letchworth. The district borders East Hertfordshire, Stevenage, Welwyn Hatfield, St Albans, Central Bedfordshire, Luton, and South Cambridgeshire.

Hinxworth is a village and civil parish in North Hertfordshire, England. It sits just off the Great North Road between Baldock and Biggleswade. It has a village hall, a park, a pub, a small church, a bus stop and a post box. The population at the 2011 Census was 313.
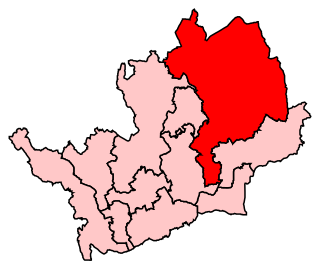
North East Hertfordshire is a constituency represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament since 1997 by Oliver Heald, a Conservative.

Therfield Heath is a biological Site of Special Scientific Interest and Local Nature Reserve on the chalk escarpment just north of Therfield, Hertfordshire. Since it lies south-west of the town of Royston, it is also known locally as Royston Heath. The heath is a common on which sheep are still regularly grazed. The site offers views towards the north, over the valley of the Cam as far as Cambridge.

Caer Caradoc is a hill in the English county of Shropshire. It overlooks the town of Church Stretton and the village of All Stretton and offers panoramic views to the north towards the Wrekin, east to Wenlock Edge, and west over the nearby Long Mynd. It is not to be confused with another hillfort of the same name 1 km west of Chapel Lawn near Bucknell.

British Camp is an Iron Age hill fort located at the top of Herefordshire Beacon in the Malvern Hills. The hill fort is protected as a Scheduled Ancient Monument and is owned and maintained by Malvern Hills Conservators. The fort is thought to have been first constructed in the 2nd century BC. A Norman castle was built on the site.

Arbury Hill, at 225 m (738 ft), is the joint highest point in the English county of Northamptonshire. It is 9 km (5.6 mi) southwest of the town of Daventry.
Voley Castle is an Iron Age hill fort situated close to Parracombe in north Devon, England. The fort is situated on a promontory on the eastern side of Heale Down, approximately 230 metres (750 ft) above sea level. It is close to another Iron Age hill fort at Beacon Castle. Voley Castle is a slight univallate hillfort, a rare type of hill fort found mainly in Devon, and is unusual for its type because it has an outer earthwork.
Wilbury Hill Camp is a late Bronze Age hill fort west of Letchworth in Hertfordshire. It and Arbury Banks near Ashwell are two of a line of six similar hill forts along the northern Chilterns. It is a scheduled ancient monument. The site is marked by two circular defences formed by single banks and external ditches. Although these are no longer conspicuous on the ground, distinct cropmarks generated by the buried features have been recorded by aerial photography since the 1950s.

Nordy Bank is an Iron Age hill fort on Brown Clee Hill in the Shropshire Hills Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty in South Shropshire, England.

Croft Ambrey is an Iron Age hill fort in Herefordshire, England.

Maiden Castle is an Iron Age hill fort, one of many fortified hill-top settlements constructed across Britain during the Iron Age, but one of only seven in the county of Cheshire in northern England. The hill fort was probably occupied from its construction in 600 BC until the Roman conquest of Britain in the 1st century AD. At this time the Cornovii tribe are recorded to have occupied parts of the surrounding area but, because they left no distinctive pottery or metalworking, their occupation has not been verified. Since then it has been quarried and used for military exercises. It is protected as a Scheduled Ancient Monument, and is owned by the National Trust. The hill fort is open to visitors, but unrestricted access to the site has resulted in it being classified as "at high risk" from erosion.

Hunsbury Hill is an Iron Age hill fort two miles (3 km) south-west of the centre of the town of Northampton in the county of Northamptonshire.
Arbury Banks may refer to

Midsummer Hill is situated in the range of Malvern Hills that runs approximately 13 kilometres (8 mi) north-south along the Herefordshire-Worcestershire border. It lies to the south of Herefordshire Beacon with views to Eastnor Castle. It has an elevation of 284 metres (932 ft). To the north is Swinyard Hill. It is the site of an Iron Age hill fort which spans Midsummer Hill and Hollybush Hill. The hillfort is protected as a Scheduled Ancient Monument and is owned by Natural England. It can be accessed via a footpath which leads south from the car park at British Camp on the A449 or a footpath which heads north from the car park in Hollybush on the A438.

Helsby hill fort is an Iron Age hillfort overlooking the village of Helsby in Cheshire, northwest England. Helsby Hill has steep cliffs on the northern and western sides, providing a natural semicircular defence. Double rampart earthworks extend to the south and east to provide protection to those flanks. Two additional banks have been discovered enclosing a rock ledge on the cliff to the north side. Excavations last century revealed a wall composed of sand and rubble, revetted with stone to the back and front. The hill has a summit of 141 m AOD, and is a prominent landmark rising above the Cheshire Plain, with fine views overlooking the Mersey Estuary and into Wales. Much of the hill is owned and managed by the National Trust. The surrounding areas are well wooded to the southwest, northwest and northeast with farmland to the southeast. The hill fort is protected as a Scheduled Ancient Monument.
Blainsburg is an unincorporated outlier community of West Brownsville, PA; by tradition a hamlet sized neighborhood with more actual housing acreage than West Brownsville proper in Washington County, Pennsylvania, United States. Named after a U.S. Senator, James G. Blaine. Blainsburg is part of the California Area School District. West Brownsville residence students attend Brownsville Area School District in Fayette County, Pennsylvania. The bedroom community is situated on the bluff above and slightly North-northwest of West Brownsville on the river bottom below. Blainsburg is located alongside but above the climb PA Route 88 makes from the W. Brownsville river flats which bends right entering a shelf where it connects with the northwest streets of Blainsburg before taking a second ascent towards California. The parent and child communities are on the inside curve of a great meander in the Monongahela River in Southwestern Pennsylvania creating a degraded cut bank turned ramp and terrace on the opposite shore where Brownsville is situated. Blainsburg is often misspelled with an "E" in it, to match the spelling of its namesake, James G. Blaine. Blainsburg as of official records was founded in 1906 and is still spelled without the "E".

Castle Rings is a univallate hill fort in the parish of Donhead St Mary in Wiltshire, England. The site is a Scheduled Ancient Monument. Castle Rings has been dated to the Iron Age and is at an altitude of 228 metres (748 ft) upon Upper Greensand sandstone beds. The bulk of the fort enclosure lies within the boundaries of Donhead St Mary parish but some of the outlying earthworks are in the neighbouring Sedgehill and Semley parish. In the mid-1980s a metal detectorist unearthed a hoard of stater coins of the Durotriges tribe within the hill fort.

Caesar's Camp is an Iron Age hill fort straddling the border of the counties of Surrey and Hampshire in southern England. The fort straddles the borough of Waverley in Surrey and the borough of Rushmoor and the district of Hart, both in Hampshire. Caesar's Camp is a Scheduled Ancient Monument with a list entry identification number of 1007895. It lies approximately 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) north of the town of Farnham, and a similar distance west of Aldershot. The hillfort lies entirely within the Bourley and Long Valley Site of Special Scientific Interest. Caesar's Camp is a multivallate hillfort, a fort with multiple defensive rings, occupying an irregular promontory, with an entrance on the south side. The site has been much disturbed by military activity, especially at the southeast corner. The remains of the hillfort are considered to be of national importance.
Johnson Creek, originally known as Cottonwood Creek, is a stream in iron County, Utah, United States. Its mouth is in the Cedar Valley at an elevation of 5,407 feet (1,648 m), 1.5 miles (2.4 km) south of Rush Lake, where is dissipates into the ground. Its source is a group of springs, formerly known as Elkhorn Springs, later Johnson Springs, running from north to south, at the foot of the south end of the Red Hills at 37°46′32″N113°01′31″W at an elevation of 5,500 to 5,510 feet in what is now Enoch, Utah.
















