Danebury is an Iron Age hillfort in Hampshire, England, about 19 kilometres (12 mi) north-west of Winchester. The site, covering 5 hectares, was excavated by Barry Cunliffe in the 1970s. Danebury is considered a type-site for hill forts, and was important in developing the understanding of hillforts, as very few others have been so intensively excavated.

Rainsborough Camp is an Iron Age hillfort in West Northamptonshire, England, between the villages of Croughton, Aynho, and Charlton.

Huntsham Castle, Devon, England is an Iron Age Hill fort enclosure near the village of Huntsham, it is located 260 m (850 ft) above sea level on the edge of the former Parish of Tiverton. The monument includes a slight univallate hillfort situated on a prominent hill overlooking the valleys of two separate tributaries to the River Lowman. The monument survives as a sub-circular enclosure, defining an area which slopes gently down to the south and measures approximately 150m in diameter. It is clearly demarcated on all sides by a rampart which varies in height from 1m up to 2.4m internally, being generally of greater height on the northern side of the enclosure. Externally this rampart is up to 2.9m high. Surrounding the rampart is an outer ditch which measures up to 5.4m wide and 0.4m deep and this is visible on all sides of the monument, although it is predominantly preserved as a buried feature. On the north eastern side, the outer edge of this ditch is defined by a field boundary bank and the infilled ditch has been used in the past as a track. There is an inturned entrance on the north eastern side which measures 7m wide, and the inturned banks are up to 2.2m wide and 0.4m high. The enclosure is crossed by a parish boundary bank which measures up to 2m wide and 1.5m high, and has been partially cut at the north eastern corner by a quarry, approximately 20m long, 15m wide and up to 2.8m deep, which lies to the north of the entrance. A further quarry lies to the south of the parish boundary bank, on the western side of the enclosure and measures 8.7 metres (29 ft) long, 5.3 metres (17 ft) wide and up to 1 metre (3.3 ft) deep. A third quarry lies to the north west and has partially cut into the ditch and rampart on this side; however much of this quarry lies just beyond the monument itself. A further entrance to the enclosure may lie on the western side, where the rampart is seen to kink slightly inwards. The stock proof fences around the rampart and ditch, the gates and gateposts which facilitate access, the Ordnance Survey triangulation point which is situated on the north eastern side of the enclosure just above the quarry, and the field boundary bank which defines the outer edge of the ditch in the north eastern corner are excluded from the scheduling, although the ground beneath all these features is included.

Embury Beacon is the site of an Iron Age promontory fort on the west of the Hartland Peninsula, north of Bude and west of Clovelly, in north Devon. The fort has almost entirely been lost to coastal erosion, but a fraction of the eastern ramparts still exist at approximately 150 metres (490 ft) above Sea Level. It is part of the National Trust property of Bideford Bay and Hartland, which also includes two other hill forts at Windbury Head and Bucks Mills earthworks. The site’s name suggests it was the location of a beacon, possibly during the Elizabethan period, but there is no archaeological evidence of this.
Kirkmaiden is a parish in the Rhins of Galloway, the most southerly in Scotland; the present Church of Scotland parish has the same name as and is approximately coterminous with the original pre-Reformation parish.

Maiden Castle is an Iron Age hill fort, one of many fortified hill-top settlements constructed across Britain during the Iron Age, but one of only seven in the county of Cheshire in northern England. The hill fort was probably occupied from its construction in 600 BC until the Roman conquest of Britain in the 1st century AD. At this time the Cornovii tribe are recorded to have occupied parts of the surrounding area but, because they left no distinctive pottery or metalworking, their occupation has not been verified. Since then it has been quarried and used for military exercises. It is protected as a Scheduled Ancient Monument, and is owned by the National Trust. The hill fort is open to visitors, but unrestricted access to the site has resulted in it being classified as "at high risk" from erosion.

Kelsborrow Castle is an Iron Age hill fort in Cheshire, northern England. Hill forts were fortified hill-top settlements constructed across Britain during the Iron Age. It is one of only seven hill forts in the county of Cheshire and was probably in use for only a short time. In the 19th century, a bronze palstave was recovered from the site. It is protected as a Scheduled Ancient Monument.
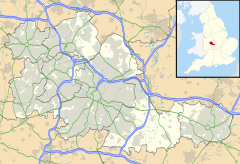
Berry Mound is an Iron Age hill fort in the Bromsgrove district of Worcestershire, near Shirley, West Midlands, on the outskirts of Birmingham. It has been dated to the 1st or 2nd century BC.

Buckland Rings is the site of an Iron Age hill fort in the town of Lymington, Hampshire. Today, the mounds and dykes around the outside which once constituted its defences are still clearly visible, although the outer bank lies under the road on the west side, and on the south-east it is nearly ploughed-out. Excavations of the inner and middle ramparts in 1935 revealed that they were of wall-and-fill construction, retained at the front by upright timber beams and walls of cut and laid turf. The entrance, which lies on the east side, was also excavated revealing a long entrance passage and the postholes for a pair of stout gateposts. The site was bought by Hampshire County Council in 1989 to ensure its preservation, and it is open to the public from the A337 road onto which part of it faces.

Scratchbury Camp is the site of an Iron Age univallate hillfort on Scratchbury Hill, overlooking the Wylye valley about 1 km northeast of the village of Norton Bavant in Wiltshire, England. The fort covers an area of 37 acres (15 ha) and occupies the summit of the hill on the edge of Salisbury Plain, with its four-sided shape largely following the natural contours of the hill.

Cholesbury Camp is a large and well-preserved Iron Age hill fort on the northern edge of the village of Cholesbury in Buckinghamshire, England. It is roughly oval-shaped and covers an area, including ramparts, of 15 acres (6.1 ha), and measures approximately 310 m (1,020 ft) north-east to south-west by 230 m (750 ft) north-west to south-east. The interior is a fairly level plateau which has been in agricultural use since the medieval period. The hill fort is now a scheduled ancient monument.

Cornish promontory forts, commonly known in Cornwall as cliff castles, are coastal equivalents of the hill forts and Cornish "rounds" found on Cornish hilltops and slopes. Similar coastal forts are found on the north–west European seaboard, in Normandy, Brittany and around the coastlines of the British Isles, especially in Wales, Scotland and Ireland. Many are known in southwest England, particularly in Cornwall and its neighbouring county, Devon. Two have been identified immediately west of Cornwall, in the Isles of Scilly.

Castle Rings is a univallate hill fort in the parish of Donhead St Mary in Wiltshire, England. The site is a Scheduled Ancient Monument. Castle Rings has been dated to the Iron Age and is at an altitude of 228 metres (748 ft) upon Upper Greensand sandstone beds. The bulk of the fort enclosure lies within the boundaries of Donhead St Mary parish but some of the outlying earthworks are in the neighbouring Sedgehill and Semley parish. In the mid-1980s a metal detectorist unearthed a hoard of stater coins of the Durotriges tribe within the hill fort.

Berry Ring is an Iron Age hillfort in Staffordshire, England, lying some two miles southwest of the county town of Stafford, a mile to the southwest of Stafford Castle and half a mile to the west of the M6 motorway.

Bigbury Camp is a univallate hill fort in the parish of Harbledown and Rough Common in Kent in England. The fort is a Scheduled Ancient Monument, with a list entry identification number of 1005169. Bigbury Camp is the only confirmed Iron Age hill fort in east Kent. It is managed by Kent Wildlife Trust.

Caesar's Camp is an Iron Age hill fort straddling the border of the counties of Surrey and Hampshire in southern England. The fort straddles the borough of Waverley in Surrey and the borough of Rushmoor and the district of Hart, both in Hampshire. Caesar's Camp is a Scheduled Ancient Monument with a list entry identification number of 1007895. It lies approximately 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) north of the town of Farnham, and a similar distance west of Aldershot. The hillfort lies entirely within the Bourley and Long Valley Site of Special Scientific Interest. Caesar's Camp is a multivallate hillfort, a fort with multiple defensive rings, occupying an irregular promontory, with an entrance on the south side. The site has been much disturbed by military activity, especially at the southeast corner. The remains of the hillfort are considered to be of national importance.

Warbstow Bury is an Iron Age hillfort about 0.5 miles (0.80 km) west of the village of Warbstow, in Cornwall, England. It is a scheduled monument.
Dungeon Hill is an Iron Age hillfort, about 1+1⁄4 miles north of the village of Buckland Newton in Dorset, England. It is a scheduled monument.

Buzbury Rings is an Iron Age hillfort about 2 miles (3.2 km) east of Blandford Forum and 1 mile (1.6 km) northwest of the village of Tarrant Keyneston, in Dorset, England.

Northshield Rings is a prehistoric site, a hillfort near the village of Eddleston and about 6 miles (10 km) north of Peebles, in the Scottish Borders, Scotland. It is a Scheduled Monument.