The Aquificota phylum is a diverse collection of bacteria that live in harsh environmental settings. The name Aquificota was given to this phylum based on an early genus identified within this group, Aquifex, which is able to produce water by oxidizing hydrogen. They have been found in springs, pools, and oceans. They are autotrophs, and are the primary carbon fixers in their environments. These bacteria are Gram-negative, non-spore-forming rods. They are true bacteria as opposed to the other inhabitants of extreme environments, the Archaea.
The Thermomicrobia is a group of thermophilic green non-sulfur bacteria. Based on species Thermomicrobium roseum and Sphaerobacter thermophilus, this bacteria class has the following description:

The Thermodesulfobacteriota are a phylum of thermophilic sulfate-reducing bacteria.
The Thermotogota are a phylum of the domain Bacteria. The phylum Thermotogota is composed of Gram-negative staining, anaerobic, and mostly thermophilic and hyperthermophilic bacteria.

Methanococci is a class of methanogenic archaea in the phylum Euryarchaeota. They can be mesophilic, thermophilic or hyperthermophilic.
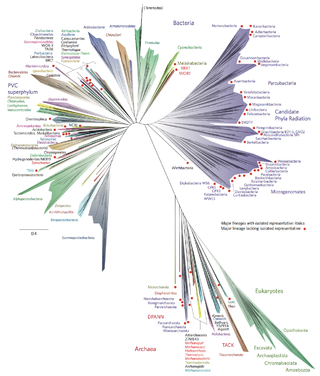
Bacterial phyla constitute the major lineages of the domain Bacteria. While the exact definition of a bacterial phylum is debated, a popular definition is that a bacterial phylum is a monophyletic lineage of bacteria whose 16S rRNA genes share a pairwise sequence identity of ~75% or less with those of the members of other bacterial phyla.
Armatimonadota is a phylum of gram-negative bacteria.
Caldithrix is a genus of thermophilic and anaerobic bacteria, currently assigned to its own phylum.
Thermales is an order of bacteria belonging to the Deinococcota phylum. They are particularly resistant to heat, and live in the benthic zone of the Gulf of Mexico.
Armatimonas rosea is a Gram-negative bacterium and also the first species to be characterized within the phylum Armatimonadota. The Armatimonadota were previously known as candidate phylum OP10. OP10 was composed solely of environmental 16S rRNA gene clone sequences prior to A. rosea's discovery.
Chthonomonas calidirosea is a Gram-negative bacterium and also the first representative of the new class Chthonomonadetes within the phylum Armatimonadota. The Armatimonadota were previously known as candidate phylum OP10. OP10 was composed solely of environmental 16S rRNA gene clone sequences prior to C. calidirosea's relative, Armatimonas rosea's discovery. It is now known that bacterial communities from geothermal environments, are generally constituted by, at least 5–10% of bacteria belonging to Armatimonadota.
Anaerolinea thermophila is a species of filamentous thermophilic bacteria, the type and only species of its genus. It is Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, with type strain UNI-1T.
Thermolithobacteria is a class of rod-shaped Gram-positive bacteria within phylum Bacillota. Species within this class are thermophilic lithotrophs isolated from sediment in Calcite Springs in Yellowstone National Park. Thermolithobacter ferrireducens strain JW/KA-2(T) metabolism consists of the oxidation of hydrogen gas and reduction of ferric oxide to magnetite. Thermolithobacter carboxydivorans strain R1(T) is hydrogenic and oxidizes carbon monoxide.
Anaerolineaceae is a family of bacteria from the order of Anaerolineales. Anaerolineaceae bacteria occur in marine sediments. There are a total of twelve genera in this family, most of which only encompass one species. All known members of the family are Gram-negative and non-motile. They also do not form bacterial spores and are either mesophilic or thermophilic obligate anaerobes. It is also known that all species in this family are chemoheterotrophs.
Bellilinea is a thermophilic bacteria genus from the family of Anaerolineaceae with one known species. Bellilinea caldifistulae has been isolated from thermophilic digester sludge from Niigata in Japan.
Coprothermobacterota is a phylum of nonmotile, rod-shaped bacteria.
Coprothermobacter is a genus of rod-shaped microorganisms, belonging to the bacterial family Coprothermobacteraceae of the phylum Coprothermobacterota. This taxonomic genus has been reclassified in 2018, after different phylogenetic studies showed that these bacteria represented a deeply branched taxon of the domain Bacteria; consequently, the clade including this genus has been classified in a separate phylum from Firmicutes, the phylum where it was included before reclassification.
Thermogutta is a thermophilic genus of bacteria from the family of Planctomycetaceae.
Tepidisphaera is a genus of bacteria from the family of Planctomycetaceae with one known species. Tepidisphaera mucosa has been isolated from a hot spring from the Lake Baikal in Kamchatka in Russia.
The Ignavibacteriales are an order of obligately anaerobic, non-photosynthetic bacteria that are closely related to the green sulfur bacteria.


