
A safety valve is a valve that acts as a fail-safe. An example of safety valve is a pressure relief valve (PRV), which automatically releases a substance from a boiler, pressure vessel, or other system, when the pressure or temperature exceeds preset limits. Pilot-operated relief valves are a specialized type of pressure safety valve. A leak tight, lower cost, single emergency use option would be a rupture disk.

A check valve, non-return valve, reflux valve, retention valve, foot valve, or one-way valve is a valve that normally allows fluid to flow through it in only one direction.
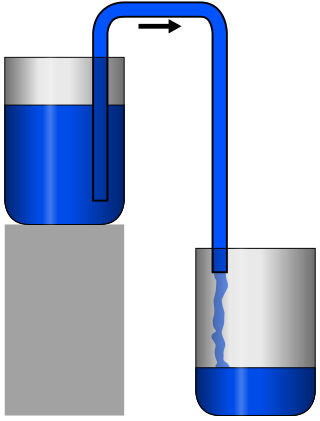
A siphon is any of a wide variety of devices that involve the flow of liquids through tubes. In a narrower sense, the word refers particularly to a tube in an inverted "U" shape, which causes a liquid to flow upward, above the surface of a reservoir, with no pump, but powered by the fall of the liquid as it flows down the tube under the pull of gravity, then discharging at a level lower than the surface of the reservoir from which it came.

A tap is a valve controlling the release of a fluid.
Drip irrigation or trickle irrigation is a type of micro-irrigation system that has the potential to save water and nutrients by allowing water to drip slowly to the roots of plants, either from above the soil surface or buried below the surface. The goal is to place water directly into the root zone and minimize evaporation. Drip irrigation systems distribute water through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters. Depending on how well designed, installed, maintained, and operated it is, a drip irrigation system can be more efficient than other types of irrigation systems, such as surface irrigation or sprinkler irrigation.

A backflow prevention device is used to protect potable water supplies from contamination or pollution due to backflow.

A double check valve or double check assembly (DCA) is a backflow prevention device designed to protect water supplies from contamination. It is different from the two-way check valves used in air brake systems on heavy trucks which select from the highest pressure source.

Hydronics is the use of liquid water or gaseous water (steam) or a water solution as a heat-transfer medium in heating and cooling systems. The name differentiates such systems from oil and refrigerant systems.

An air gap, as related to the plumbing trade, is the unobstructed vertical space between the water outlet and the flood level of a fixture. Air gaps of appropriate design are legally required by water health and safety regulations in many countries. An air gap is the simplest form of a backflow prevention device.
A hydrostatic loop, though not often used in plumbing practice, is an arrangement of pipes formed into a vertical loop to prevent backflow of water within the plumbing potable water system. Since a siphon has a maximum height that it can work, a hydrostatic loop is built higher than 33 feet. There are several ways to prevent siphonage and an undesirable backflow of the water in a plumbing system.
An Atmospheric Vacuum Breaker (AVB) is a backflow prevention device used in plumbing to prevent backflow of non-potable liquids into the drinking water system.
A vacuum breaker is an attachment commonly placed on a bibcock valve or toilet or urinal flush valve, that prevents water from being siphoned backward into the public drinking water system. This prevents contamination should the public drinking water system's pressure drop. A vacuum breaker is also used in steam distribution systems to prevent collapse of steam coils and pipes by letting in air when the pipe pressure becomes sub-atmospheric.
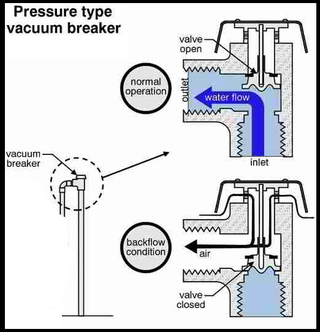
A pressure vacuum breaker (PVB) is a type of backflow prevention device, used to keep non-potable water from entering the water supply. A PVB is similar to an atmospheric vacuum breaker (AVB), except that the PVB contains a spring-loaded poppet. This makes it acceptable for applications that are high hazard or where valves are downstream. Pressure vacuum breakers must be protected from freezing when installed outdoors. PVBs usually have test cocks, to which specially-calibrated gauges are attached, in order to ensure that they are functioning properly.

A reduced pressure zone device is a type of backflow prevention device used to protect water supplies from contamination. RPZDs may also be known as reduced pressure principle (RP), reduced pressure principle backflow prevention devices, reduced pressure zone assemblies (RPZA), or reduced pressure principle assembly (RPPA).

Fertigation is the injection of fertilizers, used for soil amendments, water amendments and other water-soluble products into an irrigation system.
A backwater valve is a backflow prevention device used to prevent outbound water through a dwelling's drain pipes from re-entering -- "back flowing"—into a home. The valve contains a flap that allows water to exit the home, but closes to prevent the back flow into the home.

Backflow is a term in plumbing for an unwanted flow of water in the reverse direction. It can be a serious health risk for the contamination of potable water supplies with foul water. In the most obvious case, a toilet flush cistern and its water supply must be isolated from the toilet bowl. For this reason, building codes mandate a series of measures and backflow prevention devices to prevent backflow.

Pulse drip irrigation is an experimental irrigation technique primarily used with drip irrigation. Maintaining a high level of soil moisture for germination of seed is one reason this technique may be used.
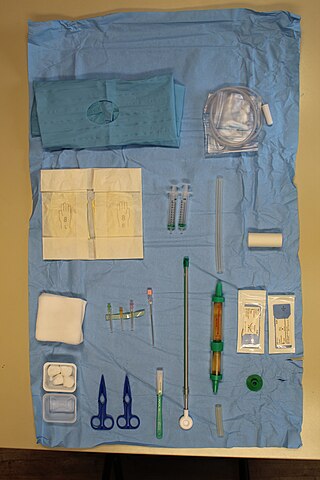
Chest drains are surgical drains placed within the pleural space to facilitate removal of unwanted substances in order to preserve respiratory functions and hemodynamic stability. Some chest drains may utilize a flutter valve to prevent retrograde flow, but those that do not have physical valves employ a water trap seal design, often aided by continuous suction from a wall suction or a portable vacuum pump.













