
The government budget balance, also referred to as the general government balance, public budget balance, or public fiscal balance, is the difference between government revenues and spending. For a government that uses accrual accounting the budget balance is calculated using only spending on current operations, with expenditure on new capital assets excluded. A positive balance is called a government budget surplus, and a negative balance is a government budget deficit. A government budget presents the government's proposed revenues and spending for a financial year.
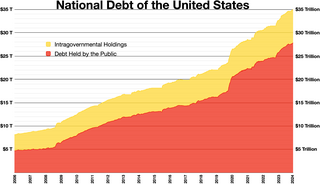
The national debt of the United States is the total national debt owed by the federal government of the United States to Treasury security holders. The national debt at any point in time is the face value of the then-outstanding Treasury securities that have been issued by the Treasury and other federal agencies. The terms "national deficit" and "national surplus" usually refer to the federal government budget balance from year to year, not the cumulative amount of debt. In a deficit year the national debt increases as the government needs to borrow funds to finance the deficit, while in a surplus year the debt decreases as more money is received than spent, enabling the government to reduce the debt by buying back some Treasury securities. In general, government debt increases as a result of government spending and decreases from tax or other receipts, both of which fluctuate during the course of a fiscal year. There are two components of gross national debt:

"Starve the beast" is a political strategy employed by American conservatives to limit government spending by cutting taxes, to deprive the federal government of revenue in a deliberate effort to force it to reduce spending. The term "the beast", in this context, refers to the United States federal government and the programs it funds, primarily with American tax money, particularly social programs such as education, welfare, Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid.

In economic policy, austerity is a set of political-economic policies that aim to reduce government budget deficits through spending cuts, tax increases, or a combination of both. There are three primary types of austerity measures: higher taxes to fund spending, raising taxes while cutting spending, and lower taxes and lower government spending. Austerity measures are often used by governments that find it difficult to borrow or meet their existing obligations to pay back loans. The measures are meant to reduce the budget deficit by bringing government revenues closer to expenditures. Proponents of these measures state that this reduces the amount of borrowing required and may also demonstrate a government's fiscal discipline to creditors and credit rating agencies and make borrowing easier and cheaper as a result.

Peter George Peterson was an American investment banker who served as United States Secretary of Commerce from February 29, 1972, to February 1, 1973, under the Richard Nixon administration. Peterson was also chairman and CEO of Bell & Howell from 1963 to 1971. From 1973 to 1984 he was chairman and CEO of Lehman Brothers. In 1985, he co-founded the private equity firm The Blackstone Group, and served as chairman. In the same year, Peterson became chairman of the Council on Foreign Relations, a position he held until his retirement in 2007, after which he was named chairman emeritus. In 2008, Peterson was ranked 149th on the "Forbes 400 Richest Americans" with a net worth of $2.8 billion. He was also known as founder and principal funder of The Peter G. Peterson Foundation, which is dedicated to promoting fiscal austerity.
A balanced budget amendment is a constitutional rule requiring that a state cannot spend more than its income. It requires a balance between the projected receipts and expenditures of the government.
PAYGO is the practice in the United States of financing expenditures with funds that are currently available rather than borrowed.

A fiscal adjustment is a reduction in the government primary budget deficit, and it can result from a reduction in government expenditures, an increase in tax revenues, or both simultaneously.

Fiscal policy is any changes the government makes to the national budget to influence a nation's economy. "An essential purpose of this Financial Report is to help American citizens understand the current fiscal policy and the importance and magnitude of policy reforms essential to make it sustainable. A sustainable fiscal policy is explained as the debt held by the public to Gross Domestic Product which is either stable or declining over the long term". The approach to economic policy in the United States was rather laissez-faire until the Great Depression. The government tried to stay away from economic matters as much as possible and hoped that a balanced budget would be maintained. Prior to the Great Depression, the economy did have economic downturns and some were quite severe. However, the economy tended to self-correct so the laissez faire approach to the economy tended to work.

The United States budget comprises the spending and revenues of the U.S. federal government. The budget is the financial representation of the priorities of the government, reflecting historical debates and competing economic philosophies. The government primarily spends on healthcare, retirement, and defense programs. The non-partisan Congressional Budget Office provides extensive analysis of the budget and its economic effects. CBO estimated in February 2024 that Federal debt held by the public is projected to rise from 99 percent of GDP in 2024 to 116 percent in 2034 and would continue to grow if current laws generally remained unchanged. Over that period, the growth of interest costs and mandatory spending outpaces the growth of revenues and the economy, driving up debt. Those factors persist beyond 2034, pushing federal debt higher still, to 172 percent of GDP in 2054.
In American political theory, fiscal conservatism or economic conservatism is a political and economic philosophy regarding fiscal policy and fiscal responsibility with an ideological basis in capitalism, individualism, limited government, and laissez-faire economics. Fiscal conservatives advocate tax cuts, reduced government spending, free markets, deregulation, privatization, free trade, and minimal government debt. Fiscal conservatism follows the same philosophical outlook as classical liberalism. This concept is derived from economic liberalism.
A government budget or a budget is a projection of the government's revenues and expenditure for a particular period of time often referred to as a financial or fiscal year, which may or may not correspond with the calendar year. Government revenues mostly include taxes while expenditures consist of government spending. A government budget is prepared by the Central government or other political entity. In most parliamentary systems, the budget is presented to the legislature and often requires approval of the legislature. Through this budget, the government implements economic policy and realizes its program priorities. Once the budget is approved, the use of funds from individual chapters is in the hands of government ministries and other institutions. Revenues of the state budget consist mainly of taxes, customs duties, fees and other revenues. State budget expenditures cover the activities of the state, which are either given by law or the constitution. The budget in itself does not appropriate funds for government programs, hence need for additional legislative measures. The word budget comes from the Old French bougette.
The Concord Coalition is a political advocacy group in the United States, formed in 1992. A bipartisan organization, it was founded by U.S. Senator Warren Rudman, former Secretary of Commerce Peter George Peterson, and U.S. Senator Paul Tsongas. The Concord Coalition's advocacy centers on ending deficit spending and promoting a balanced budget in the U.S. federal government. The group's mission statement is to educate "the public about the causes and consequences of federal budget deficits, the long-term challenges facing America's unsustainable entitlement programs, and how to build a sound foundation for economic growth."

I.O.U.S.A. is a 2008 American documentary film directed by Patrick Creadon. The film focuses on the shape and impact of the United States national debt. The film features Robert Bixby, director of the Concord Coalition, and David Walker, the former U.S. Comptroller General, as they travel around the United States on a tour to let communities know of the potential dangers of the national debt. The tour was carried out through the Concord Coalition, and was known as the "Fiscal Wake-Up Tour."
The Peter G. Peterson Foundation is an American billionaire-funded foundation established in 2008 by Peter G. Peterson, former US Secretary of Commerce in the Nixon Administration and co-founder of the Blackstone Group, an American financial-services company.
The Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget (CRFB) is a non-profit public policy organization based in Washington, D.C. that addresses federal budget and fiscal issues. It was founded in 1981 by former United States Representative Robert Giaimo (D-CT) and United States Senator Henry Bellmon (R-OK), and its board of directors includes past heads of the House and Senate Budget Committees, the Congressional Budget Office, the Office of Management and Budget, and the Government Accountability Office.
The National Commission on Fiscal Responsibility and Reform was a bipartisan Presidential Commission on deficit reduction, created in 2010 by President Barack Obama to identify "policies to improve the fiscal situation in the medium term and to achieve fiscal sustainability over the long run". The 18-member Commission, consisting of 12 members of Congress and six private citizens, first met on April 27, 2010. A report was released on December 1, recommending a combination of spending cuts and tax increases.
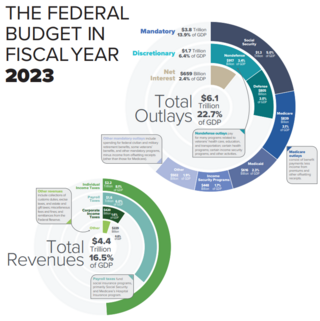
The United States federal budget consists of mandatory expenditures, discretionary spending for defense, Cabinet departments and agencies, and interest payments on debt. This is currently over half of U.S. government spending, the remainder coming from state and local governments.
Political debates about the United States federal budget discusses some of the more significant U.S. budgetary debates of the 21st century. These include the causes of debt increases, the impact of tax cuts, specific events such as the United States fiscal cliff, the effectiveness of stimulus, and the impact of the Great Recession, among others. The article explains how to analyze the U.S. budget as well as the competing economic schools of thought that support the budgetary positions of the major parties.

Deficit reduction in the United States refers to taxation, spending, and economic policy debates and proposals designed to reduce the federal government budget deficit. Government agencies including the Government Accountability Office (GAO), Congressional Budget Office (CBO), the Office of Management and Budget (OMB), and the U.S. Treasury Department have reported that the federal government is facing a series of important long-run financing challenges, mainly driven by an aging population, rising healthcare costs per person, and rising interest payments on the national debt.








