The A1, also known as the Great North Road, is the longest numbered road in the United Kingdom, at 410 miles (660 km). It connects London, the capital of England, with Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. The numbering system for A-roads, devised in the early 1920s, was based around patterns of roads radiating from two hubs at London and Edinburgh. The first number in the system, A1, was given to the most important part of that system: the road from London to Edinburgh, joining the two central points of the system and linking the UK's (then) two mainland capital cities. It passes through or near north London, Hatfield, Stevenage, Baldock, Biggleswade, Peterborough, Stamford, Grantham, Newark-on-Trent, Retford, Doncaster, Pontefract, York, Wetherby, Ripon, Darlington, Durham, Gateshead, Newcastle upon Tyne, Morpeth, Alnwick, Berwick-upon-Tweed, Dunbar, Haddington, Musselburgh, and east Edinburgh.

In Great Britain, there is a numbering scheme used to classify and identify all roads. Each road is given a single letter and a subsequent number. Though this scheme was introduced merely to simplify funding allocations, it soon became used on maps and as a method of navigation. There are two sub-schemes in use: one for motorways, and another for non-motorway roads.
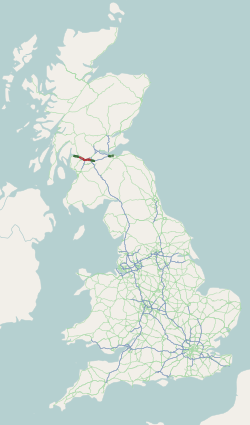
The A8 is a major road in Scotland, connecting Edinburgh to Greenock via Glasgow. Its importance diminished following the construction of the M8 motorway which also covers the route between Edinburgh and Glasgow.

The M8 is the busiest motorway in Scotland. It connects the country's two largest cities, Glasgow and Edinburgh, and serves other large communities including Airdrie, Coatbridge, Greenock, Livingston and Paisley. The motorway is 60 miles (97 km) long. A major construction project to build the final section between Newhouse and Baillieston was completed on 30 April 2017. The motorway has one service station, Heart of Scotland Services, previously named Harthill due to its proximity to the village.

The M9 is a major motorway in Scotland. It runs from the outskirts of Edinburgh, bypassing the towns of Linlithgow, Falkirk, Grangemouth and Stirling to end at Dunblane.

The A68 is a major road in the United Kingdom, running from Darlington in England to the A720 in Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. It crosses the Anglo-Scottish border at Carter Bar and is the only road to do so for some distance either way; the next major crossings are the A697 from Coldstream to Cornhill-on-Tweed in the east, and the A7 near Canonbie to the west.
The N7 road is a national primary road in Ireland, connecting Limerick and Dublin. The majority of the route is motorway standard and is designated as the M7 motorway. At the Rosbrien interchange in Limerick the route continues as the N18 dual carriageway to Galway, Shannon and Ennis. The road passes through the midlands of Ireland, and acts as a trunk route out of Dublin for the N8 and N9 national primary routes to Cork and Waterford respectively. It forms part of European route E20.
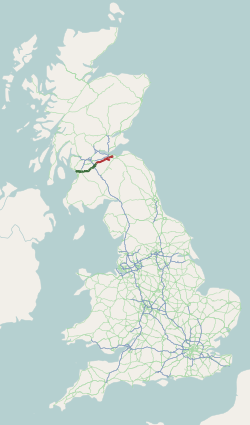
The A71 is a major road in Scotland linking Edinburgh with Lanarkshire and Ayrshire. It adjoins the Livingston Bypass A899.

The M80 is a motorway in Scotland's central belt, running between Glasgow and Stirling via Cumbernauld and Denny and linking the M8, M73 and M9 motorways. Following completion in 2011, the motorway is 25 miles (40 km) long. Despite being only a two lane motorway, parts of the M80 Stepps Bypass are used by around 60,000 vehicles per day.

The A702 is a major road in Scotland, that runs from Edinburgh to St. John's Town of Dalry in Dumfries and Galloway. It is the last section of the route from London via the West Midlands and North West England to Edinburgh, which follows the M1, M6, A74(M) and finally the A702.
Sighthill is a suburb in the west of Edinburgh, Scotland. The area is bordered by Broomhouse and Parkhead to the east, South Gyle to the north, the industrial suburb of Bankhead and the Calders neighbourhood to the west, and Wester Hailes to the south. It is sometimes included in the Wester Hailes area, while the Calders, Bankhead and Parkhead are sometimes considered parts of Sighthill. Administratively it has formed a core part of the City of Edinburgh Council's Sighthill/Gorgie ward since 2007.

Bankhead is a non-residential area of western Edinburgh, Scotland. It borders the Edinburgh City Bypass (A720) and Hermiston Gait to the west, the Calders neighbourhood to the south – accessed via a pedestrian underpass, Sighthill to the east, and South Gyle/Edinburgh Park to the north. It is mostly occupied by a large industrial park. Amongst the companies here, Royal Mail and Burtons Biscuits have a large presence. Ethicon also had a plant here, but it has closed, and will reportedly be replaced by a sports facilities. Edinburgh College, the former Stevenson College and the Sighthill campus of Napier University are just to the west.

Edinburgh is a major transport hub in east central Scotland and is at the centre of a multi-modal transport network with road, rail and air communications connecting the city with the rest of Scotland and internationally.
The B800 is a short road in eastern Scotland, connecting the Forth Road Bridge to Kirkliston. It is a two-way single carriageway road.

Newbridge is a village in the civil parish of Kirkliston, west of Edinburgh in Scotland. It formerly belonged to Midlothian, but it has been on the western fringe of to the City of Edinburgh since 1975. The original village consists of a small crossroads settlement to the east of the eponymous New Bridge, which spans the River Almond. Around it is a confusion of roads and industrial estates converging on the Newbridge Roundabout, the meeting point of the M8 and M9 motorways.

The A726 road in Scotland is a major route with several distinct sections with different characteristics and names; owing to its stages of construction, since 2005 it has two separate parts, the first running between Strathaven in South Lanarkshire and Junction 5 of the M77 motorway south of Newton Mearns in East Renfrewshire via East Kilbride, and the other running between Junction 3 of the M77 and the M898 motorway near the Erskine Bridge, via Paisley and Junction 29 of the M8 motorway near Glasgow International Airport.

The A89 is a trunk road in Scotland, United Kingdom. It runs from High Street, Glasgow to Newbridge in Edinburgh. It was once the A8, which has now been replaced, mostly by the M8.

The A700 road is a short but important link skirting Edinburgh City Centre between the A8 and A7 roads.

The City of Peterborough in East Anglia has an extensive and well integrated road network, owing partly to its status as a new town. Since the 1960s, the city has seen considerable expansion and its various suburbs are linked by a system of parkways.

The A772 was a major A road located in Edinburgh, Scotland. The A772 was originally the A7 before a major renumbering of the roads into Edinburgh and also begins there, at a junction with the A701 in the neighbourhood of Nether Liberton. From this junction, the A772 heads south-east through Gilmerton, a suburb of Edinburgh. This part is known as Gilmerton Road and has a 30 mph speed limit. At the edge of Gilmerton, the road becomes Drum Street, where it passes The Drum, an 18th-century country house, before reverting to Gilmerton Road.




















