
The economy of Bhutan, one of the world's smallest and least developed countries, is based on agriculture and forestry, which provide the main livelihood for more than 60% of the population. Agriculture consists largely of subsistence farming and animal husbandry. Rugged mountains dominate the terrain and make the building of roads and other infrastructure difficult and expensive.

The Benelux Union, also known as simply Benelux, is a politico-economic union and formal international intergovernmental cooperation of three neighboring states in western Europe: Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg. The name is a portmanteau formed from joining the first few letters of each country's name—Belgium, Netherlands, Luxembourg—and was first used to name the customs agreement that initiated the union. It is now used more generally to refer to the geographic, economic, and cultural grouping of the three countries.

The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), known informally as the Biodiversity Convention, is a multilateral treaty. The convention has three main goals: the conservation of biological diversity ; the sustainable use of its components; and the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from genetic resources. Its objective is to develop national strategies for the conservation and sustainable use of biological diversity, and it is often seen as the key document regarding sustainable development.
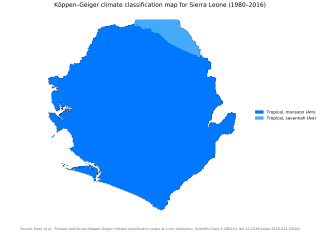
Sierra Leone is located on the west coast of Africa, between the 7th and 10th parallels north of the equator. Sierra Leone is bordered by Guinea to the north and northeast, Liberia to the south and southeast, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west.

The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe is one of the five regional commissions under the jurisdiction of the United Nations Economic and Social Council. It was established in order to promote economic cooperation and integrations among its member States.
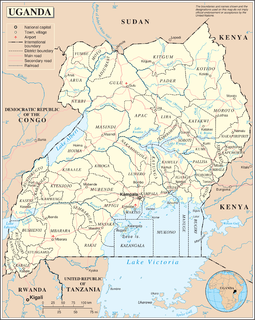
Uganda is located in eastern Africa, west of Kenya, south of South Sudan, east of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and north of Rwanda and Tanzania. It is in the heart of the Great Lakes region, and is surrounded by three of them, Lake Edward, Lake Albert, and Lake Victoria. While much of its border is lakeshore, Uganda is landlocked with no access to the sea.

Iceland is an island country at the confluence of the North Atlantic and Arctic oceans, east of Greenland and immediately south of the Arctic Circle, atop the constructive boundary of the northern Mid-Atlantic Ridge about 860 km (530 mi) from Scotland and 4,200 km (2,600 mi) from New York City. One of the world's most sparsely populated countries, Iceland's boundaries are almost the same as the main island – the world's 18th largest in area and possessing almost all of the country's area and population and also it is world's 9th largest island country. It is the westernmost European country and has more land covered by glaciers than in all of continental Europe. The total size is 103,125 km2 (39,817 sq mi). It has an Exclusive Economic Zone of 751,345 km2 (290,096 sq mi).
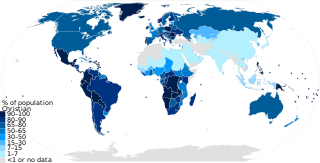
As of the year 2020, Christianity had approximately 2.5 billion adherents out of a worldwide population of about 7.8 billion people. It represents nearly one-third of the world's population and is the largest religion in the world, with the three largest groups of Christians being the Catholic Church, Protestantism, and the Eastern Orthodox Church. The largest Christian denomination is the Catholic Church, with 1.3 billion baptized members. The second largest Christian branch is either Protestantism, or the Eastern Orthodox Church.

Turkey hosts more than three thousand endemic plant species, has high diversity of other taxa, and is almost entirely covered by three of the world's thirty-five biodiversity hotspots. Although some environmental pressures have been decoupled from economic growth the environment still faces many threats, such as coal and diesel fuel emitting greenhouse gases and deadly fine particulate air pollution. As of 2019 there is no fine particulate limit and coal in Turkey is subsidized. Some say the country is a pollution haven.

Sustainable forest management (SFM) is the management of forests according to the principles of sustainable development. Sustainable forest management has to keep the balance between three main pillars: ecological, economic and socio-cultural. Successfully achieving sustainable forest management will provide integrated benefits to all, ranging from safeguarding local livelihoods to protecting biodiversity and ecosystems provided by forests, reducing rural poverty and mitigating some of the effects of climate change. Forest conservation is essential to stop climate change.

The United Nations Forum on Forests (UNFF) is a high-level intergovernmental policy forum. The forum includes all United Nations member states and permanent observers, the UNFF Secretariat, the Collaborative Partnership on Forests, Regional Organizations and Processes and Major Groups.
A fishery is an area with an associated fish or aquatic population which is harvested for its commercial value. Fisheries can be wild or farmed. Most of the world's wild fisheries are in the ocean. This article is an overview of ocean fisheries.

Lupinus nootkatensis, the Nootka lupine, is a perennial plant of the genus Lupinus in the legume family, Fabaceae. It is native to North America. The Nootka lupine grows up to 60 cm tall. Late in the 18th century it was first introduced to Europe.

Belasitsa Nature Park covers the northern slopes of Belasitsa Mountain in the Southwest Region of Bulgaria. The total area of the park is 117 km². Belasitsa is part of the European ecological network NATURA 2000 and is managed by the Belasitsa Nature Park Directorate which is a legal entity under the authority of the Executive Forest Agency of Ministry of Agriculture and Food. The Directorate office is located in the village of Kolarovo.

The European Centre for Nature Conservation (ECNC) was a Dutch non-profit foundation which was active in the field of European nature and biodiversity policy between 1993 and 2017. It was set up as a network of university departments, expert centres and government agencies and operated as a European biodiversity expertise centre. The organization promoted sustainable management of natural resources and biodiversity, and aimed to stimulate interaction between science, society and policy.

The National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) is a statutory autonomous body under the Ministry of Environment, Forests and climate change, Government of India established in 2003 to implement the provisions under the Biological Diversity Act, 2002, after India signed Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) in 1992.

The Canadian forestry industry is a major contributor to the Canadian economy. With 39 percent of the land acreage of Canada covered by forests, the country contains 9 percent of the world's forested land. The forests are made up primarily of spruce, poplar and pine. The Canadian forestry industry is composed of three main sectors: Solid wood manufacturing, pulp and paper and logging. The Forests and forestry are managed by The Department of Natural Resources Canada, the Canadian Forest Service, in cooperation with several organizations which represent government groups, officials, policy experts and numerous other stakeholders. Extensive deforestation by European settlers during the 18th and 19th centuries has been halted by more modern policies. Today less than 1 percent of Canada's forests are affected by logging each year. Canada is the second largest exporter of wood products, and produces 12.3% of the global market share. Economic concerns related to forestry include greenhouse gas emissions, biotechnology, biological diversity and infestations of pests, such as the mountain pine beetle.
The Ministerial Conference on the Protection of Forests in Europe is a pan-European ministerial level voluntary political process for the promotion of sustainable management of European forests.















