Examples
The ECM-construction is licensed by a relatively small number of verbs in English (e.g., believe, judge, prove, want, let, etc.):
- Tim believes him to be innocent. – Exceptional case-marking of the object/subject him.
- We judge them to be ridiculous. – Exceptional case-marking of the object/subject them.
- The prosecutor proved her to be guilty. – Exceptional case-marking of the object/subject her.
- They want us to be respectful. – Exceptional case-marking of the object/subject us.
The strings in bold are the ECM-constructions. The pronouns are marked with object case morphology, but they function semantically as the subjects of the infinitival verbs to their right, i.e., they acquire their theta roles from the verb to their right. Many ECM-verbs allow the same meaning to be expressed with a full object clause (a finite clause), e.g.:
- Tom believes that he is innocent. – ECM-construction alternates with full clause.
- The prosecutor proved that she is guilty. – ECM-construction alternates with full clause.
- They want that we are respectful. – ECM-construction alternates with full clause.
Since the meaning across these clauses remains consistent, one tendency has been to view the ECM-material (i.e., the material in bold in the first four examples) as a type of small clause that is analogous to the full clausal counterpart. On this approach, the object forms a constituent with the infinitive to its right. The primary trait of the ECM-object/subject is that it is not a semantic argument of the matrix predicate, which means that it is not semantically selected by the matrix verb. [2] In this area, ECM-constructions should not be confused with control constructions, since control predicates semantically select their object (e.g., They told us to start).
Structural analyses
An interesting aspect of ECM-constructions concerns the underlying structure. There are two basic possibilities in this area: a flat structure or a more layered one. [3] The following trees illustrate the "flat" analysis. For each example, both a constituency-based analysis of a phrase structure grammar and a dependency-based analysis of a dependency grammar are shown:
-
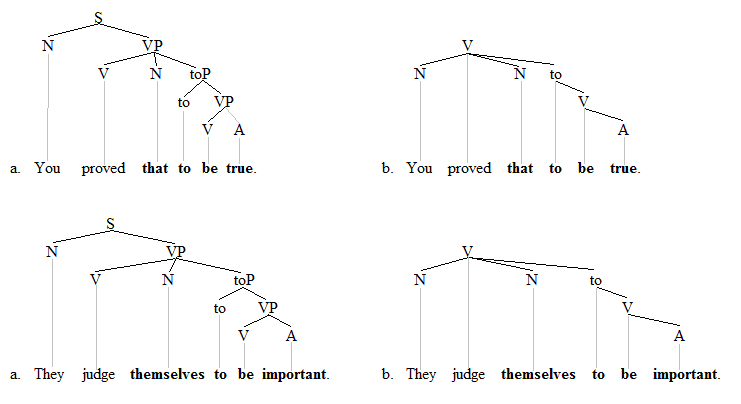
The phrase structure grammar trees are the a-trees on the left, and the dependency grammar trees are the b-trees on the right. Both types of analysis show a relatively flat structure insofar as the material in bold consists of two separate sister constituents. The object/subject pronouns are shown as dependents of the matrix verb each time. The two do NOT form a single constituent with the predicates to their right. The alternative, more layered analysis of these sentences might be as follows: [4]
-
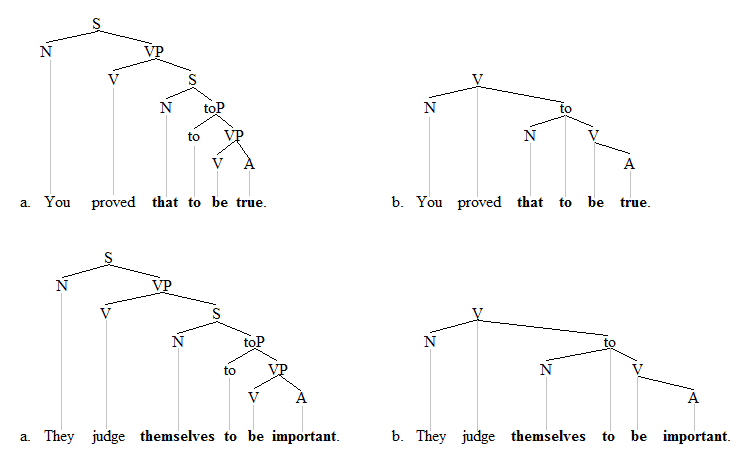
The constituency-based trees are again on the left, and the dependency-based trees on the right. The material in bold now forms a single constituent. This is accomplished in the constituency trees by adding the clause node S, and in the dependency trees, it is accomplished by subordinating the ECM object/subject to the particle to. One can now debate which of the two analyses is better. The more layered analysis has the advantage that it accommodates the insight that the subject/object constituent is a semantic argument of the infinitival verb. The flat analysis has the advantage that it is more consistent with data delivered by operational considerations: the object morphology on the pronoun (e.g. him, her, them, etc.), the ability of the object/subject to become the subject in the passive counterpart (e.g. That was proved to be true), the obligatory appearance of the reflexive pronoun when coindexation occurs with the subject (e.g. They1 judge themselves1/*them1 to be important), and the inability of constituency tests to clearly identify a clausal constituent (e.g. Topicalization: ??That to be true, you proved). [5]
The more layered analysis is favored in the GB framework and a variation of it certainly obtains in current Minimalism as well. The flat analysis is certainly the one preferred by dependency grammars.

In linguistics, syntax is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). There are numerous approaches to syntax that differ in their central assumptions and goals.
A syntactic category is a syntactic unit that theories of syntax assume. Word classes, largely corresponding to traditional parts of speech, are syntactic categories. In phrase structure grammars, the phrasal categories are also syntactic categories. Dependency grammars, however, do not acknowledge phrasal categories.
A noun phrase – or NP or nominal (phrase) – is a phrase that usually has a noun or pronoun as its head, and has the same grammatical functions as a noun. Noun phrases are very common cross-linguistically, and they may be the most frequently occurring phrase type.
In language, a clause is a constituent that comprises a semantic predicand and a semantic predicate. A typical clause consists of a subject and a syntactic predicate, the latter typically a verb phrase composed of a verb with any objects and other modifiers. However, the subject is sometimes unvoiced if it is retrievable from context, especially in null-subject language but also in other languages, including English instances of the imperative mood.
A subject is one of the two main parts of a sentence.
Dependency grammar (DG) is a class of modern grammatical theories that are all based on the dependency relation and that can be traced back primarily to the work of Lucien Tesnière. Dependency is the notion that linguistic units, e.g. words, are connected to each other by directed links. The (finite) verb is taken to be the structural center of clause structure. All other syntactic units (words) are either directly or indirectly connected to the verb in terms of the directed links, which are called dependencies. Dependency grammar differs from phrase structure grammar in that while it can identify phrases it tends to overlook phrasal nodes. A dependency structure is determined by the relation between a word and its dependents. Dependency structures are flatter than phrase structures in part because they lack a finite verb phrase constituent, and they are thus well suited for the analysis of languages with free word order, such as Czech or Warlpiri.
In generative grammar and related frameworks, a node in a parse tree c-commands its sister node and all of its sister's descendants. In these frameworks, c-command plays a central role in defining and constraining operations such as syntactic movement, binding, and scope. Tanya Reinhart introduced c-command in 1976 as a key component of her theory of anaphora. The term is short for "constituent command".
The term predicate is used in two ways in linguistics and its subfields. The first defines a predicate as everything in a standard declarative sentence except the subject, and the other defines it as only the main content verb or associated predicative expression of a clause. Thus, by the first definition, the predicate of the sentence Frank likes cake is likes cake, while by the second definition, it is only the content verb likes, and Frank and cake are the arguments of this predicate. The conflict between these two definitions can lead to confusion.
In theoretical linguistics, a distinction is made between endocentric and exocentric constructions. A grammatical construction is said to be endocentric if it fulfils the same linguistic function as one of its parts, and exocentric if it does not. The distinction reaches back at least to Bloomfield's work of the 1930s, who based it on terms by Pāṇini and Patañjali in Sanskrit grammar. Such a distinction is possible only in phrase structure grammars, since in dependency grammars all constructions are necessarily endocentric.
In linguistics, raising constructions involve the movement of an argument from an embedded or subordinate clause to a matrix or main clause. A raising predicate/verb appears with a syntactic argument that is not its semantic argument but rather the semantic argument of an embedded predicate. In other words, the sentence is expressing something about a phrase taken as a whole. For example, in they seem to be trying, "to be trying" is the subject of seem. English has raising constructions, unlike some other languages.
In linguistics, control is a construction in which the understood subject of a given predicate is determined by some expression in context. Stereotypical instances of control involve verbs. A superordinate verb "controls" the arguments of a subordinate, nonfinite verb. Control was intensively studied in the government and binding framework in the 1980s, and much of the terminology from that era is still used today. In the days of Transformational Grammar, control phenomena were discussed in terms of Equi-NP deletion. Control is often analyzed in terms of a null pronoun called PRO. Control is also related to raising, although there are important differences between control and raising.
In linguistics, an argument is an expression that helps complete the meaning of a predicate, the latter referring in this context to a main verb and its auxiliaries. In this regard, the complement is a closely related concept. Most predicates take one, two, or three arguments. A predicate and its arguments form a predicate-argument structure. The discussion of predicates and arguments is associated most with (content) verbs and noun phrases (NPs), although other syntactic categories can also be construed as predicates and as arguments. Arguments must be distinguished from adjuncts. While a predicate needs its arguments to complete its meaning, the adjuncts that appear with a predicate are optional; they are not necessary to complete the meaning of the predicate. Most theories of syntax and semantics acknowledge arguments and adjuncts, although the terminology varies, and the distinction is generally believed to exist in all languages. Dependency grammars sometimes call arguments actants, following Lucien Tesnière (1959).
In linguistics, a small clause consists of a subject and its predicate, but lacks an overt expression of tense. Small clauses have the semantic subject-predicate characteristics of a clause, and have some, but not all, properties of a constituent. Structural analyses of small clauses vary according to whether a flat or layered analysis is pursued. The small clause is related to the phenomena of raising-to-object, exceptional case-marking, accusativus cum infinitivo, and object control.
In generative linguistics, PRO is a pronominal determiner phrase (DP) without phonological content. As such, it is part of the set of empty categories. The null pronoun PRO is postulated in the subject position of non-finite clauses. One property of PRO is that, when it occurs in a non-finite complement clause, it can be bound by the main clause subject or the main clause object. The presence of PRO in non-finite clauses lacking overt subjects allows a principled solution for problems relating to binding theory.
In linguistics, inversion is any of several grammatical constructions where two expressions switch their canonical order of appearance, that is, they invert. There are several types of subject-verb inversion in English: locative inversion, directive inversion, copular inversion, and quotative inversion. The most frequent type of inversion in English is subject–auxiliary inversion in which an auxiliary verb changes places with its subject; it often occurs in questions, such as Are you coming?, with the subject you is switched with the auxiliary are. In many other languages, especially those with a freer word order than English, inversion can take place with a variety of verbs and with other syntactic categories as well.
Scrambling is a syntactic phenomenon wherein sentences can be formulated using a variety of different word orders without any change in meaning. Scrambling often results in a discontinuity since the scrambled expression can end up at a distance from its head. Scrambling does not occur in English, but it is frequent in languages with freer word order, such as German, Russian, Persian and Turkic languages. The term was coined by Haj Ross in his 1967 dissertation and is widely used in present work, particularly with the generative tradition.
In syntax, shifting occurs when two or more constituents appearing on the same side of their common head exchange positions in a sense to obtain non-canonical order. The most widely acknowledged type of shifting is heavy NP shift, but shifting involving a heavy NP is just one manifestation of the shifting mechanism. Shifting occurs in most if not all European languages, and it may in fact be possible in all natural languages including sign languages. Shifting is not inversion, and inversion is not shifting, but the two mechanisms are similar insofar as they are both present in languages like English that have relatively strict word order. The theoretical analysis of shifting varies in part depending on the theory of sentence structure that one adopts. If one assumes relatively flat structures, shifting does not result in a discontinuity. Shifting is often motivated by the relative weight of the constituents involved. The weight of a constituent is determined by a number of factors: e.g., number of words, contrastive focus, and semantic content.

This article describes the syntax of clauses in the English language, chiefly in Modern English. A clause is often said to be the smallest grammatical unit that can express a complete proposition. But this semantic idea of a clause leaves out much of English clause syntax. For example, clauses can be questions, but questions are not propositions. A syntactic description of an English clause is that it is a subject and a verb. But this too fails, as a clause need not have a subject, as with the imperative, and, in many theories, an English clause may be verbless. The idea of what qualifies varies between theories and has changed over time.
Subject–verb inversion in English is a type of inversion marked by a predicate verb that precedes a corresponding subject, e.g., "Beside the bed stood a lamp". Subject–verb inversion is distinct from subject–auxiliary inversion because the verb involved is not an auxiliary verb.
The Ancient Greek infinitive is a non-finite verb form, sometimes called a verb mood, with no endings for person or number, but it is inflected for tense and voice.



