
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels.
A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the tyrosine residues of specific proteins inside a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions.
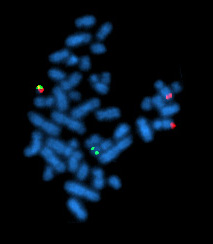
The Philadelphia chromosome or Philadelphia translocation (Ph) is a specific genetic abnormality in chromosome 22 of leukemia cancer cells. This chromosome is defective and unusually short because of reciprocal translocation, t(9;22)(q34;q11), of genetic material between chromosome 9 and chromosome 22, and contains a fusion gene called BCR-ABL1. This gene is the ABL1 gene of chromosome 9 juxtaposed onto the breakpoint cluster region BCR gene of chromosome 22, coding for a hybrid protein: a tyrosine kinase signalling protein that is "always on", causing the cell to divide uncontrollably by interrupting the stability of the genome and impairing various signaling pathways governing the cell cycle.

Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 also known as ABL1 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ABL1 gene located on chromosome 9. c-Abl is sometimes used to refer to the version of the gene found within the mammalian genome, while v-Abl refers to the viral gene, which was initially isolated from the Abelson murine leukemia virus.

Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 also known as Grb2 is an adaptor protein involved in signal transduction/cell communication. In humans, the GRB2 protein is encoded by the GRB2 gene.
Paxillin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PXN gene. Paxillin is expressed at focal adhesions of non-striated cells and at costameres of striated muscle cells, and it functions to adhere cells to the extracellular matrix. Mutations in PXN as well as abnormal expression of paxillin protein has been implicated in the progression of various cancers.

Proto-oncogene c-KIT is the gene encoding the receptor tyrosine kinase protein known as tyrosine-protein kinase KIT, CD117 or mast/stem cell growth factor receptor (SCFR). Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. KIT was first described by the German biochemist Axel Ullrich in 1987 as the cellular homolog of the feline sarcoma viral oncogene v-kit.

The breakpoint cluster region protein (BCR) also known as renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-26 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCR gene. BCR is one of the two genes in the BCR-ABL complex, which is associated with the Philadelphia chromosome. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.

Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3, also known as p44MAPK and ERK1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAPK3 gene.

Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HCK gene.

Crk-like protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CRKL gene.

Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src, also known as proto-oncogene c-Src, or simply c-Src, is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase protein that in humans is encoded by the SRC gene. It belongs to a family of Src family kinases and is similar to the v-Src gene of Rous sarcoma virus. It includes an SH2 domain, an SH3 domain and a tyrosine kinase domain. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene.

Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Yes is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase that in humans is encoded by the YES1 gene.

Gardner-Rasheed feline sarcoma viral (v-fgr) oncogene homolog, also known as FGR, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the FGR gene.

Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AXL gene. The gene was initially designated as UFO, in allusion to the unidentified function of this protein. However, in the years since its discovery, research into AXL's expression profile and mechanism has made it an increasingly attractive target, especially for cancer therapeutics. In recent years, AXL has emerged as a key facilitator of immune escape and drug-resistance by cancer cells, leading to aggressive and metastatic cancers.

Tyrosine-protein kinase Tec is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TEC gene.

Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL2 also known as Abelson-related gene (Arg) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ABL2 gene.

Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase FER is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FER gene.

Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase MER is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MERTK gene.
Non-receptor tyrosine kinases (nRTKs) are cytosolic enzymes that are responsible for catalysing the transfer of a phosphate group from a nucleoside triphosphate donor, such as ATP, to tyrosine residues in proteins. Non-receptor tyrosine kinases are a subgroup of protein family tyrosine kinases, enzymes that can transfer the phosphate group from ATP to a tyrosine residue of a protein (phosphorylation). These enzymes regulate many cellular functions by switching on or switching off other enzymes in a cell.


























