Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) is one among numerous growth factors that regulate cell growth and division. In particular, PDGF plays a significant role in blood vessel formation, the growth of blood vessels from already-existing blood vessel tissue, mitogenesis, i.e. proliferation, of mesenchymal cells such as fibroblasts, osteoblasts, tenocytes, vascular smooth muscle cells and mesenchymal stem cells as well as chemotaxis, the directed migration, of mesenchymal cells. Platelet-derived growth factor is a dimeric glycoprotein that can be composed of two A subunits (PDGF-AA), two B subunits (PDGF-BB), or one of each (PDGF-AB).
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), originally known as vascular permeability factor (VPF), is a signal protein produced by many cells that stimulates the formation of blood vessels. To be specific, VEGF is a sub-family of growth factors, the platelet-derived growth factor family of cystine-knot growth factors. They are important signaling proteins involved in both vasculogenesis and angiogenesis.

Endostatin is a naturally occurring, 20-kDa C-terminal fragment derived from type XVIII collagen. It is reported to serve as an anti-angiogenic agent, similar to angiostatin and thrombospondin.

Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are the high-affinity cell surface receptors for many polypeptide growth factors, cytokines, and hormones. Of the 90 unique tyrosine kinase genes identified in the human genome, 58 encode receptor tyrosine kinase proteins. Receptor tyrosine kinases have been shown not only to be key regulators of normal cellular processes but also to have a critical role in the development and progression of many types of cancer. Mutations in receptor tyrosine kinases lead to activation of a series of signalling cascades which have numerous effects on protein expression. Receptor tyrosine kinases are part of the larger family of protein tyrosine kinases, encompassing the receptor tyrosine kinase proteins which contain a transmembrane domain, as well as the non-receptor tyrosine kinases which do not possess transmembrane domains.

Angiopoietin is part of a family of vascular growth factors that play a role in embryonic and postnatal angiogenesis. Angiopoietin signaling most directly corresponds with angiogenesis, the process by which new arteries and veins form from preexisting blood vessels. Angiogenesis proceeds through sprouting, endothelial cell migration, proliferation, and vessel destabilization and stabilization. They are responsible for assembling and disassembling the endothelial lining of blood vessels. Angiopoietin cytokines are involved with controlling microvascular permeability, vasodilation, and vasoconstriction by signaling smooth muscle cells surrounding vessels. There are now four identified angiopoietins: ANGPT1, ANGPT2, ANGPTL3, ANGPT4.

VEGF receptors are receptors for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). There are three main subtypes of VEGFR, numbered 1, 2 and 3. Also, they may be membrane-bound (mbVEGFR) or soluble (sVEGFR), depending on alternative splicing.

SHC-transforming protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SHC1 gene. SHC has been found to be important in the regulation of apoptosis and drug resistance in mammalian cells.

Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FLT1 gene.
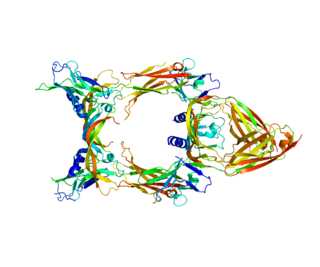
Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) is a protein that is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor / vascular endothelial growth factor (PDGF/VEGF) family. It is encoded in humans by the VEGFC gene, which is located on chromosome 4q34.

Neuropilin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NRP1 gene. In humans, the neuropilin 1 gene is located at 10p11.22. This is one of two human neuropilins.

Placental growth factor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PGF gene.

C-fos-induced growth factor (FIGF) is a vascular endothelial growth factor that in humans is encoded by the FIGF gene.
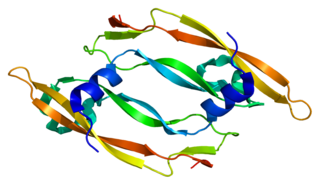
Vascular endothelial growth factor B also known as VEGF-B is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the VEGF-B gene. VEGF-B is a growth factor that belongs to the vascular endothelial growth factor family, of which VEGF-A is the best-known member.

Vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VEGFA gene.

Fms-related tyrosine kinase 4, also known as FLT4, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the FLT4 gene.

SHC-transforming protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SHC2 gene.

AEE788 is a multitargeted human epidermal receptor (HER) 1/2 and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) 1/2 receptor family tyrosine kinases inhibitor with IC50 of 2, 6, 77, 59 nM for EGFR, ErbB2, KDR, and Flt-1. In cells, growth factor-induced EGFR and ErbB2 phosphorylation was also efficiently inhibited with IC50s of 11 and 220 nM, respectively. It efficiently inhibited growth factor-induced EGFR and ErbB2 phosphorylation in tumors for >72 h, a phenomenon correlating with the antitumor efficacy of intermittent treatment schedules. It also inhibits VEGF-induced angiogenesis in a murine implant model. It has potential as an anticancer agent targeting deregulated tumor cell proliferation as well as angiogenic parameters.

Kari Kustaa Alitalo is a Finnish MD and a medical researcher. He is a foreign associated member of the National Academy of Sciences of the US. He became famous for his discoveries of several receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and the first growth factor capable of inducing lymphangiogenesis: vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C). In the years 1996–2007 he was Europe's second most cited author in the field of cell biology. Alitalo is currently serving as an Academy Professor for the Academy of Finland.
VEGFR-2 inhibitor, also known as kinase insert domain receptor(KDR) inhibitor, are tyrosine kinase receptor inhibitors that reduce angiogenesis or lymphangiogenesis, leading to anticancer activity. Generally they are small, synthesised molecules that bind competitively to the ATP-site of the tyrosine kinase domain. VEGFR-2 selective inhibitor can interrupt multiple signaling pathways involved in tumor, including proliferation, metastasis and angiogenesis.

Nader Rahimi is a Molecular Biologist and is currently an Associate Professor at the Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine at Boston University.