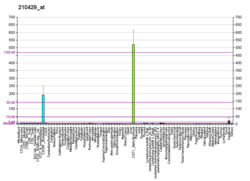
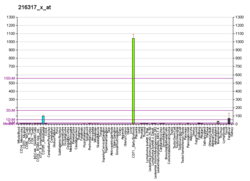
Glycophorin C plays a functionally important role in maintaining erythrocyte shape and regulating membrane material properties, possibly through its interaction with protein 4.1. Moreover, it has previously been shown that membranes deficient in protein 4.1 exhibit decreased content of glycophorin C. It is also an integral membrane protein of the erythrocyte and acts as the receptor for the Plasmodium falciparum protein PfEBP-2.

The Rh blood group system is a human blood group system. It contains proteins on the surface of red blood cells. After the ABO blood group system, it is the most likely to be involved in transfusion reactions. The Rh blood group system consisted of 49 defined blood group antigens in 2005. As of 2023, there are over 50 antigens among which the five antigens D, C, c, E, and e are the most important. There is no d antigen. Rh(D) status of an individual is normally described with a positive (+) or negative (−) suffix after the ABO type. The terms Rh factor, Rh positive, and Rh negative refer to the Rh(D) antigen only. Antibodies to Rh antigens can be involved in hemolytic transfusion reactions and antibodies to the Rh(D) and Rh antigens confer significant risk of hemolytic disease of the newborn.

Spectrin alpha chain, erythrocyte is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPTA1 gene.

H/ACA ribonucleoprotein complex subunit 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the gene DKC1.

Rh-associated glycoprotein (RHAG) is an ammonia transporter protein that in humans is encoded by the RHAG gene. RHAG has also recently been designated CD241. Mutations in the RHAG gene can cause stomatocytosis.

CD177 antigen is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD177 gene.

Glycophorin B (MNS blood group) (gene designation GYPB) also known as sialoglycoprotein delta and SS-active sialoglycoprotein is a protein which in humans is encoded by the GYPB gene. GYPB has also recently been designated CD235b (cluster of differentiation 235b).

Galactoside 2-alpha-L-fucosyltransferase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FUT2 gene. It affects the secretor status of ABO antigens.
Basal cell adhesion molecule, also known as Lutheran antigen, is a plasma membrane glycoprotein that in humans is encoded by the BCAM gene. BCAM has also recently been designated CD239.

N-acetyllactosaminide beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyl-transferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GCNT2 gene.

Urea transporter 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC14A1 gene.
ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX3Y is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DDX3Y gene.

Rh family, C glycoprotein, also known as RHCG, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RHCG gene.

Erythroid membrane-associated protein is a protein that in humans is responsible for the Scianna blood group system, and is encoded by the ERMAP gene.

Transmembrane protein 50A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TMEM50A gene.

Zinc finger protein ZFPM1 also known as friend of GATA protein 1(FOG-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZFPM1 gene. It is a cofactor of the GATA1 transcription factor.

DnaJ homolog subfamily C member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAJC2 gene.

Zinc finger protein 22 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF22 gene.

GDP-L-fucose synthetase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TSTA3 gene.

Rh blood group, D antigen also known as Rh polypeptide 1 (RhPI) or cluster of differentiation 240D (CD240D) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RHD gene.