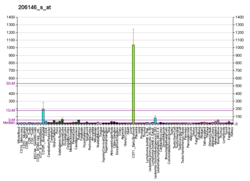
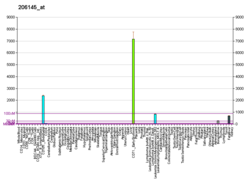
Function
The Rh blood group antigens (MIM 111700) are associated with human erythrocyte membrane proteins of approximately 30 kD, the so-called Rh30 polypeptides. Heterogeneously glycosylated membrane proteins of 50 and 45 kD, the Rh50 glycoproteins, are coprecipitated with the Rh30 polypeptides on immunoprecipitation with anti-Rh-specific mono- and polyclonal antibodies. The Rh antigens appear to exist as a multisubunit complex of CD47 (MIM 601028), LW (MIM 111250), glycophorin B (MIM 111740), and play a critical role in the Rh50 glycoprotein [supplied by OMIM]. [6]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.