
HLA-DR is an MHC class II cell surface receptor encoded by the human leukocyte antigen complex on chromosome 6 region 6p21.31. The complex of HLA-DR and peptide, generally between 9 and 30 amino acids in length, constitutes a ligand for the T-cell receptor (TCR). HLA were originally defined as cell surface antigens that mediate graft-versus-host disease. Identification of these antigens has led to greater success and longevity in organ transplant.

CD1D is the human gene that encodes the protein CD1d, a member of the CD1 family of glycoproteins expressed on the surface of various human antigen-presenting cells. They are non-classical MHC proteins, related to the class I MHC proteins, and are involved in the presentation of lipid antigens to T cells. CD1d is the only member of the group 2 CD1 molecules.

CD59 glycoprotein, also known as MAC-inhibitory protein (MAC-IP), membrane inhibitor of reactive lysis (MIRL), or protectin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD59 gene. It is an LU domain and belongs to the LY6/uPAR/alpha-neurotoxin protein family.

Leukocyte surface antigen CD53 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD53 gene.
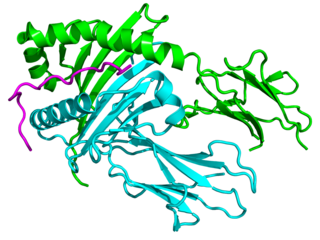
Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ alpha 1, also known as HLA-DQA1, is a human gene present on short arm of chromosome 6 (6p21.3) and also denotes the genetic locus which contains this gene. The protein encoded by this gene is one of two proteins that are required to form the DQ heterodimer, a cell surface receptor essential to the function of the immune system.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DP(W2) beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DPB1 gene.

CD244 is a human protein encoded by the CD244 gene. It is also known as Natural Killer Cell Receptor 2B4

Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DL4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIR2DL4 gene.

Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIR3DL2 gene.

Corneodesmosin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDSN gene.

Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 3 (CEACAM3) also known as CD66d, is a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) gene family..
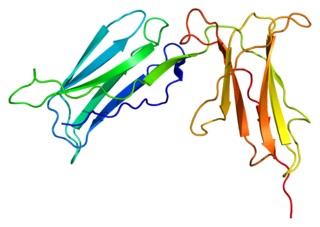
Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DS4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIR2DS4 gene.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DQ(6) alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DQA2 gene. Also known as HLA-DXA or DAAP-381D23.2, it is part of the human leucocyte antigen system.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DX beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DQB2 gene.

TAP2 is a gene in humans that encodes the protein Antigen peptide transporter 2.

Immunoglobulin superfamily, member 2 (IGSF2) also known as CD101, is a human gene.

CD1a is a human protein encoded by the CD1A gene.

CD300A is a human gene.

CMRF35-like molecule 6 (CLM-6) also known as CD300 antigen-like family member C (CD300c) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD300C gene.

Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIR3DL3 gene.













