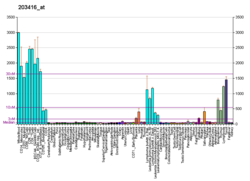
CD11c, also known as Integrin, alpha X (ITGAX), is a gene that encodes for CD11c.

Complement receptor type 2 (CR2), also known as complement C3d receptor, Epstein-Barr virus receptor, and CD21, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CR2 gene.

B-lymphocyte antigen CD19, also known as CD19 molecule, B-Lymphocyte Surface Antigen B4, T-Cell Surface Antigen Leu-12 and CVID3 is a transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the gene CD19. In humans, CD19 is expressed in all B lineage cells. Contrary to some early doubts, human plasma cells do express CD19, as confirmed by others. CD19 plays two major roles in human B cells: on the one hand, it acts as an adaptor protein to recruit cytoplasmic signaling proteins to the membrane; on the other, it works within the CD19/CD21 complex to decrease the threshold for B cell receptor signaling pathways. Due to its presence on all B cells, it is a biomarker for B lymphocyte development, lymphoma diagnosis and can be utilized as a target for leukemia immunotherapies.

CD49d is an integrin alpha subunit. It makes up half of the α4β1 lymphocyte homing receptor.
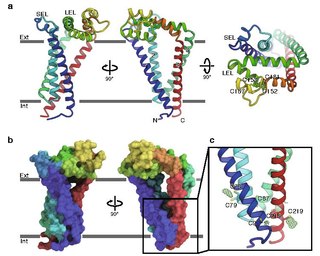
CD9 is a gene encoding a protein that is a member of the transmembrane 4 superfamily also known as the tetraspanin family. It is a cell surface glycoprotein that consists of four transmembrane regions and has two extracellular loops that contain disulfide bonds which are conserved throughout the tetraspanin family. Also containing distinct palmitoylation sites that allows CD9 to interact with lipids and other proteins.

Leukocyte antigen CD37 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD37 gene.

CD63 antigen is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the CD63 gene. CD63 is mainly associated with membranes of intracellular vesicles, although cell surface expression may be induced.

CD151 molecule, also known as CD151, is a human gene.

Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 4, also known as HLA-DRB4, is a human gene.
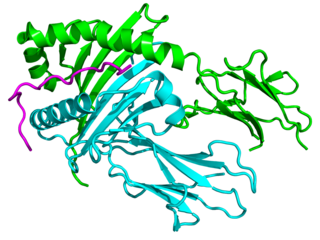
Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ alpha 1, also known as HLA-DQA1, is a human gene present on short arm of chromosome 6 (6p21.3) and also denotes the genetic locus which contains this gene. The protein encoded by this gene is one of two proteins that are required to form the DQ heterodimer, a cell surface receptor essential to the function of the immune system.

CD81 molecule, also known as CD81, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CD81 gene. It is also known as 26 kDa cell surface protein, TAPA-1, and Tetraspanin-28 (Tspan-28).

CD82, or KAI1, is a human protein encoded by the CD82 gene.

Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DL1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIR2DL1 gene.

Tetraspanin-7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TSPAN7 gene.

Tetraspanin-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TSPAN4 gene.

Prostaglandin F2 receptor negative regulator is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PTGFRN gene. PTGFRN has also been designated as CD315.

Immunoglobulin superfamily member 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGSF8 gene. IGSF8 has also been designated as CD316.

Tetraspanin-8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TSPAN8 gene.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DX beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DQB2 gene.

Immunoglobulin superfamily, member 2 (IGSF2) also known as CD101, is a human gene.