
L1, also known as L1CAM, is a transmembrane protein member of the L1 protein family, encoded by the L1CAM gene. This protein, of 200-220 kDa, is a neuronal cell adhesion molecule with a strong implication in cell migration, adhesion, neurite outgrowth, myelination and neuronal differentiation. It also plays a key role in treatment-resistant cancers due to its function. It was first identified in 1984 by M. Schachner who found the protein in post-mitotic mice neurons.

Selectin P ligand, also known as SELPLG or CD162, is a human gene.
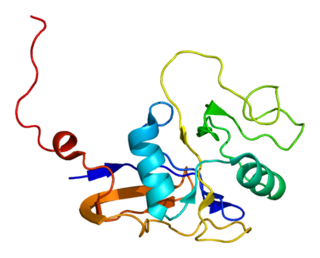
The CD44 antigen is a cell-surface glycoprotein involved in cell–cell interactions, cell adhesion and migration. In humans, the CD44 antigen is encoded by the CD44 gene on chromosome 11. CD44 has been referred to as HCAM, Pgp-1, Hermes antigen, lymphocyte homing receptor, ECM-III, and HUTCH-1.

Sialomucin core protein 24 also known as endolyn or CD164 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD164 gene. CD164 functions as a cell adhesion molecule.

CD146 also known as the melanoma cell adhesion molecule (MCAM) or cell surface glycoprotein MUC18, is a 113kDa cell adhesion molecule currently used as a marker for endothelial cell lineage. In humans, the CD146 protein is encoded by the MCAM gene.

The Lutheran antigen systems is a classification of human blood based on the presence of substances called Lutheran antigens on the surfaces of red blood cells. There are 19 known Lutheran antigens. The name Lutheran stems from a blood donor's misspelled last name, reportedly named Lutteran or Lutheran. All of these antigens arise from variations in a gene called BCAM. The system is based on the expression of two codominant alleles, designated Lua and Lub. The antigens Aua and Aub, known as the Auberger antigens, were once thought to make up a separate blood group but were later shown to be Lutheran antigens arising from variations in the BCAM gene.

Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1) also known as CD66a, is a human glycoprotein, and a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) gene family.

Laminin subunit alpha-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LAMA5 gene.

Laminin subunit gamma-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LAMC2 gene.

Signal regulatory protein α (SIRPα) is a regulatory membrane glycoprotein from SIRP family expressed mainly by myeloid cells and also by stem cells or neurons.

Cell adhesion molecule 1 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the CADM1 gene.
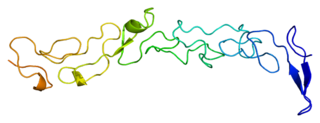
Laminin subunit gamma-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LAMC1 gene.

Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM), also known as CD326 among other names, is a transmembrane glycoprotein mediating Ca2+-independent homotypic cell–cell adhesion in epithelia. EpCAM is also involved in cell signaling, migration, proliferation, and differentiation. Additionally, EpCAM has oncogenic potential via its capacity to upregulate c-myc, e-fabp, and cyclins A & E. Since EpCAM is expressed exclusively in epithelia and epithelial-derived neoplasms, EpCAM can be used as diagnostic marker for various cancers. It appears to play a role in tumorigenesis and metastasis of carcinomas, so it can also act as a potential prognostic marker and as a potential target for immunotherapeutic strategies.

Laminin subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LAMB1 gene.

Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) also known as CD66c, is a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) gene family..

CD166 antigen is a 100-105 kD typeI transmembrane glycoprotein that is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of proteins. In humans it is encoded by the ALCAM gene. It is also called CD166, MEMD, SC-1/DM-GRASP/BEN in the chicken, and KG-CAM in the rat.

Neuronal cell adhesion molecule is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NRCAM gene.
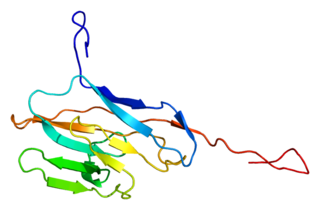
Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8 (CEACAM8) also known as CD66b, is a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) gene family. Its main function is cell adhesion, cell migration, and pathogen binding.

Laminin subunit gamma-3 also known as LAMC3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LAMC3 gene.

Gene HEPACAM*, named based on its original site of identification - hepatocytes and the nature of its protein product - a cell adhesion molecule (CAM), was first discovered and characterised in human liver and reported by Shali Shen in 2005. The gene encodes a protein of 416 amino acids, designated as hepaCAM**, which is a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of cell adhesion molecules. The main biological functions of hepaCAM include a) modulating cell-matrix adhesion and migration, and b) inhibiting cancer cell growth.
























