
The City and Borough of Wrangell is a borough in Alaska, United States. As of the 2010 census the population was 2,369, up from 2,308 in 2000.

Fort Vancouver was a 19th-century fur trading post that was the headquarters of the Hudson's Bay Company's Columbia Department, located in the Pacific Northwest. Named for Captain George Vancouver, the fort was located on the northern bank of the Columbia River in present-day Vancouver, Washington. The fort was a major center of the regional fur trading. Every year trade goods and supplies from London arrived either via ships sailing to the Pacific Ocean or overland from Hudson Bay via the York Factory Express. Supplies and trade goods were exchanged with a plethora of Indigenous cultures for fur pelts. Furs from Fort Vancouver were often shipped to the Chinese port of Guangzhou where they were traded for Chinese manufactured goods for sale in the United Kingdom. At its pinnacle, Fort Vancouver watched over 34 outposts, 24 ports, six ships, and 600 employees. Today, a full-scale replica of the fort, with internal buildings, has been constructed and is open to the public as Fort Vancouver National Historic Site.

Fort Hall was a fort that was built in 1834 as a fur trading post by Nathaniel Jarvis Wyeth. It was located on the Snake River in the eastern Oregon Country, now part of present-day Bannock County in southeastern Idaho, United States. Mr. Wyeth was an inventor and businessman from Boston, Massachusetts, who also founded a post at Fort William, in present-day Portland, Oregon, as part of a plan for a new trading and fisheries company. Unable to compete with the powerful British Hudson's Bay Company, based at Fort Vancouver, in 1837 Wyeth sold both posts to it. Great Britain and the United States both operated in the Oregon Country in these years.

Fort Astoria was the primary fur trading post of John Jacob Astor's Pacific Fur Company (PFC). A maritime contingent of PFC staff was sent on board the Tonquin, while another party traveled overland from St. Louis. This land based group later became known as the Astor Expedition. Built at the entrance of the Columbia River in 1811, Fort Astoria was the first American-owned settlement on the Pacific coast of North America.

The Taku River is a river running from British Columbia, Canada, to the northwestern coast of North America, at Juneau, Alaska. The river basin spreads across 27,500 square kilometres (10,600 sq mi). The Taku is a very productive salmon river and its drainage basin is primarily wilderness.

Fort Nisqually was an important fur trading and farming post of the Hudson's Bay Company in the Puget Sound area, part of the Hudson's Bay Company's Columbia Department. It was located in what is now DuPont, Washington. Today it is a living history museum located in Tacoma, Washington, USA, within the boundaries of Point Defiance Park. The Fort Nisqually Granary, moved along with the Factor's House from the original site of the second fort to this park, is a U.S. National Historic Landmark. Built in 1843, the granary is the oldest building in Washington state and one of the only surviving examples of a Hudson's Bay Company "post on sill" structure. The Factor's House and the granary are the only surviving Hudson's Bay Company buildings in the United States.

Russian America was the name of the Russian colonial possessions in North America from 1799 to 1867. Its capital was Novo-Arkhangelsk, which is now Sitka, Alaska, United States. Settlements spanned parts of what are now the U.S. states of California, Alaska and three forts in Hawaii. Formal incorporation of the possessions by Russia did not take place until the Ukase of 1799 which established a monopoly for the Russian–American Company and also granted the Russian Orthodox Church certain rights in the new possessions. Many of its possessions were abandoned in the 19th century. In 1867, Russia sold its last remaining possessions to the United States of America for $7.2 million.

The Columbia District was a fur trading district in the Pacific Northwest region of British North America in the 19th century. Much of its territory overlapped with the disputed Oregon Country. It was explored by the North West Company between 1793 and 1811, and established as an operating fur district around 1810. The North West Company was absorbed into the Hudson's Bay Company in 1821 under which the Columbia District became known as the Columbia Department. The Oregon Treaty of 1846 marked the effective end of the Hudson's Bay Company's Columbia Department.
Fort Espérance was a North West Company trading post near Rocanville, Saskatchewan from 1787 until 1819. It was moved three times and was called Fort John from 1814 to 1816. There was a competing XY Company post from 1801 to 1805 and a Hudson's Bay post nearby from 1813 to 1816. It was on the Qu'Appelle River about 20 km from that river's junction with the Assiniboine River and about 7 km west of the Manitoba border. It was on the prairie in buffalo country and was mainly used as a source of pemmican which was sent down the river to Fort Bas de la Rivière at the mouth of the Winnipeg River.

Fort Langley National Historic Site, commonly shortened to Fort Langley, is a former fur trading post of the Hudson's Bay Company in the community of Fort Langley of Langley, British Columbia, Canada. The national historic site sits above the banks of the Bedford Channel across McMillan Island. The national historic site contains a visitor centre and a largely reconstructed trading post that contains ten structures surrounded by wooden palisades.

The Taku are an Alaskan Native people, a ḵwáan or geographic subdivision of the Tlingit, known in their own language as the Tʼaaḵu Ḵwáan or "Geese Flood Upriver Tribe". The Taku lived along the northwestern coast of North America, in the area that is now the Alexander Archipelago of Alaska, and on the lower basin of the Taku River of the adjoining British Columbia mainland above that river's mouth.
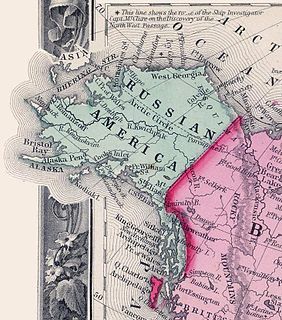
The Treaty of Saint Petersburg of 1825 or the Anglo-Russian Convention of 1825, officially the Convention Concerning the Limits of Their Respective Possessions on the Northwest Coast of America and the Navigation of the Pacific Ocean, defined the boundaries between Russian America and British claims and possessions of the Pacific Coast, and the later Yukon and Arctic regions of North America. It was agreed that along the coast at the southern tip of Prince of Wales island northward to the 56 parallel, with the island wholly belonging to Russia, then to 10 marine leagues inland going north to the 60th Parallel, and then to the north of the 60th Parallel at the 141st line of longitude all the way to the "Frozen Ocean", the current Alaska/Canadian Yukon boundary, would be the boundary. The coastal limit had, the year before, been established as the limit of overlapping American claims in the parallel Russo-American Treaty of 1824. The Russian sphere in the region was later sold to the United States, eventually becoming the State of Alaska, while the British claim, along the coast to the south of parallel 54°40′ is now the coast of the Canadian province of British Columbia, and for inland regions it defined the western limit of what became the modern day Canadian territory of Yukon. It also defined associated rights and obligations concerning waters and ports in the region. The treaty, in establishing a vague division of coastal Russian interests and inland British interests between 56 and 60 degrees north latitude, led to conflicting interpretations of the meaning of the treaty's wording which later manifested in the Alaska Boundary Dispute between the United States on the one hand, and Canada on the other.
Taku Harbor is a small, remote bay located on the eastern shore of Stephens Passage about 22 miles southeast of central Juneau, Alaska, United States.
Fort McLoughlin was a fur trading post established in 1833 by the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) on Campbell Island in present-day British Columbia, Canada. At the time the Hudson's Bay Company performed quasi-governmental duties on behalf of the British Empire as well as undertaking trade for profit. The site is believed to have been at McLoughlin Bay on the northeast side of Campbell Island and is associated with the relocation of the Heiltsuk community of Bella Bella from its former location on islets near Denny Island. The McLoughlin name, which is that of John McLoughlin, regional head of company operations at that time, is also found in a lake and a creek entering that bay, and was conferred on these locations after the fort had closed.
Fort Simpson was a fur trading post established in 1831 by the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) near the mouth of the Nass River in present-day British Columbia, Canada. In 1834, it was moved to the Tsimpsean Peninsula, about halfway between the Nass River and the Skeena River, and was later referred to as Port Simpson or as the native name Lax Kw'alaams. The fort was part of the HBC's Columbia Department.
Fort Stikine was a fur trade post and fortification in what is now the Alaska Panhandle, at the site of the present-day of Wrangell, Alaska, United States. Originally built as the Redoubt San Dionisio or Redoubt Saint Dionysius in 1834, the site was transferred to the British-owned Hudson's Bay Company as part of a lease signed in the region in 1838, and renamed Fort Stikine when turned into a Hudson's Bay Company post in 1839. The post was closed and decommissioned by 1843 but the name remained for the large village of the Stikine people which had grown around it, becoming known as Shakesville in reference to its ruling Chief Shakes by the 1860s. With the Alaska Purchase of 1867, the fortification became occupied by the US Army and was renamed Fort Wrangel, a reference to Baron von Wrangel, who had been Governor of Russian America when the fort was founded. The site today is now part of the city of Wrangell.

The maritime fur trade was a ship-based fur trade system that focused on acquiring furs of sea otters and other animals from the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast and natives of Alaska. The furs were mostly sold in China in exchange for tea, silks, porcelain, and other Chinese goods, which were then sold in Europe and the United States. The maritime fur trade was pioneered by Russians, working east from Kamchatka along the Aleutian Islands to the southern coast of Alaska. British and Americans entered during the 1780s, focusing on what is now the coast of British Columbia. The trade boomed around the beginning of the 19th century. A long period of decline began in the 1810s. As the sea otter population was depleted, the maritime fur trade diversified and transformed, tapping new markets and commodities, while continuing to focus on the Northwest Coast and China. It lasted until the middle to late 19th century.

The Stikine Region is an unincorporated area in northwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is the only area in the province that is not part of a regional district. The Stikine Region was left unincorporated following legislation that established the province's regional districts in 1968 and is not classified as a regional district. It contains no municipal governments which normally constitute the majority of seats on the boards of regional districts. There is only one local planning area, the Atlin Community Planning Area, which was combined in 2009 with the Atlin Community Improvement District to provide fire, landfill, water, streetlighting, sidewalks and advisory land use services. All other services not provided privately are administered directly by various provincial government ministries. The area around Dease Lake, formerly in the Stikine Region, is now within the boundaries of the Regional District of Kitimat-Stikine following a boundary amendment in 2008.
The RAC–HBC Agreement was a series of protocols signed by the Russian-American Company (RAC) and the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) in 1839. Over previous decades both monopolies secured regions for control of the Maritime fur trade, the RAC being based in Russian America and the HBC in the Columbia Department of the Oregon Country. As the outposts and trading stations of each company grew closer in proximity, a clash of interests occurred in 1834 at Redoubt Saint Dionysius on the site of modern Wrangell, Alaska. Officials from the two companies felt it was necessary to settle their long standing issues. Ferdinand Wrangel, Governor of Russian America, volunteered to negotiate on behalf of the RAC and the HBC sent George Simpson, Governor of Rupert's Land. Previously Simpson had stated to the HBC committee that if a settlement with the Russians was concluded, "we ought to be able to put down all competition on the Coast..." By removing the Russian markets, the Governor felt American merchants would lose an important revenue source. The Imperial Government of Russia in late 1838 ordered the RAC to end its disputes with the British, before it could strain relations with the United Kingdom. Simpson and Wrangel negotiated a commercial treaty in early 1839 while in Hamburg.
Urbain Héroux was a French-Canadian employee of the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), stationed primarily in the Pacific Northwest in the 1830s and 1840s.















