Interleukins (ILs) are a group of cytokines that are expressed and secreted by white blood cells (leukocytes) as well as some other body cells. The human genome encodes more than 50 interleukins and related proteins.

Interleukin 10 (IL-10), also known as human cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor (CSIF), is an anti-inflammatory cytokine. In humans, interleukin 10 is encoded by the IL10 gene. IL-10 signals through a receptor complex consisting of two IL-10 receptor-1 and two IL-10 receptor-2 proteins. Consequently, the functional receptor consists of four IL-10 receptor molecules. IL-10 binding induces STAT3 signalling via the phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic tails of IL-10 receptor 1 + IL-10 receptor 2 by JAK1 and Tyk2 respectively.

Interleukin 12 (IL-12) is an interleukin that is naturally produced by dendritic cells, macrophages, neutrophils, and human B-lymphoblastoid cells (NC-37) in response to antigenic stimulation. IL-12 belongs to the family of interleukin-12. IL-12 family is unique in comprising the only heterodimeric cytokines, which includes IL-12, IL-23, IL-27 and IL-35. Despite sharing many structural features and molecular partners, they mediate surprisingly diverse functional effects.

The interleukin 4 is a cytokine that induces differentiation of naive helper T cells (Th0 cells) to Th2 cells. Upon activation by IL-4, Th2 cells subsequently produce additional IL-4 in a positive feedback loop. IL-4 is produced primarily by mast cells, Th2 cells, eosinophils and basophils. It is closely related and has functions similar to IL-13.

Interleukin 3 (IL-3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL3 gene localized on chromosome 5q31.1. Sometimes also called colony-stimulating factor, multi-CSF, mast cell growth factor, MULTI-CSF, MCGF; MGC79398, MGC79399: the protein contains 152 amino acids and its molecular weight is 17 kDa. IL-3 is produced as a monomer by activated T cells, monocytes/macrophages and stroma cells. The major function of IL-3 cytokine is to regulate the concentrations of various blood-cell types. It induces proliferation and differentiation in both early pluripotent stem cells and committed progenitors. It also has many more specific effects like the regeneration of platelets and potentially aids in early antibody isotype switching.

The common gamma chain (γc), also known as interleukin-2 receptor subunit gamma or IL-2RG, is a cytokine receptor sub-unit that is common to the receptor complexes for at least six different interleukin receptors: IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15 and interleukin-21 receptor. The γc glycoprotein is a member of the type I cytokine receptor family expressed on most lymphocyte populations, and its gene is found on the X-chromosome of mammals.
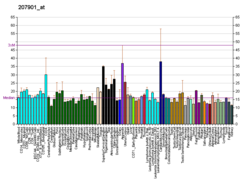
Interleukin 7 (IL-7) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL7 gene.

Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) also known as leukocytic pyrogen, leukocytic endogenous mediator, mononuclear cell factor, lymphocyte activating factor and other names, is a cytokine protein that in humans is encoded by the IL1B gene. There are two genes for interleukin-1 (IL-1): IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta. IL-1β precursor is cleaved by cytosolic caspase 1 to form mature IL-1β.

Interleukin 16 is a pro-inflammatory pleiotropic cytokine. It's precursor, pro-interleukin-16 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL16 gene. This gene was discovered in 1982 at Boston University by Dr. David Center and Dr. William Cruikshank.

Interleukin-12 subunit alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL12A gene.

Interleukin-12 receptor, beta 1, or IL-12Rβ1 in short, is a subunit of the interleukin 12 receptor and the interleukin 23 receptor. IL12RB1, is the name of its human gene. IL-12Rβ1 is also known as CD212.

Interleukin 5 receptor, alpha (IL5RA) also known as CD125 is a subunit of the Interleukin-5 receptor. IL5RA also denotes its human gene.

Interleukin 9 receptor (IL9R) also known as CD129 is a type I cytokine receptor. IL9R also denotes its human gene.

Interleukin 10 receptor, beta subunit is a subunit for the interleukin-10 receptor. IL10RB is its human gene.

Interleukin 17 receptor A, also known as IL17RA and CDw217, is a human gene.

Interleukin 21 receptor is a type I cytokine receptor. IL21R is its human gene.

Interleukin-2 receptor subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL2RB gene. Also known as CD122; IL15RB; P70-75.

Epstein-Barr virus induced gene 3, also known as interleukin-27 subunit beta or IL-27B, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the EBI3 gene.

Interleukin 3 receptor, alpha (IL3RA), also known as CD123, is a human gene.

Interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain is a protein involved in assembly of high-affinity Interleukin-2 receptor, consisting of alpha (IL2RA), beta (IL2RB) and the common gamma chain (IL2RG). As the name indicates, this receptor interacts with pleiotropic cytokine called Interleukin-2, which effect is mainly important for immune homeostasis.