Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems. Based on the PostScript language, each PDF file encapsulates a complete description of a fixed-layout flat document, including the text, fonts, vector graphics, raster images and other information needed to display it. PDF has its roots in "The Camelot Project" initiated by Adobe co-founder John Warnock in 1991. PDF was standardized as ISO 32000 in 2008. The last edition as ISO 32000-2:2020 was published in December 2020.

The CMYK color model is a subtractive color model, based on the CMY color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. The abbreviation CMYK refers to the four ink plates used: cyan, magenta, yellow, and key (black).

OpenStep is an object-oriented application programming interface (API) specification developed by NeXT. It provides a framework for building graphical user interfaces (GUIs) and developing software applications. OpenStep was designed to be platform-independent, allowing developers to write code that could run on multiple operating systems, including NeXTSTEP, Windows NT, and various Unix-based systems. It has influenced the development of other GUI frameworks, such as Cocoa for macOS, and GNUstep.
Tag Image File Format or Tagged Image File Format, commonly known by the abbreviations TIFF or TIF, is an image file format for storing raster graphics images, popular among graphic artists, the publishing industry, and photographers. TIFF is widely supported by scanning, faxing, word processing, optical character recognition, image manipulation, desktop publishing, and page-layout applications. The format was created by the Aldus Corporation for use in desktop publishing. It published the latest version 6.0 in 1992, subsequently updated with an Adobe Systems copyright after the latter acquired Aldus in 1994. Several Aldus or Adobe technical notes have been published with minor extensions to the format, and several specifications have been based on TIFF 6.0, including TIFF/EP, TIFF/IT, TIFF-F and TIFF-FX.
Color management is the process of ensuring consistent and accurate colors across various devices, such as monitors, printers, and cameras. It involves the use of color profiles, which are standardized descriptions of how colors should be displayed or reproduced.
X3D is a set of royalty-free ISO/IEC standards for declaratively representing 3D computer graphics. X3D includes multiple graphics file formats, programming-language API definitions, and run-time specifications for both delivery and integration of interactive network-capable 3D data. X3D version 4.0 has been approved by Web3D Consortium, and is under final review by ISO/IEC as a revised International Standard (IS).
ColorSync is Apple Inc.'s color management API for the Mac OS and Mac OS X Operating Systems.

sRGB is a standard RGB color space that HP and Microsoft created cooperatively in 1996 to use on monitors, printers, and the World Wide Web. It was subsequently standardized by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as IEC 61966-2-1:1999. sRGB is the current defined standard colorspace for the web, and it is usually the assumed colorspace for images that are neither tagged for a colorspace nor have an embedded color profile.
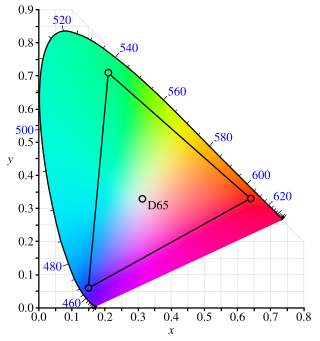
The Adobe RGB (1998) color space or opRGB is a color space developed by Adobe Inc. in 1998. It was designed to encompass most of the colors achievable on CMYK color printers, but by using RGB primary colors on a device such as a computer display. The Adobe RGB (1998) color space encompasses roughly 30% of the visible colors specified by the CIELAB color space – improving upon the gamut of the sRGB color space, primarily in cyan-green hues. It was subsequently standardized by the IEC as IEC 61966-2-5:1999 with a name opRGB and is used in HDMI.
Advanced Function Presentation (AFP) is a presentation architecture and family of associated printer software and hardware that provides for document and information presentation independent of specific applications and devices.

Multibus is a computer bus standard used in industrial systems. It was developed by Intel Corporation and was adopted as the IEEE 796 bus.
An image file format is a file format for a digital image. There are many formats that can be used, such as JPEG, PNG, and GIF. Most formats up until 2022 were for storing 2D images, not 3D ones. The data stored in an image file format may be compressed or uncompressed. If the data is compressed, it may be done so using lossy compression or lossless compression. For graphic design applications, vector formats are often used. Some image file formats support transparency.
Open XML Paper Specification is an open specification for a page description language and a fixed-document format. Microsoft developed it as the XML Paper Specification (XPS). In June 2009, Ecma International adopted it as international standard ECMA-388.

Linux color management has the same goal as the color management systems (CMS) for other operating systems, which is to achieve the best possible color reproduction throughout an imaging workflow from its source, through imaging software, and finally onto an output medium. In particular, color management attempts to enable color consistency across media and throughout a color-managed workflow.
In color management, an ICC profile is a set of data that characterizes a color input or output device, or a color space, according to standards promulgated by the International Color Consortium (ICC). Profiles describe the color attributes of a particular device or viewing requirement by defining a mapping between the device source or target color space and a profile connection space (PCS). This PCS is either CIELAB (L*a*b*) or CIEXYZ. Mappings may be specified using tables, to which interpolation is applied, or through a series of parameters for transformations.

Specifications for Web Offset Publications, invariably abbreviated to SWOP, is an organization and the name of a set of specifications that it produces, with the aim of improving the consistency and quality of professionally printed material in the United States, and of certain other products, programs and endorsements related to their work. Among other things, the organization specifies SWOP inks used in CMYK printing, colors of SWOP proofs, other physical qualities pertaining to printing. The organization publishes its own specification and ICC profile and runs a certification program.
Monitor proofing or soft-proofing is a step in the prepress printing process. It uses specialized computer software and hardware to check the accuracy of text and images used for printed products. Monitor proofing differs from conventional forms of “hard-copy” or ink-on-paper color proofing in its use of a calibrated display(s) as the output device.
PDF/VT is an international standard published by ISO in August 2010 as ISO 16612-2. It defines the use of PDF as an exchange format optimized for variable and transactional printing. Built on top of PDF/X-4, it is the first variable-data printing (VDP) format which ensures modern International Color Consortium-based (ICC) color management through the use of ICC Output Intents. It adds the notion of encapsulated groups of graphic objects to support optimized efficient processing for repeating text, graphic or image content. Introducing the concept of document part metadata (DPM), it enables reliable and dynamic management of pages for High Volume Transactional Output (HVTO) print data, like record selection or postage optimization based on metadata.
The Application Programming Interface for Windows (APIW) Standard is a specification of the Microsoft Windows 3.1 API drafted by Willows Software. It is the successor to previously proposed Public Windows Interface standard. It was created in an attempt to establish a vendor-neutral, platform-independent, open standard of the 16-bit Windows API not controlled by Microsoft.
The European Color Initiative (ECI) is an expert group that is concerned with media-neutral reproduction of color data in digital publication systems. It was formed in June 1996 by German publishers Bauer, Burda, Gruner + Jahr and Springer in Hamburg.