Related Research Articles

Canajoharie is a village in the Town of Canajoharie in Montgomery County, New York, United States. As of the 2010 census, the village had a population of 2,229. The name is said to be a Mohawk language term meaning "the pot that washes itself," referring to the "Canajoharie Boiling Pot," a circular gorge in the Canajoharie Creek, just south of the village.

Peebles Island State Park is a 190-acre (0.77 km2) state park located at the confluence of the Mohawk and Hudson rivers in New York. A majority of the park is located in Saratoga County, with a smaller portion located in Albany County.

Grouseland, the William Henry Harrison Mansion and Museum, is a National Historic Landmark important for its Federal-style architecture and role in American history. The two-story, red brick home was built between 1802 and 1804 in Vincennes, Indiana, for William Henry Harrison (1773–1841) during his tenure from 1801 to 1812 as the first governor of the Indiana Territory. The residence was completed in 1804, and Harrison reportedly named it Grouseland due to the abundance of grouse in the area.

Starved Rock State Park is a state park in the U.S. state of Illinois, characterized by the many canyons within its 2,630 acres (1,064 ha). Located just southeast of the village of Utica, in Deer Park Township, LaSalle County, Illinois, along the south bank of the Illinois River, the park hosts over two million visitors annually, the most for any Illinois state park.

Angel Mounds State Historic Site, an expression of the Mississippian culture, is an archaeological site managed by the Indiana State Museum and Historic Sites that includes more than 600 acres of land about 8 miles (13 km) southeast of present-day Evansville, in Vanderburgh and Warrick counties in Indiana. The large residential and agricultural community was constructed and inhabited from AD 1100 to AD 1450, and served as the political, cultural, and economic center of the Angel chiefdom. It extended within 120 miles (190 km) of the Ohio River valley to the Green River in present-day Kentucky. The town had as many as 1,000 inhabitants inside the walls at its peak, and included a complex of thirteen earthen mounds, hundreds of home sites, a palisade (stockade), and other structures.

Fort Orange was the first permanent Dutch settlement in New Netherland; the present-day city and state capital Albany, New York developed near this site. It was built in 1624 as a replacement for Fort Nassau, which had been built on nearby Castle Island and served as a trading post until 1617 or 1618, when it was abandoned due to frequent flooding. Both forts were named in honor of the Dutch House of Orange-Nassau. Due to a dispute between the Director-General of New Netherland and the patroonship of Rensselaerswyck regarding jurisdiction over the fort and the surrounding community, the fort and community became an independent municipality, paving the way for the future city of Albany. After the English reconquered the region they soon abandoned Fort Orange in favor of a new fort: Fort Frederick, constructed in 1676.

Ganondagan State Historic Site, also known as Boughton Hill, is a Native American historic site in Ontario County, New York in the United States. Location of the largest Seneca village of the 17th century, the site is in the present-day Town of Victor, southwest of the Village of Victor. The village was also referred to in various spellings as Gannagaro, Canagora, Gandagora, Gandagaro and Gannontaa.

Old Fort Johnson is a historic house museum and historic site at 2 Mergner Road in Fort Johnson, New York. It is the site of Fort Johnson, a two-story stone house originally enclosed in fortifications built by Sir William Johnson about 1749. The fort served as Johnson's home, business office and trading center until 1763 when he moved to Johnson Hall in what is now Johnstown, New York. Sir William's son Sir John Johnson owned the house from 1763 until 1776, when it was confiscated by the local Committee of Safety. The house remains and is owned and operated as a museum by the Montgomery County Historical Society. It was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1972.

Crystal River State Archaeological Site is a 61-acre (250,000 m2) Florida State Park located on the Crystal River and within the Crystal River Preserve State Park. The park is located two miles (3 km) northwest of the city of Crystal River, on Museum Point off U.S. 19/98.

Mohawk Upper Castle Historic District is a historic district in Herkimer County, New York that was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1993. Located south of the Mohawk River, it includes the Indian Castle Church, built in 1769 by Sir William Johnson, British Superintendent of Indian Affairs, as a missionary church for the Mohawk in the western part of their territory; the Brant Family Barn, a rare surviving example of Dutch colonial barns in the Mohawk Valley; as well as important archaeological site areas revealing life in Nowadaga, as the western part of the Mohawk village of Canajoharie was known. The fortified village was called the Upper Castle by European colonists.

Schoharie Crossing State Historic Site, also known as Erie Canal National Historic Landmark, is a historic district that includes the ruins of the Erie Canal aqueduct over Schoharie Creek, and a 3.5-mile (5.6 km) long part of the Erie Canal, in the towns of Glen and Florida within Montgomery County, New York. It was the first part of the old canal to be designated a National Historic Landmark, prior to the designation of the entire New York State Barge Canal as an NHL in 2017.
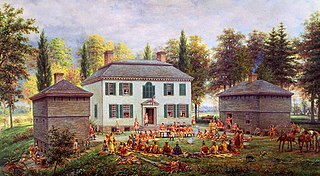
Johnson Hall State Historic Site was the home of Sir William Johnson (1715–1774) an Irish pioneer who became the influential British Superintendent of Indian Affairs in the Province of New York, known for his strong relationship especially with the Mohawk and other Iroquois League nations.

The Menard–Hodges site (3AR4), is an archaeological site in Arkansas County, Arkansas. It includes two large platform mounds as well as several house mounds. It is the type site for the Menard phase, a protohistoric Mississippian culture group.
Garoga Site is an archaeological site located at Ephratah in Fulton County, New York. It is also known as Las-7, New York State Office of Parks, Recreation, and Historic Preservation Unique Site No. A035-04-0001. It is one of three Mohawk Indian village sites excavated by archaeologist Robert E. Funk in 1969–1970.
Smith Pagerie Site, also known as Las. 11–4, New York State Office of Parks, Recreation, and Historic Preservation Unique Site No. A035-04-0002, is an archaeological site located at Ephratah in Fulton County, New York, US. It is one of three Mohawk Indian village sites excavated by the archaeologist Robert E. Funk in 1969–1970.

Caughnawaga Indian Village Site is an archaeological site located just west of Fonda in Montgomery County, New York. It is the location of a 17th-century Mohawk nation village. One of the original Five Nations of the Iroquois League, or Haudenosaunee, the Mohawk lived west of Albany and occupied much of the Mohawk Valley. Other Iroquois nations were located west of them and south of the Great Lakes.
Rice's Woods is an archaeological site located at Canajoharie in Montgomery County, New York. S. L. Frey, the pioneer Mohawk Valley archaeologist, believed that the Mohawk village site in Rice's Woods, on Big Nose, was Canajorha, the Middle Castle of the Mohawks after about 1677. Other authorities believe that it was the Lower Castle at this same period.

The Ware Mounds and Village Site (11U31), also known as the Running Lake Site, located west of Ware, Illinois, is an archaeological site comprising three platform mounds and a 160-acre (65 ha) village site. The site was inhabited by the Late Woodland and Mississippian cultures from c. 800 to c. 1300. The village may be the only Mississippian village known to have existed in the Mississippi River valley in Southern Illinois. As the village was located near two major sources of chert, which Mississippian cultures used to make agricultural tools, it was likely a trading center for the mineral.
Tionondogen was the westernmost and most important of the three large palisaded towns of the Mohawk Nation of Iroquois. These towns were termed "castles" by the Europeans. Because of its position as the farthest upstream on the Mohawk River Tionondogen is often referred to as the "Upper Castle".

The T. C. Steele State Historic Site is located in rural Brown County, Indiana, one and a half miles south of Belmont, between Bloomington and Nashville, Indiana. The property was the studio and home of Hoosier Group landscape and portrait artist Theodore Clement Steele (1847–1926) and Selma Neubacher Steele (1870–1945), the artist's second wife. Shortly before her death in 1945, Selma donated the property on 211 acres of land to the Indiana Department of Conservation to establish a state historic site in memory of her husband. The property was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1973 as the Theodore Clement Steele House and Studio. The Indiana State Museum operates the historic site, which is open to the public and offers guided tours of the home and studio.
References
- 1 2 "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places . National Park Service. March 13, 2009.
- ↑ Funk, Robert E. and Robert D. Kuhn (2003). Three Sixteenth-Century Mohawk Iroquois Village Sites (book) (Museum Bulletin 503 ed.). New York State Museum, Albany NY. pp. 482pp. ISBN 1-55557-147-6.
- ↑ Snow, Dean (1995). Mohawk Valley Archaeology: The Sites (PDF). Matson Museum of Archaeology, Penn State University. ISBN 0-9647913-0-7. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 14, 2017. Retrieved May 2, 2016.

