Maps
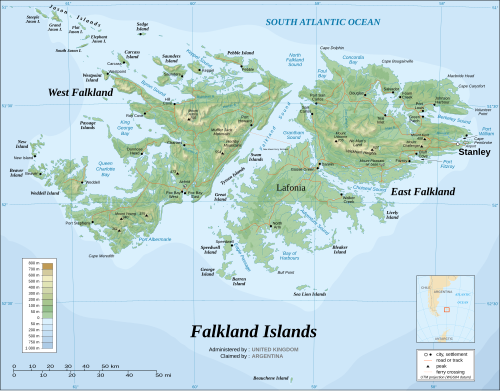 |  |
This is a list of English and Spanish language placenames in the Falkland Islands . Most of the Spanish language names are quite different in origin to their English equivalents, and many have religious resonances. Some names were given by the Spanish conquistadores , while others were given later by the Argentine government.
The Spanish names are almost never used by residents of the islands themselves, and some, such as Malvinas and Puerto Argentino, may be considered offensive by them due to their association with the 1982 invasion of the Falkland Islands. [1] Under a declaration issued jointly following the 1999 agreement lifting travel restrictions to the islands, Argentina undertook to review the Argentine place names for Falkland Island locations, imposed under decree by General Galtieri. [2] However, to date, Argentina still continues to use these placenames to the frustration of the islanders. [3] Many are not generally in use as Spanish names, rather they are names conferred by an Argentine Government committee where there is no Spanish language equivalent.
The Falkland Islands take their name from the Falkland Sound, a strait separating the archipelago's two main islands. [4] The name "Falkland" was applied to the channel by John Strong, captain of an English expedition, which landed on the islands in 1690. Strong named the strait in honour of Anthony Cary, 5th Viscount of Falkland, the Treasurer of the Navy who sponsored their journey. [5] The Viscount's title originates from the town of Falkland, Scotland, whose name comes from "folkland" (land held by folk-right). [6] The name was not applied to the islands until 1765, when British captain John Byron of the Royal Navy, claimed them for King George III as "Falkland's Islands". [7] The term "Falklands" is a short name used to refer to the islands.
The Spanish name for the archipelago, Islas Malvinas, derives from the French Îles Malouines — the name given to the islands by French explorer Louis-Antoine de Bougainville in 1764. [8] Bougainville, who founded the islands' first settlement, named the area after the port of Saint-Malo (the point of departure for his ships and colonists). [9] The port, located in the Brittany region of western France, was in turn named after St. Malo (or Maclou), the Christian evangelist who founded the city. [10]
At the twentieth session of the United Nations General Assembly, the Fourth Committee determined that, in all languages other than Spanish, all UN documentation would designate the territory as Falkland Islands (Malvinas). In Spanish, the territory was designated as Islas Malvinas (Falkland Islands). [11] The nomenclature used by the United Nations for statistical processing purposes is Falkland Islands (Malvinas). [12]
A few names have the same form in both English and Spanish; for example Darwin, San Carlos, Salvador and Rincon Grande.
 |  |
| English language name | Spanish language name | Notes |
| Falkland Islands | Islas Malvinas | The Spanish name for the islands, "Islas Malvinas", is derived from a French original "Îles Malouines" (St Malo/Maclevine Islands) |
| West Falkland | Isla Gran Malvina | Despite the Spanish name, East Falkland is larger |
| East Falkland | Isla Soledad | |
| Barren Island | Isla Pelada | Direct translation |
| Beaver Island | Isla San Rafael | |
| Beauchene Island | Isla Beauchéne | |
| Bleaker Island | Isla María | |
| Carcass Island | Isla del Rosario | |
| Eddystone | Roca Remolinos | English name commemorates Eddystone off Devon and Cornwall |
| George Island | Isla Jorge | Direct translation |
| Great Island | Isla Grande | Direct translation |
| Jason Islands | Isla Sebaldes | "Sebald Islands" was once applied to the whole archipelago, and is derived from Sebald de Weert, the first European explorer widely credited with sighting the islands. The Jason Islands are subdivided into two groups in Spanish. |
| Leeward part of Jason Islands | Islas los Salvajes | Grand Jason and Steeple Jason |
| Windward part of Jason Islands | Islas las Llaves | Flat Jason, Seal Rocks and North Fur Island |
| Keppel Island | Isla de la Vigía | |
| Lively Island | Isla Bougainville | |
| New Island | Isla Goicoechea | |
| Pebble Island | Isla (de) Borbón/Isla Bourbon | |
| Ruggles Island | Isla Calista | |
| Saunders Island | Isla Trinidad | |
| Sea Lion Island | Isla de los Leones Marinos | Direct translation |
| Sedge Island | Isla Culebra | |
| Speedwell Island | Isla Águila | Formerly "Eagle Island" in English |
| Staats Island | Isla Staats | Direct translation |
| Weddell Island | Isla San José | Formerly "Swan Island" in English (cf Swan Islands) |
| West Point Island | Isla Remolinos | Formerly "Albatross Island" |
| English language name | Spanish language name | Notes |
| Stanley | Puerto Stanley (Puerto Argentino) | Both Spanish names are currently used, "Puerto Argentino" was first used during the Falklands War and is favoured by supporters of the Argentine claim. "Port Stanley" persists in unofficial English usage [13] |
| Port San Carlos | Puerto San Carlos | Direct translation |
| Goose Green | Pradera del Ganso, Ganso Verde [sic] | |
| Port Louis | Puerto Luis | Both names derive from the original French name of "Port St Louis", during the Spanish occupation it was renamed "Puerto Soledad", the settlement was briefly named "Anson's Harbour" by the British but reverted to Port Louis [14] |
| Port Howard | Puerto Mitre | |
| Teal Inlet | Caleta Trullo | |
| Johnson's Harbour | Puerto Johnson | Indirect translation |
| English language name | Spanish language name | Notes |
| Cape Dolphin | Cabo Leal | |
| Mount Usborne | Cerro Alberdi | |
| Mount Adam | Monte Independencia/Monte Beaufort [13] | |
| Mount Robinson | Monte Independencia until it was found Mount Adam was higher [13] | |
| NA | Peninsula de Freycinet | The peninsula north of Port William (no English equivalent) |
| NA | Peninsula de San Luis | The north east peninsula containing Johnson Harbour, Port Louis and Rincon Grande (no English equivalent) |
| English language name | Spanish language name | Notes |
| Falkland Sound | Estrecho de San Carlos | English name comes from the Sound, San Carlos Water has a narrower meaning in English |
| Scotia Sea | Mar del Scotia | The name Scotia Sea was conferred in about 1932 after the Scotia, the expedition ship used in these waters by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition (1902–04). |
| Choiseul Sound | Seno Choiseul | Originally named by Louis de Bougainville after the French Foreign Secretary, the Duc de Choiseul |
| Berkeley Sound | Bahía de la Anunciación | |
| Adventure Sound | Bahía del Laberinto | |
| Bay of Harbours | Bahía de los Abrigos | |
| Grantham Sound | Bahía de Ruiz Puente | |
| Foul Bay | Bahía Sucla | |
| Port Albemarle | Bahía Santa Eufemia | |
| Port William | Puerto Groussac | |
| Queen Charlotte Bay | Bahía San Julián | |
| Port Edgar | Puerto Edgardo | |
| King George Bay | Bahía 9 de Julio | |
| Byron Sound | Bahía San Francisco de Paula | |
| Keppel Sound | Bahía de la Cruzada | |
| Stanley Harbour | Originally known as "Beau Porte" (French), [15] and later as "Port Jackson" by the British. Occasionally called Port Stanley. |