This article does not cite any sources .(March 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| Sovereign states by year | ||
|---|---|---|
| List of sovereign states in 1778 | Events of 1779 | List of sovereign states in 1780 |
This article does not cite any sources .(March 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| Sovereign states by year | ||
|---|---|---|
| List of sovereign states in 1778 | Events of 1779 | List of sovereign states in 1780 |

The Sultanate of Aceh, officially the Kingdom of Aceh Darussalam, was a Sultanate centered in the modern-day Indonesian province of Aceh. It was a major regional power in the 16th and 17th centuries, before experiencing a long period of decline. Its capital was Kutaraja, the present-day Banda Aceh.

The Adal Sultanate, or Kingdom of Adal, was a Muslim Somali kingdom and sultanate located in the Horn of Africa. It was founded by Sabr ad-Din II after the fall of the Sultanate of Ifat. The kingdom flourished from around 1415 to 1577. The sultanate and state were established by the local inhabitants of Zeila. At its height, the polity controlled most of the territory in the Horn region immediately east of the Ethiopian Empire (Abyssinia). The Adal Empire maintained a robust commercial and political relationship with the Ottoman Empire.

Andorra, officially the Principality of Andorra, also called the Principality of the Valleys of Andorra, is a sovereign landlocked microstate on the Iberian Peninsula, in the eastern Pyrenees, bordering France to the north and Spain to the south. Believed to have been created by Charlemagne, Andorra was ruled by the Count of Urgell until 988, when it was transferred to the Roman Catholic Diocese of Urgell, and the present principality was formed by a charter in 1278. It is known as a principality as it is a diarchy headed by two Princes: the Catholic Bishop of Urgell in Catalonia, Spain, and the President of France.
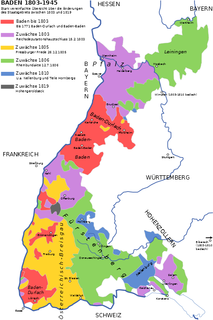
Baden is a historical territory in South Germany, on the right bank of the Upper Rhine.

Bali is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. Located east of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller neighbouring islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and Nusa Ceningan. The provincial capital, Denpasar, is the most populous city in the Lesser Sunda Islands and the second largest, after Makassar, in Eastern Indonesia. Bali is the only Hindu-majority province in Indonesia, with 83.5% of the population adhering to Balinese Hinduism.

The Bamana Empire was a large West African state based at Ségou, now in Mali. This state was established after the fall of the Mali Empire and the Keita dynasty, as a smaller Bambara Empire founded by other Bambara families related to the Keita clan. It was ruled by the Kulubali or Coulibaly dynasty established c. 1640 by Kaladian Coulibaly also known as Fa Sine or Biton-si-u. The empire existed as a centralized state from 1712 until the 1862 invasion of Toucouleur conqueror, El Hadj Umar Tall.

The Carnatic region is the region of peninsular South India lying between the Eastern Ghats and the Western Ghats, in the modern Indian states of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and southern Andhra Pradesh.

Cayor was the largest and most powerful kingdom (1549–1879) that split off from the Jolof Empire in what is now Senegal. Cayor was located in northern and central Senegal, southeast of Walo, west of the kingdom of Jolof, and north of Baol and the Kingdom of Sine.
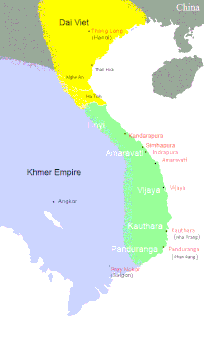
Champa was a collection of independent Cham polities that extended across the coast of what is today central and southern Vietnam from approximately the 2nd century AD before being absorbed and annexed by Vietnamese Emperor Minh Mạng in AD 1832. The kingdom was known variously as nagara Campa in the Chamic and Cambodian inscriptions, Chăm Pa in Vietnamese and 占城 (Zhànchéng) in Chinese records.

The name Tây Sơn is used in Vietnamese history in various ways to refer to the period of peasant rebellions and decentralized dynasties established between the end of the figurehead Lê dynasty in 1770 and the beginning of the Nguyễn dynasty in 1802. The name of the rebel leaders' home district, Tây Sơn, came to be applied to the leaders themselves, their uprising or their rule.
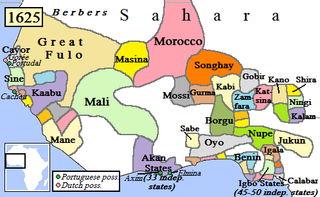
The Dendi Kingdom (1591–1901) was a West African state in modern-day Niger founded by the Dendi people after the collapse of the Songhai Empire. It was conquered by France in 1901.

Denmark–Norway, also known as the Dano–Norwegian Realm, the Oldenburg Monarchy or the Oldenburg realms, was an early modern multi-national and multi-lingual real union consisting of the Kingdom of Denmark, the Kingdom of Norway, the Duchy of Schleswig, and the Duchy of Holstein. The state also claimed sovereignty over two historical peoples: Wends and Goths. Denmark–Norway had several colonies, namely the Danish Gold Coast, the Nicobar Islands, Serampore, Tharangambadi, and the Danish West Indies.

The Gakhars are a clan found predominantly on the Potohar plateau in the northern part of Pakistan's Punjab province. In the 1990s, Gakhars who professed Islam were reported to be most prevalent in Hazara district and in northern districts of Punjab such as Rawalpindi district. Hindu Gakhars have also been recorded, historically in areas such as the Punjab where a Gakhar ruled in the time of Babur.
The Kingdom of Garo, also known as Bosha after its ruling dynasty, was an ancient kingdom in the Horn of Africa. Established by the mecha oromo, it was situated on the periphery of the Gibe region. The garo oromo was named from the word (gaara) means "the upper site", the place where they were living at that time.

The Kingdom of Kartli-Kakheti (1762–1801) was created in 1762 by the unification of two eastern Georgian kingdoms of Kartli and Kakheti. From the early 16th century, according to the 1555 Peace of Amasya, these two kingdoms were under Iranian control. In 1744, Nader Shah granted the kingship of Kartli to Teimuraz II and that of Kakheti to his son Heraclius II, as a reward for their loyalty. When Nader Shah died in 1747, Teimuraz II and Heraclius II capitalized on the instability in Iran proper, and declared de facto independence. After Teimuraz II died in 1762, Heraclius succeeded him as ruler of Kartli, thus unifying the two.

Hamburg is the second-largest city in Germany with a population of over 1.8 million, after the capital Berlin.

The Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg was an Electorate of the Holy Roman Empire, located in northwestern Germany. It was colloquially known as the Electorate of Hanover, after its capital city of Hanover. For most of its existence, the electorate was ruled in personal union with Great Britain.

The Hausa are the largest ethnic group in Africa and the second largest language after Arabic in the Afroasiatic family of languages. The Hausa are a diverse but culturally homogeneous people based primarily in the Sahelian and the sparse savanna areas of southern Niger and northern Nigeria respectively, numbering over 70 million people with significant indegenized populations in Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Chad, Togo, Ghana, Sudan, Eritrea, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Senegal and the Gambia.