
The Discovery Program is a series of Solar System exploration missions funded by the US National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) through its Planetary Missions Program Office. The cost of each mission is capped at a lower level than missions from NASA's New Frontiers or Flagship Programs. As a result, Discovery missions tend to be more focused on a specific scientific goal rather than serving a general purpose.

The Constellation program was a crewed spaceflight program developed by NASA, the space agency of the United States, from 2005 to 2009. The major goals of the program were "completion of the International Space Station" and a "return to the Moon no later than 2020" with a crewed flight to the planet Mars as the ultimate goal. The program's logo reflected the three stages of the program: the Earth (ISS), the Moon, and finally Mars—while the Mars goal also found expression in the name given to the program's booster rockets: Ares. The technological aims of the program included the regaining of significant astronaut experience beyond low Earth orbit and the development of technologies necessary to enable sustained human presence on other planetary bodies.
The Planetary Observer program is a cancelled space exploration program designed by NASA to provide cheaper planetary orbiters by using Earth-orbiting satellite components and technology, using solar panels for power, and a common spacecraft bus platform for all Planetary Observer-class probes. Only one spacecraft of this class was eventually constructed—the Mars Observer.
As a federal agency, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) receives its funding from the annual federal budget passed by the United States Congress. The following charts detail the amount of federal funding allotted to NASA each year over its history to pursue programs in aeronautics research, robotic spaceflight, technology development, and human space exploration programs.

Mariner Mark II was NASA's planned family of unmanned spacecraft for the exploration of the outer Solar System that were to be developed and operated by JPL between 1980 through the year 2010.
The Apollo Applications Program (AAP) was created as early as 1966 by NASA headquarters to develop science-based human spaceflight missions using hardware developed for the Apollo program. AAP was the ultimate development of a number of official and unofficial Apollo follow-on projects studied at various NASA labs. However, the AAP's ambitious initial plans became an early casualty when the Johnson Administration declined to support it adequately, partly in order to implement its Great Society set of domestic programs while remaining within a $100 billion budget. Thus, Fiscal Year 1967 ultimately allocated $80 million to the AAP, compared to NASA's preliminary estimates of $450 million necessary to fund a full-scale AAP program for that year, with over $1 billion being required for FY 1968. The AAP eventually led to Skylab, which absorbed much of what had been developed under Apollo Applications.

A lunar outpost is a concept of a permanent or semi-permanent presence of humans on the Moon, a moonbase, by the United States space administration NASA. NASA requested an increase in the 2020 budget of $1.6 billion, in order to make another crewed mission to the Moon by 2025, followed by a sustained presence on the Moon by 2028.

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is an independent agency of the U.S. federal government responsible for the civilian space program, as well as aeronautics and space research.

The Review of United States Human Space Flight Plans Committee was a group convened by NASA at the request of the Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP), to review the nation's human spaceflight plans to ensure "a vigorous and sustainable path to achieving its boldest aspirations in space." The review was announced by the OSTP on May 7, 2009. It covered human spaceflight options after the time NASA had planned to retire the Space Shuttle. A summary report was provided to the OSTP Director John Holdren, White House Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP), and NASA Administrator on September 8, 2009. The estimated cost associated with the review was expected to be US$3 million. The committee was scheduled to be active for 180 days; the report was released on October 22, 2009.

NASA's large strategic science missions or large strategic missions, formerly known as Flagship missions or Flagship-class missions, are the costliest and most capable NASA science spacecraft. Flagship missions exist within all four divisions of NASA's Science Mission Directorate (SMD): the astrophysics, Earth science, heliophysics and planetary science divisions.

The Space Exploration Vehicle (SEV) is a modular vehicle concept developed by NASA. It would consist of a pressurized cabin that can be mated either with a wheeled chassis to form a rover for planetary surface exploration or to a flying platform for open space missions such as servicing satellites and missions to near-Earth asteroids. The concept evolved from the Lunar Electric Rover (LER) concept, which in turn was a development of the Small Pressurized Rover (SPR) concept.

The Space Launch System is an American super heavy-lift expendable launch vehicle under development by NASA since 2011. As of April 2022, the first launch is scheduled for no earlier than August 2022, pending the success of a wet dress rehearsal test. It replaces the Ares I and Ares V launch vehicles, which were cancelled along with the rest of the Constellation program, a previous program aimed to return to the moon. The SLS is intended to become the successor to the retired Space Shuttle, and the primary launch vehicle of NASA's deep space exploration plans through the 2020s. Crewed lunar flights are planned as part of the Artemis program, leading to a possible human mission to Mars. The SLS is being developed in three major phases with increasing capabilities: Block 1, Block 1B, and Block 2. As of August 2019, SLS Block 1 launch vehicles are to launch the first three Artemis missions and five subsequent SLS flights are planned to use Block 1B, after which all flights will use Block 2.

Mars Exploration Program (MEP) is a long-term effort to explore the planet Mars, funded and led by NASA. Formed in 1993, MEP has made use of orbital spacecraft, landers, and Mars rovers to explore the possibilities of life on Mars, as well as the planet's climate and natural resources. The program is managed by NASA's Science Mission Directorate by Doug McCuistion of the Planetary Science Division. As a result of 40% cuts to NASA's budget for fiscal year 2013, the Mars Program Planning Group (MPPG) was formed to help reformulate the MEP, bringing together leaders of NASA's technology, science, human operations, and science missions.

Orion is a class of partially reusable crewed spacecraft to be used in NASA's Artemis program. The spacecraft consists of a Crew Module (CM) space capsule designed by Lockheed Martin and the European Service Module (ESM) manufactured by Airbus Defence and Space. Capable of supporting a crew of six beyond low Earth orbit, Orion can last up to 21 days undocked and up to six months docked. It is equipped with solar panels, an automated docking system, and glass cockpit interfaces modeled after those used in the Boeing 787 Dreamliner. A single AJ10 engine provides the spacecraft's primary propulsion, while eight R-4D-11 engines, and six pods of custom reaction control system engines developed by Airbus, provide the spacecraft's secondary propulsion. Although compatible with other launch vehicles, Orion is primarily intended to launch atop a Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, with a tower launch escape system.

Artemis 2, is the second scheduled mission of NASA's Artemis program, and the first scheduled crewed mission of NASA's Orion spacecraft, currently planned to be launched by the Space Launch System (SLS) in May 2024. The crewed Orion spacecraft will perform a lunar flyby test and return to Earth. This is planned to be the first crewed spacecraft to travel beyond low Earth orbit since Apollo 17 in 1972. Formerly known as Exploration Mission-2 (EM-2), the mission was renamed after the introduction of the Artemis program. Originally, the crewed mission was intended to collect samples from a captured asteroid in lunar orbit by the now canceled robotic Asteroid Redirect Mission.

The Lunar Gateway, or simply Gateway, is a planned small space station in lunar orbit intended to serve as a solar-powered communication hub, science laboratory, short-term habitation module for government-agency astronauts, as well as a holding area for rovers and other robots. It is a multinational collaborative project involving four of the International Space Station partner agencies: NASA, European Space Agency (ESA), Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), and Canadian Space Agency (CSA). It is planned to be both the first space station beyond low Earth orbit and the first space station to orbit the Moon.
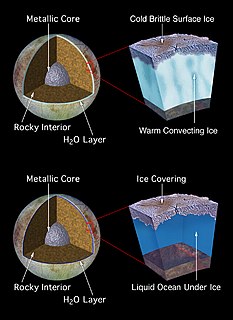
The Ocean Worlds Exploration Program (OWEP) is a NASA program to explore ocean worlds in the outer Solar System that could possess subsurface oceans to assess their habitability and to seek biosignatures of simple extraterrestrial life.

The Artemis program is a human spaceflight program that is being led by NASA with multiple international and US domestic partners. The primary goal of Artemis is to return humans to the Moon, specifically the lunar south pole, by 2025. If successful, it will include the first crewed lunar landing mission since Apollo 17 in 1972, which was the final lunar flight of the Apollo program.














