The Byerley Turk, also spelled Byerly Turk, was the earliest of three stallions that were the founders of the modern Thoroughbred horse racing bloodstock.
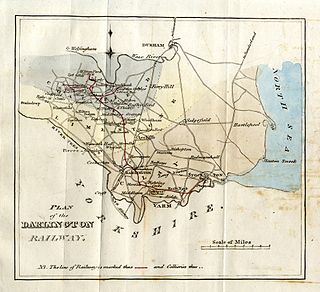
The Stockton and Darlington Railway (S&DR) was a railway company that operated in north-east England from 1825 to 1863. The world's first public railway to use steam locomotives, its first line connected collieries near Shildon with Darlington and Stockton in County Durham, and was officially opened on 27 September 1825. The movement of coal to ships rapidly became a lucrative business, and the line was soon extended to a new port at Middlesbrough. While coal waggons were hauled by steam locomotives from the start, passengers were carried in coaches drawn by horses until carriages hauled by steam locomotives were introduced in 1833.

Peterlee is a town in County Durham, England. It is located south of Sunderland, north of Hartlepool, west of the Durham Coast and east of Durham. It gained town status in 1948 under the New Towns Act 1946. The act also created the nearby settlement of Newton Aycliffe and later Washington, Tyne and Wear.

Sedgefield District was, from 1974 to 2009, a local government district and, borough in County Durham, in North East England. It had a population of about 87,000. It was named after Sedgefield, but its largest town was Newton Aycliffe. Other places included Shildon, Ferryhill and Spennymoor.

Newton Aycliffe is a town in County Durham, England. Founded in 1947 under the New Towns Act of 1946, the town is 5 miles (8.0 km) to the north of Darlington and 10 miles (16 km) to the south of Durham. It is the oldest new town in the north of England. Together with the bordering Aycliffe Village and the north part of School Aycliffe, it forms the civil parish of Great Aycliffe. The population of the town at the time of the 2021 census was 26,415.
Belmont is a suburb forming the north-eastern parts of the city of Durham, England. Belmont Parish covers four old coal mining villages of Belmont, Carrville, Broomside and Gilesgate Moor, which have been joined by industrial and suburban developments since the 1950s. As such Belmont can be used either to refer narrowly to the old village area, or the wider parish, particularly the parts to the east of the A1(M) motorway which bisects the area. At the 2011 census, the parish had a population of 8,881.

Brafferton is a village and civil parish in County Durham, England. It is administered as part of the borough of Darlington. The population of Brafferton Parish taken at the 2011 census was 154. It is situated between Darlington and Newton Aycliffe, a short distance from Coatham Mundeville.

Brandon is a village in County Durham, England. It is situated a short distance to the southwest of Durham. Brandon was originally one of the seven townships within the ancient parish of Brancepeth. It grew from a sparsely populated agricultural area into a populous mining district after the establishment of collieries and later coke and fireclay works. Until the 19th century Brandon village, formerly known as East Brandon, was one of the larger settlements in Brancepeth Parish.

Shotton Colliery is a village in County Durham, England.

Mordon is a village and civil parish in County Durham, England. It is situated a few miles to the north-east of Newton Aycliffe. The population recorded by the 2011 census for the parish was 260.
Heighington is a village in the borough of Darlington and ceremonial county of County Durham, England. The population of the civil parish at the 2011 census was 2,395. It is situated between Darlington and Shildon, near Newton Aycliffe. One of its most significant features is St Michael's Church, which sits in the middle of a large village green. The church is Norman, except for the 13th-century south aisle and the 19th-century north aisle. A rare feature in this church is a pre-Reformation oak pulpit with six traceried linen fold panels, with an inscription bearing prayers for its donor: an Alexander Flettcher and his wife Agnes.

Redworth is a village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Heighington in the borough of Darlington and the ceremonial county of Durham, England. It is west of Newton Aycliffe being situated between Darlington and Shildon.

Bishop Auckland is a constituency in County Durham that is represented in the House of Commons since 2024 by Sam Rushworth of the Labour Party.

Goldsborough Hall is a Jacobean stately home located in the village of Goldsborough, North Yorkshire, England. It is a member of the Historic Houses Association. The house itself is a Grade II* listed building. The Hall was built for Sir Richard Hutton (1560–1639) after he acquired the Goldsborough Estate in 1598, and in the 20th century it was home to Princess Mary, Countess of Harewood as her first family home.
Witton Park Colliery was a coal mine located in Witton Park, near Witton-le-Wear and Bishop Auckland in County Durham, Northern England.

Robert Byerley (1660–1714), of Middridge Grange, Heighington, County Durham, and Goldsborough, Yorkshire, was an English soldier and Tory politician who sat in the English and British House of Commons between 1685 and 1714. He is credited with capturing the Byerley Turk, a famous stallion considered one of the three major foundation sires of the Thoroughbred breed of race horse.
Middridge Colliery was a colliery based in and near the village of Middridge in County Durham, England. The colliery, which was owned by The Weardale Iron and Coal Company, consisted of two mines: Eden Pit, sunk in 1872 and Charles Pit, sunk in 1874.