Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme.

Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate, and in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells, the cytosol. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes.

In biochemistry, a kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule donates a phosphate group to the substrate molecule. This transesterification produces a phosphorylated substrate and ADP. Conversely, it is referred to as dephosphorylation when the phosphorylated substrate donates a phosphate group and ADP gains a phosphate group. These two processes, phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, occur four times during glycolysis.

Adenosine monophosphate (AMP), also known as 5'-adenylic acid, is a nucleotide. AMP consists of a phosphate group, the sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine. It is an ester of phosphoric acid and the nucleoside adenosine. As a substituent it takes the form of the prefix adenylyl-.

ATPases (EC 3.6.1.3, Adenosine 5'-TriPhosphatase, adenylpyrophosphatase, ATP monophosphatase, triphosphatase, SV40 T-antigen, ATP hydrolase, complex V (mitochondrial electron transport), (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase, HCO3−-ATPase, adenosine triphosphatase) are a class of enzymes that catalyze the decomposition of ATP into ADP and a free phosphate ion or the inverse reaction. This dephosphorylation reaction releases energy, which the enzyme (in most cases) harnesses to drive other chemical reactions that would not otherwise occur. This process is widely used in all known forms of life.
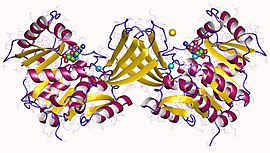
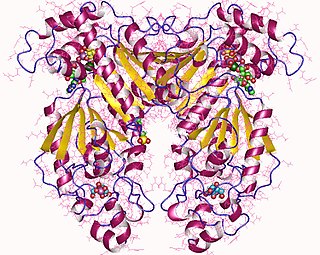
Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) is one of the most important regulatory enzymes of glycolysis. It is an allosteric enzyme made of 4 subunits and controlled by many activators and inhibitors. PFK-1 catalyzes the important "committed" step of glycolysis, the conversion of fructose 6-phosphate and ATP to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate and ADP. Glycolysis is the foundation for respiration, both anaerobic and aerobic. Because phosphofructokinase (PFK) catalyzes the ATP-dependent phosphorylation to convert fructose-6-phosphate into fructose 1,6-bisphosphate and ADP, it is one of the key regulatory steps of glycolysis. PFK is able to regulate glycolysis through allosteric inhibition, and in this way, the cell can increase or decrease the rate of glycolysis in response to the cell's energy requirements. For example, a high ratio of ATP to ADP will inhibit PFK and glycolysis. The key difference between the regulation of PFK in eukaryotes and prokaryotes is that in eukaryotes PFK is activated by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. The purpose of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate is to supersede ATP inhibition, thus allowing eukaryotes to have greater sensitivity to regulation by hormones like glucagon and insulin.
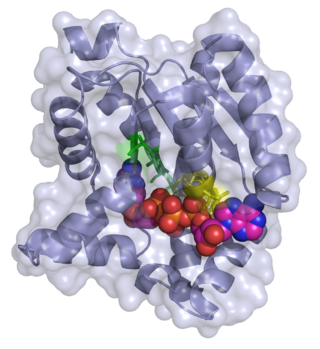
Adenylate kinase is a phosphotransferase enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of the various adenosine phosphates. By constantly monitoring phosphate nucleotide levels inside the cell, ADK plays an important role in cellular energy homeostasis.
The adenylate energy charge is an index used to measure the energy status of biological cells.
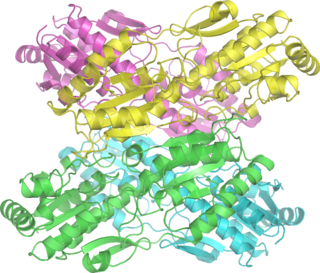
Phosphofructokinase-2 (6-phosphofructo-2-kinase, PFK-2) or fructose bisphosphatase-2 (FBPase-2), is an enzyme indirectly responsible for regulating the rates of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in cells. It catalyzes formation and degradation of a significant allosteric regulator, fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (Fru-2,6-P2) from substrate fructose-6-phosphate. Fru-2,6-P2 contributes to the rate-determining step of glycolysis as it activates enzyme phosphofructokinase 1 in the glycolysis pathway, and inhibits fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 in gluconeogenesis. Since Fru-2,6-P2 differentially regulates glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, it can act as a key signal to switch between the opposing pathways. Because PFK-2 produces Fru-2,6-P2 in response to hormonal signaling, metabolism can be more sensitively and efficiently controlled to align with the organism's glycolytic needs. This enzyme participates in fructose and mannose metabolism. The enzyme is important in the regulation of hepatic carbohydrate metabolism and is found in greatest quantities in the liver, kidney and heart. In mammals, several genes often encode different isoforms, each of which differs in its tissue distribution and enzymatic activity. The family described here bears a resemblance to the ATP-driven phospho-fructokinases, however, they share little sequence similarity, although a few residues seem key to their interaction with fructose 6-phosphate.
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase, PNP, PNPase or inosine phosphorylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NP gene. It catalyzes the chemical reaction

Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, abbreviated Fru-2,6-P2, is a metabolite that allosterically affects the activity of the enzymes phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK-1) and fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase-1) to regulate glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. Fru-2,6-P2 itself is synthesized and broken down by the bifunctional enzyme phosphofructokinase 2/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase (PFK-2/FBPase-2).

Phosphofructokinase (PFK) is a kinase enzyme that phosphorylates fructose 6-phosphate in glycolysis.
Fructokinase, also known as D-fructokinase or D-fructose (D-mannose) kinase, is an enzyme of the liver, intestine, and kidney cortex. Fructokinase is in a family of enzymes called transferases, meaning that this enzyme transfers functional groups; it is also considered a phosphotransferase since it specifically transfers a phosphate group. Fructokinase specifically catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from adenosine triphosphate to fructose as the initial step in its utilization. The main role of fructokinase is in carbohydrate metabolism, more specifically, sucrose and fructose metabolism. The reaction equation is as follows:

ADP-ribosylation is the addition of one or more ADP-ribose moieties to a protein. It is a reversible post-translational modification that is involved in many cellular processes, including cell signaling, DNA repair, gene regulation and apoptosis. Improper ADP-ribosylation has been implicated in some forms of cancer. It is also the basis for the toxicity of bacterial compounds such as cholera toxin, diphtheria toxin, and others.

In enzymology, 1-phosphofructokinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Adenosine kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of gamma-phosphate from Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to adenosine (Ado) leading to formation of Adenosine monophosphate (AMP). In addition to its well-studied role in controlling the cellular concentration of Ado, AdK also plays an important role in the maintenance of methylation reactions. All S-adenosylmethionine-dependent transmethylation reactions in cells lead to production of S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH), which is cleaved by SAH hydrolase into Ado and homocysteine. The failure to efficiently remove these end products can result in buildup of SAH, which is a potent inhibitor of all transmethylation reactions. The disruption of AdK gene (-/-) in mice causes neonatal hepatic steatosis, a fatal condition characterized by rapid microvesicular fat infiltration, leading to early postnatal death. The liver was the main organ affected in these animals and in it the levels of adenine nucleotides were decreased, while those of SAH were elevated. Recently, missense mutations in the AdK gene in humans which result in AdK deficiency have also been shown to cause hypermethioninemia, encephalopathy and abnormal liver function.

In enzymology, an inosine kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a nucleoside-phosphate kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a tagatose-6-phosphate kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The Walker A and Walker B motifs are protein sequence motifs, known to have highly conserved three-dimensional structures. These were first reported in ATP-binding proteins by Walker and co-workers in 1982.