
The River Derwent, also known as timtumili minanya in palawa kani, is a significant river and tidal estuary in Tasmania, Australia. It begins its journey as a freshwater river in the Central Highlands at Lake St Clair, descending over 700 metres (2,300 ft) across a distance of more than 200 kilometres (120 mi). At the settlement of New Norfolk in the Derwent Valley its waters become brackish, flowing through Hobart, the capital city of Tasmania, its seawater estuary eventually empties into Storm Bay and the Tasman Sea.

The Tasman Peninsula, officially Turrakana / Tasman Peninsula, is a peninsula located in south-east Tasmania, Australia, approximately 75 km (47 mi) by the Arthur Highway, south-east of Hobart.
The history of Tasmania begins at the end of the Last Glacial Period when it is believed that the island was joined to the Australian mainland. Little is known of the human history of the island until the British colonisation of Tasmania in the 19th century.

Clarence City Council is a local government body in Tasmania, and one of the five municipalities that constitutes the Greater Hobart Area. The Clarence local government area has a population of 61,531, covering the eastern shore of the Derwent River from Otago to the South Arm Peninsula and the smaller localities of Cambridge, Richmond, and Seven Mile Beach.
Richmond is a town in Tasmania about 25 km north-east of Hobart, in the Coal River region, between the Midland Highway and Tasman Highway. At the 2006 census, Richmond had a population of 880.

Sorell is a town in Tasmania, Australia, north-east of Hobart. It is located on the Tasman Highway at the junction with the Arthur Highway. Sorell is one of Tasmania's oldest towns, being first settled in 1808 as a small farming community and becoming an official township in 1821. At the 2006 census, Sorell had a population of 1,546, and at the 2011 census, a population of 2,476. and at the 2016 census, a population of 2,907.

The Tasman Highway is a highway in Tasmania, Australia. Like the Midland Highway, it connects the major cities of Hobart and Launceston – however it takes a different route, via the north-eastern and eastern coasts of the state. The Highway also acts as a major commuter road to Hobart residents living on the eastern side of the Derwent River. The designation "Tasman Highway" arises from its location facing the Tasman Sea – named, like the state itself, after Abel Tasman. The highway is one of the longest in Tasmania – 410 km (250 mi), with an average travelling time of 41⁄2 hours.

Midway Point is a residential locality in the local government area (LGA) of Sorell in the South-east LGA region of Tasmania. The locality is about 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) south-west of the town of Sorell. The 2016 census recorded a population of 2859 for the state suburb of Midway Point. It is located on a small peninsula with Orielton Lagoon on its eastern side and Pittwater on its southern and western sides. The suburb meets the mid-way point of the Sorell Causeway from Hobart to Sorell, hence the name. Mcgees Bridge is connected to Midway Point on the Pittwater side. The suburb lies close to Hobart International Airport and is approximately 21 km to Hobart via the Tasman Highway. In recent years Midway Point has become a popular commuter town for people working in Hobart.

The Forestier Peninsula is a peninsula located in south-east Tasmania, Australia, approximately 60 kilometres (37 mi) by the Arthur Highway, south-east of Hobart. The peninsula is connected to mainland Tasmania at East Bay Neck, near the town of Dunalley at its northern end. At Eaglehawk Neck, the southern end of the Forestier Peninsula is connected to the Tasman Peninsula.

The Bridgewater Bridge is a combined road and rail bridge that carries the Midland Highway and South Railway Line across the Derwent River in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. This steel truss vertical lift bridge and specially-built causeway connect the Hobart suburbs of Bridgewater and Granton. The bridge was completed in 1946 and accommodates a two-lane highway, a single track railway and a grade-separated footpath.
The Arthur Highway (A9) is a Tasmanian highway which runs from Sorell in the near south to Port Arthur in the far south-east.
The modern history of the Australian city of Hobart in Tasmania dates to its foundation as a British colony in 1804. Prior to British settlement, the area had been occupied definitively for at least 8,000 years, and possibly for as long as 35,000 years, by the semi-nomadic Mouheneener tribe, a sub-group of the Nuenonne, or South-East tribe. The descendants of theses indigenous Tasmanians now refer to themselves as 'Palawa'. Little is known about the region from prehistoric times. As with many other Australia cities, urbanisation has destroyed much of the archaeological evidence of indigenous occupation, although aboriginal middens are often still present in coastal areas.

Eaglehawk Neck, officially Teralina / Eaglehawk Neck, is a narrow isthmus that connects the Tasman Peninsula with the Forestier Peninsula and hence to the rest of Tasmania, Australia.

McGees Bridge is a road bridge that carries the Tasman Highway across Pitt Water, near Sorell in the south-east of Tasmania, Australia. The bridge and adjacent Sorell Causeway provide vital links between Hobart and two of Tasmania's principal tourist attractions - Port Arthur Historic Site on the Tasman Peninsula and the picturesque East Coast via the Tasman Highway.
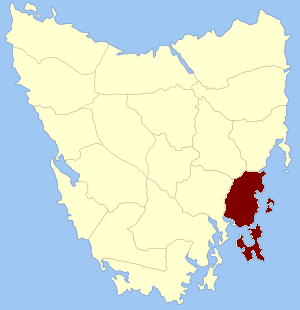
Pembroke Land District is one of the twenty land districts of Tasmania which are part of the cadastral divisions of Tasmania. It was formerly one of the 18 counties of Tasmania. It includes Tasman Peninsula and Port Arthur, as well as Forestier Peninsula, Dodges Ferry and Maria Island. The Electoral division of Pembroke is not actually within the land district, but is close by in Monmouth.
The Orielton Lagoon is a shallow dystrophic lagoon located west of Sorell in south east Tasmania, Australia.
Dunalley is a rural / residential locality in the local government areas (LGA) of Sorell (37%) and Tasman (63%) in the South-east LGA region of Tasmania. The locality is about 31 kilometres (19 mi) south-east of the town of Sorell. The 2021 census recorded a population of 304 for the state suburb of Dunalley. It is a small fishing village on the east coast of Tasmania.

The South Arm Important Bird Area is a disjunct tract of mainly intertidal land on the eastern outskirts of Hobart, Tasmania, Australia.
Orielton is a rural locality in the local government area of Sorell in the Central and Hobart regions of Tasmania, Australia. It is located about 10 kilometres (6 mi) north-west of the town of Sorell. The 2016 census determined a population of 355 for the state suburb of Orielton.











