
The Tasman Bridge is a prestressed concrete girder bridge connecting the Tasman Highway over the River Derwent in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. When it opened on 29 March 1965, the Tasman was the longest prestressed concrete bridge in Australia, with a total length measuring 1,396 metres (4,580 ft), including approaches. The bridge provides a vital link between Hobart's city centre on the western shore and the City of Clarence on the eastern shore. Averaging 73,029 vehicle crossings per day, the bridge is the highest volume road section in Tasmania. It features five lanes of traffic including a central lane equipped for tidal flow operations and separated shared-use walkways on both sides, with ramp upgrades for improved access and cyclists completed in 2010.

Clarence City Council is a local government body in Tasmania, and one of the five municipalities that constitutes the Greater Hobart Area. The Clarence local government area has a population of 61,531, covering the eastern shore of the Derwent River from Otago to the South Arm Peninsula and the smaller localities of Cambridge, Richmond, and Seven Mile Beach.
Richmond is a town in Tasmania about 25 km north-east of Hobart, in the Coal River region, between the Midland Highway and Tasman Highway. At the 2006 census, Richmond had a population of 880.

Sorell is a town in Tasmania, Australia, north-east of Hobart. It is located on the Tasman Highway at the junction with the Arthur Highway. Sorell is one of Tasmania's oldest towns, being first settled in 1808 as a small farming community and becoming an official township in 1821. At the 2006 census, Sorell had a population of 1,546, and at the 2011 census, a population of 2,476. and at the 2016 census, a population of 2,907.

The Clyde River is an open intermediate tide-dominated drowned valley estuary or perennial river that flows into the Tasman Sea at Batemans Bay, located in the South Coast region of New South Wales, Australia.

The Brooker Highway is a highway in the Australian state of Tasmania. As one of Hobart's three major radials, the highway connects traffic from the city centre with the northern suburbs and is the major road connection to the cities and towns of northern Tasmania. With an annual average daily traffic of 48,000, the highway is one of the busiest in Tasmania. The Brooker Highway has recently been declared part of the National Highway.

The Tasman Highway is a highway in Tasmania, Australia. Like the Midland Highway, it connects the major cities of Hobart and Launceston – however it takes a different route, via the north-eastern and eastern coasts of the state. The Highway also acts as a major commuter road to Hobart residents living on the eastern side of the Derwent River. The designation "Tasman Highway" arises from its location facing the Tasman Sea – named, like the state itself, after Abel Tasman. The highway is one of the longest in Tasmania – 410 km (250 mi), with an average travelling time of 41⁄2 hours.

Midway Point is a residential locality in the local government area (LGA) of Sorell in the South-east LGA region of Tasmania. The locality is about 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) south-west of the town of Sorell. The 2016 census recorded a population of 2859 for the state suburb of Midway Point. It is located on a small peninsula with Orielton Lagoon on its eastern side and Pittwater on its southern and western sides. The suburb meets the mid-way point of the Sorell Causeway from Hobart to Sorell, hence the name. Mcgees Bridge is connected to Midway Point on the Pittwater side. The suburb lies close to Hobart International Airport and is approximately 21 km to Hobart via the Tasman Highway. In recent years Midway Point has become a popular commuter town for people working in Hobart.

The Bridgewater Bridge is a combined road and rail bridge that carries the Midland Highway and South Railway Line across the Derwent River in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. This steel truss vertical lift bridge and specially-built causeway connect the Hobart suburbs of Bridgewater and Granton. The bridge was completed in 1946 and accommodates a two-lane highway, a single track railway and a grade-separated footpath.

Macquarie Street a major one way street passing through the outskirts of the Hobart central business district in Tasmania, Australia. Macquarie street is named after Lachlan Macquarie, who oversaw the planning of Hobart’s inner city grid layout. The street forms a one-way couplet with nearby Davey Street connecting traffic from the Southern Outlet in the south with traffic from the Tasman Highway to the east and the Brooker Highway to the north of the city. With annual average daily traffic of 28,500, the road is one of the busier streets in Hobart.
The Arthur Highway (A9) is a Tasmanian highway which runs from Sorell in the near south to Port Arthur in the far south-east.

The Sorell Causeway is a causeway that carries the Tasman Highway across Pitt Water-Orielton Lagoon, from the western side of Midway Point to Sorell in the south-east of Tasmania, Australia. The causeway and adjacent McGees Bridge provide vital links between Hobart and two of Tasmania's principal tourist attractions - Port Arthur Historic Site on the Tasman Peninsula and the picturesque East Coast via the Tasman Highway.
The Domain Highway is a highway in Tasmania, Australia. The highway acts as a link road connecting traffic between Hobart's two busiest highways; The Tasman Highway and the Brooker Highway while also bypassing the Hobart city centre. With recorded annual average daily traffic of 25,000, the single carriageway road is busier than some of Hobart's dual carriageway highways. Commencing at the Brooker Highway at Cornelian Bay and heading southeast between the banks of the Derwent River and the Domain and Botanical Gardens. The highway ends at the Tasman Highway, on the western approach of the Tasman Bridge.

The Brighton Bypass is a A$191 million north/south bypass of the Midland Highway diverting traffic away from the northern Hobart satellite suburbs of Brighton and Pontville. Construction of the 9.5 km federally funded dual carriageway started in April 2009, and was opened on 12 November 2012.
The Lindisfarne Interchange is a Directional T interchange which connects the Tasman Bridge to the Tasman Highway and the East Derwent Highway, on the eastern shore of the River Derwent within Hobart, Tasmania. The Interchange was constructed in 1960 in conjunction with the Tasman Bridge and opened to Traffic on 23 December 1964.

The Southern Transport Investment Program is a road and rail transport plan for the northern outskirts of Hobart instituted in 2007 by the Tasmanian state government. It outlines most prominently an extensive upgrade of the Midland Highway, including the Brighton Bypass, the Bagdad Bypass and the replacement of the Bridgewater Bridge. The plan also outlines the construction of the Brighton Transport Hub and various rail alignment improvements to the Main North/South Line.
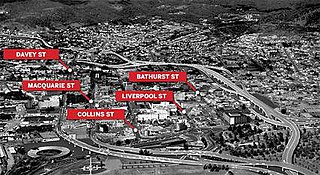
The Hobart Bypass is a proposed concept to bypass the Central Business District of Hobart, Tasmania. Currently, through traffic travels from the Tasman/Brooker Highways down the one-way Davey/Macquarie couplet to the Southern Outlet. As well as traffic concerns, there is also a call to build the bypass on the grounds that the current traffic arrangement cuts the central business district off from Hobart's waterfront.
Dunalley is a rural / residential locality in the local government areas (LGA) of Sorell (37%) and Tasman (63%) in the South-east LGA region of Tasmania. The locality is about 31 kilometres (19 mi) south-east of the town of Sorell. The 2021 census recorded a population of 304 for the state suburb of Dunalley. It is a small fishing village on the east coast of Tasmania.

The Hobart Area Transportation Study was a comprehensive transport plan released in 1965 for the purpose of examining the transport needs of the Australian Hobart metropolitan area over the proceeding 20 years. The study predicted the majority of the proposed traffic corridors would need to be operational by the 1985 target year.














