Related Research Articles

Human rights are moral principles or norms for standards of human behaviour and are regularly protected as substantive rights in substantive law, municipal and international law. They are commonly understood as inalienable, fundamental rights "to which a person is inherently entitled simply because she or he is a human being" and which are "inherent in all human beings", regardless of their age, ethnic origin, location, language, religion, ethnicity, or any other status. They are applicable everywhere and at every time in the sense of being universal, and they are egalitarian in the sense of being the same for everyone. They are regarded as requiring empathy and the rule of law, and imposing an obligation on persons to respect the human rights of others; it is generally considered that they should not be taken away except as a result of due process based on specific circumstances.
International human rights instruments are the treaties and other international texts that serve as legal sources for international human rights law and the protection of human rights in general. There are many varying types, but most can be classified into two broad categories: declarations, adopted by bodies such as the United Nations General Assembly, which are by nature declaratory, so not legally-binding although they may be politically authoritative and very well-respected soft law;, and often express guiding principles; and conventions that are multi-party treaties that are designed to become legally binding, usually include prescriptive and very specific language, and usually are concluded by a long procedure that frequently requires ratification by each states' legislature. Lesser known are some "recommendations" which are similar to conventions in being multilaterally agreed, yet cannot be ratified, and serve to set common standards. There may also be administrative guidelines that are agreed multilaterally by states, as well as the statutes of tribunals or other institutions. A specific prescription or principle from any of these various international instruments can, over time, attain the status of customary international law whether it is specifically accepted by a state or not, just because it is well-recognized and followed over a sufficiently long time.

The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) is a department of the United Nations Secretariat that works to promote and protect human rights that are guaranteed under international law and stipulated in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights of 1948. The office was established by the United Nations General Assembly on 20 December 1993 in the wake of the 1993 World Conference on Human Rights.

The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN committee chaired by Eleanor Roosevelt, it was accepted by the General Assembly as Resolution 217 during its third session on 10 December 1948 at the Palais de Chaillot in Paris, France. Of the 58 members of the United Nations at the time, 48 voted in favour, none against, eight abstained, and two did not vote.

The International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) is a multilateral treaty that commits nations to respect the civil and political rights of individuals, including the right to life, freedom of religion, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, electoral rights and rights to due process and a fair trial. It was adopted by United Nations General Assembly Resolution 2200A (XXI) on 16 December 1966 and entered into force on 23 March 1976 after its thirty-fifth ratification or accession. As of June 2022, the Covenant has 173 parties and six more signatories without ratification, most notably the People's Republic of China and Cuba; North Korea is the only state that has tried to withdraw.
International human rights law (IHRL) is the body of international law designed to promote human rights on social, regional, and domestic levels. As a form of international law, international human rights law is primarily made up of treaties, agreements between sovereign states intended to have binding legal effect between the parties that have agreed to them; and customary international law. Other international human rights instruments, while not legally binding, contribute to the implementation, understanding and development of international human rights law and have been recognized as a source of political obligation.

The United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) is a United Nations body whose mission is to promote and protect human rights around the world. The Council has 47 members elected for staggered three-year terms on a regional group basis. The headquarters of the Council are at the United Nations Office at Geneva in Switzerland.
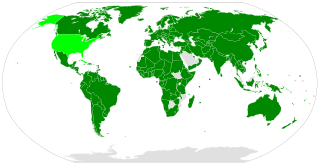
The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR) is a multilateral treaty adopted by the United Nations General Assembly (GA) on 16 December 1966 through GA. Resolution 2200A (XXI), and came into force on 3 January 1976. It commits its parties to work toward the granting of economic, social, and cultural rights (ESCR) to all individuals including those living in Non-Self-Governing and Trust Territories. The rights include labour rights, the right to health, the right to education, and the right to an adequate standard of living. As of February 2024, the Covenant has 172 parties. A further four countries, including the United States, have signed but not ratified the Covenant.
The International Narcotics Control Board (INCB) is an independent treaty body, one of the four treaty-mandated bodies under international drug control law.
Economic, social and cultural rights (ESCR) are socio-economic human rights, such as the right to education, right to housing, right to an adequate standard of living, right to health, victims' rights and the right to science and culture. Economic, social and cultural rights are recognised and protected in international and regional human rights instruments. Member states have a legal obligation to respect, protect and fulfil economic, social and cultural rights and are expected to take "progressive action" towards their fulfilment.

The Committee on the Rights of the Child (CRC) is a body of experts that monitor and report on the implementation of the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child.
The International Service for Human Rights (ISHR) is an independent, non-profit organization with offices in Geneva and New York which promotes and protects human rights by supporting human rights defenders, strengthening human rights standards and systems, and leading and participating in coalitions for human rights change.

The Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities is an international human rights treaty of the United Nations intended to protect the rights and dignity of persons with disabilities. Parties to the convention are required to promote, protect, and ensure the full enjoyment of human rights by persons with disabilities and ensure that persons with disabilities enjoy full equality under the law. The Convention serves as a major catalyst in the global disability rights movement enabling a shift from viewing persons with disabilities as objects of charity, medical treatment and social protection towards viewing them as full and equal members of society, with human rights. The convention was the first U.N. human rights treaty of the twenty-first century.

Discussions of LGBT rights at the United Nations have included resolutions and joint statements in the United Nations General Assembly and the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC), attention to the expert-led human rights mechanisms, as well as by the UN Agencies.

The United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights (UNGPs) is an instrument consisting of 31 principles implementing the United Nations' (UN) "Protect, Respect and Remedy" framework on the issue of human rights and transnational corporations and other business enterprises. Developed by the Special Representative of the Secretary-General (SRSG) John Ruggie, these Guiding Principles provided the first global standard for preventing and addressing the risk of adverse impacts on human rights linked to business activity, and continue to provide the internationally accepted framework for enhancing standards and practice regarding business and human rights. On June 16, 2011, the United Nations Human Rights Council unanimously endorsed the Guiding Principles for Business and Human Rights, making the framework the first corporate human rights responsibility initiative to be endorsed by the UN.

Development is a human right that belongs to everyone, individually and collectively. Everyone is “entitled to participate in, contribute to, and enjoy economic, social, cultural and political development, in which all human rights and fundamental freedoms can be fully realized,” states the groundbreaking UN Declaration on the Right to Development, proclaimed in 1986.
The proposed Convention on the Rights of Older Persons (UNCROP) is likely to be the next major human rights treaty adopted by the United Nations. The proposed treaty will seek to remedy the fragmented human rights structure for Older Persons, and will focus on reaffirming critical human rights which are of concern to older persons. The focus of the treaty will be persons over 60 years of age, which is a growing demographic worldwide due to increased population ageing. The treaty follows from the success of the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child which has seen near universal acceptance since 1989. Where the UNCRC focuses on the rights of younger persons, the UNCROP will address those who form the older portion of society, who according to United Nations reports, are becoming increasingly vulnerable as a group without applicable normative standards of human rights law. Support for a Convention is becoming increasingly popular, as human rights groups including the Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (CESCR), HelpAge International, the Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women, the International Labour Organization, and many other NGOs and states have expressed support for a universal instrument. A raising number of NGOs from across the world have joined forces in advocating for a Convention in the Global Alliance for the Rights of Older Persons (GAROP) which has been set up out of the need to strengthen the rights of older persons worldwide. With population ageing, the human rights of the growing number of older persons have become an increasingly important issue. Among the human rights issues faced by older persons are ageist attitudes leading to discrimination, exclusion and constraints on the legal capacity, autonomy and independent living of older people. Existing human rights violations have been further exacerbated and put on the spotlight by the COVID-19 pandemic. Older people have been denied access to health services and became prone to physical and social isolation. The stigmatisation of older people and ageist images of older persons have also become more evident. The debate surrounding the convention focuses on the implementation and safeguarding of older persons’ human rights aiming to set normative standards of human rights for older persons in an international legally binding instrument. An underlying common factor and root cause of many of human rights violations experienced by older persons, along with its ubiquitous, prevalent, and surreptitious nature, is ageism. Ageism, as defined by the World Health Organization, refers to the stereotypes, prejudice and discrimination towards others or oneself based on age. A UNCROP would go a long way to tackle ageism. Individual relationships generally fall outside of current human rights law, which seeks to present standards of relations between states and individuals. Therefore, it has been suggested that the proposed human rights convention for older persons ought to be drafted as an anti-discrimination convention. However, this would not be consistent with other multilateral human rights conventions such as the ICCPR and ICESCR which set normative standards.
Mihir Kanade is an author and professor of international law, human rights and development at the University for Peace (UPEACE), a university founded by the United Nations. He holds the concurrent positions of the Academic Coordinator of UPEACE since 2016, the Head of its Department of International Law since 2014, and the Director of the UPEACE Human Rights Centre since 2009.
The Global Pact for the Environment project was launched in 2017 by a network of experts known as the "International Group of Experts for the Pact" (IGEP). The group is made up of more than a hundred legal experts in environmental law and is chaired by former COP21 President Laurent Fabius.

The right to a healthy environment or the right to a sustainable and healthy environment is a human right advocated by human rights organizations and environmental organizations to protect the ecological systems that provide human health. The right was acknowledged by the United Nations Human Rights Council during its 48th session in October 2021 in HRC/RES/48/13 and subsequently by the United Nations General Assembly on July 28, 2022 in A/RES/76/300. The right is often the basis for human rights defense by environmental defenders, such as land defenders, water protectors and indigenous rights activists.
References
- ↑ UN General Assembly (2019). ""Subsequent agreements and subsequent practice in relation to the interpretation of treaties" Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 20 December 2018 [A/RES/73/202]". undocs.org. Retrieved 2022-01-24.
- ↑ Kurtas, Susan. "Research Guides: UN Documentation: Human Rights: Treaty-based Bodies". research.un.org. Retrieved 2022-01-24.
- ↑ "Treaty Bodies". ISHR Academy. Retrieved 2022-01-24.
- ↑ "OHCHR | TreatyBodies". www.ohchr.org. 30 April 2018. Retrieved 2022-01-24.
- ↑ Riboulet-Zemouli, Kenzi; Krawitz, Michael A. (2021-02-24). "Voluntary Contribution to INCB Guidelines on Medical Cannabis – Due Diligence, Good Faith, & Technical Concerns". Rochester, NY. SSRN 3829901.
- ↑ "UN Human Rights Treaty Bodies". International Justice Resource Center. 2010-01-31. Retrieved 2022-01-24.
- ↑ "A Rough Guide to the Human Rights Treaty Bodies". Universal Rights Group. Retrieved 2022-01-24.