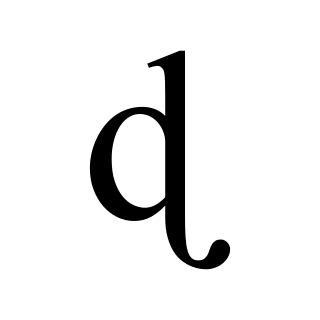The voiced retroflex lateral approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɭ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is l`.

The voiced retroflex approximant is a type of consonant used in some languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɻ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is r\`. The IPA symbol is a turned lowercase letter r with a rightward hook protruding from the lower right of the letter.

The voiced retroflex flap is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɽ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is r`.

The voiced retroflex nasal is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɳ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is n`.

The voiced retroflex sibilant fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʐ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is z`. Like all the retroflex consonants, the IPA symbol is formed by adding a rightward-pointing hook extending from the bottom of a z.
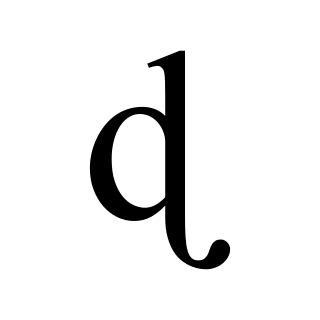
The voiced retroflex stop is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɖ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is d`. Like all the retroflex consonants, the IPA symbol is formed by adding a rightward-pointing hook extending from the bottom of a d, the letter that is used for the corresponding alveolar consonant. Many South Asian languages, such as Hindi and Urdu, have a two-way contrast between plain and murmured.

The voiceless retroflex sibilant fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʂ⟩. Like all the retroflex consonants, the IPA letter is formed by adding a rightward-pointing hook to the bottom of the ess. A distinction can be made between laminal, apical, and sub-apical articulations. Only one language, Toda, appears to have more than one voiceless retroflex sibilant, and it distinguishes subapical palatal from apical postalveolar retroflex sibilants; that is, both the tongue articulation and the place of contact on the roof of the mouth are different.
The voiced alveolar implosive is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɗ⟩. The IPA symbol is lowercase letter d with a rightward hook protruding from the upper right of the letter.
The voiced uvular implosive is an extremely rare type of consonantal sound. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʛ⟩, a small capital letter G with a rightward pointing hook extending from the upper right of the letter.
The voiced retroflex implosive is a type of consonantal sound. It is not known to be phonemically distinct from alveolar in any language. Sindhi has an implosive that varies between dental and retroflex articulation, while Oromo, Saraiki and Ngad'a have but not.

The voiceless retroflex sibilant affricate is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʈ͡ʂ⟩, sometimes simplified to ⟨tʂ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is ⟨ts`⟩.
The retroflex ejective affricate is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʈ͡ʂʼ⟩, though it is frequently simplified to ⟨tʂʼ⟩.
The retroflex ejective is a rare consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʈʼ⟩.
The retroflex ejective fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʂʼ⟩.
The voiceless retroflex nasal is an extremely rare type of consonantal sound, used in very few spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɳ̊⟩, a combination of the letter for the voiced retroflex nasal and a diacritic indicating voicelessness.
The voiceless retroflex lateral approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɭ̊⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is l`_0.
The voiceless retroflex flap or tap is a sound that has been reported to occur as a dialectal realization of in the Dhivehi language. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɽ̊⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is r`_0.
The voiceless retroflex approximant is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɻ̊⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is r\`_0.
The voiceless retroflex lateral affricate is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet is ⟨ʈ͜ɭ̊˔⟩.
A voiceless retroflex implosive is a rare consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. There is no official symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound, but ⟨ᶑ̊⟩ or ⟨ʈʼ↓⟩ may be used.