
The Equal Rights Amendment (ERA) is a proposed amendment to the United States Constitution designed to guarantee equal legal rights for all American citizens regardless of sex. Proponents assert it would end legal distinctions between men and women in matters of divorce, property, employment, and other matters. The first version of an ERA was written by Alice Paul and Crystal Eastman and introduced in Congress in December 1923.

The Virginia General Assembly is the legislative body of the Commonwealth of Virginia, the oldest continuous law-making body in the Western Hemisphere, the first elected legislative assembly in the New World, and was established on July 30, 1619. The General Assembly is a bicameral body consisting of a lower house, the Virginia House of Delegates, with 100 members, and an upper house, the Senate of Virginia, with 40 members. Combined, the General Assembly consists of 140 elected representatives from an equal number of constituent districts across the commonwealth. The House of Delegates is presided over by the Speaker of the House, while the Senate is presided over by the Lieutenant Governor of Virginia. The House and Senate each elect a clerk and sergeant-at-arms. The Senate of Virginia's clerk is known as the "Clerk of the Senate".

The 2003 Texas redistricting refers to a controversial mid-decade state plan that defined new congressional districts. In the 2004 elections, this redistricting supported the Republicans taking a majority of Texas's House seats for the first time since Reconstruction. Opponents challenged the plan in three suits, combined when the case went to the United States Supreme Court in League of United Latin American Citizens v. Perry (2006).
The Constitution of the State of Ohio is the basic governing document of the State of Ohio, which in 1803 became the 17th state to join the United States of America. Ohio has had three constitutions since statehood was granted.

The New Jersey Redistricting Commission is a constitutional body of the government of New Jersey tasked with redrawing the state's Congressional election districts after each decade's census. Like Arizona, Idaho, Hawaii, Montana, and Washington; the redistricting is completed within an independent, bipartisan commission. The apportionment of members of the Redistricting Commission is carefully balanced between legislative and executive majorities and is purposefully designed to allow the minority party an equal number of seats on the commission.

Virginia is currently divided into 11 congressional districts, each represented by a member of the United States House of Representatives. The districts were redrawn most recently in 2016 by court order.

The following is a list of the ten congressional districts in the U.S. state of Washington.

Redistricting in Pennsylvania refers to the decennial process of redrawing state legislative and federal congressional districts in Pennsylvania.

The U.S. state of Arizona, in common with the other U.S. states, must redraw its congressional and legislative districts every ten years to reflect changes in the state and national populations. Redistricting normally follows the completion of the United States census, which is carried out by the federal government the first year of every decade; the most recent census took place in 2020. Historically, Arizona's legislature had control over the redistricting process. However, Proposition 106, passed in 2000, delegated the power to draw congressional and legislative boundaries to a bipartisan independent commission. The Arizona Independent Redistricting Commission (AIRC) comprises two Democrats, two Republicans, and one independent chair. County and local redistricting, which normally takes place along the same timeline as congressional and legislative redistricting, is carried out by the individual county and local governments rather than the AIRC.

The 17th Senate District of Wisconsin is one of 33 districts in the Wisconsin State Senate. Located in southwest Wisconsin, the district comprises all of Grant, Lafayette, Juneau, and Richland counties, as well as most of Sauk County, western Iowa County, southwest Green County, and parts of eastern Vernon County.
Gerrymandering in the United States has been used to increase the power of a political party. Gerrymandering is the practice of setting boundaries of electoral districts to favor specific political interests within legislative bodies, often resulting in districts with convoluted, winding boundaries rather than compact areas. The term "gerrymandering" was coined after a review of Massachusetts's redistricting maps of 1812 set by Governor Elbridge Gerry noted that one of the districts looked like a salamander.
The National Democratic Redistricting Committee (NDRC) is a US organization that focuses on redistricting and is affiliated with the Democratic Party. The organization coordinates campaign strategy, directs fundraising, organizes ballot initiatives and files lawsuits against state redistricting maps. At launch, the organization announced that it intends to support Democratic candidates for local and state offices in order for them to control congressional map drawing in the redistricting cycle following the 2020 United States census.

The 2020 United States redistricting cycle is in progress following the completion of the 2020 United States census. In all fifty states, various bodies are re-drawing state legislative districts. States that are apportioned more than one seat in the United States House of Representatives are also drawing new districts for that legislative body.

Redistricting in Virginia has been a controversial topic due to allegations of gerrymandering. In the 2017 Virginia General Assembly, all of the redistricting reform bills were killed.
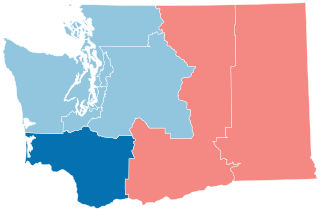
The 2022 United States House of Representatives elections in Washington were held on November 8, 2022, to elect the 10 U.S. representatives from the state of Washington, one from each of the state's 10 congressional districts. The elections coincided with other elections to the House of Representatives, elections to the United States Senate and various state and local elections. Going into this election, the Democratic Party represented seven seats, while the Republican Party represented three seats.

Virginia state elections in 2020 was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020. With the exception of its Democratic Party presidential primary election held on March 3, 2020, its primary elections were held on June 23 of that year.

League of Women Voters of Pennsylvania et al. v. Commonwealth of Pennsylvania et al.—abbreviated League of Women Voters v. Commonwealth—was a decision of the Pennsylvania Supreme Court on gerrymandering, concerning the power of the Pennsylvania General Assembly to draw maps based on partisan advantage. The Court ruled that the maps adopted by the Republican controlled legislature in 2011 was an unconstitutional partisan gerrymander under the Constitution of Pennsylvania.

Redistricting in Wisconsin is the process by which boundaries are redrawn for municipal wards, Wisconsin State Assembly districts, Wisconsin State Senate districts, and Wisconsin's congressional districts. Redistricting occurs—as in other U.S. states—once every decade, usually in the year after the decennial United States census. According to the Wisconsin Constitution, redistricting in Wisconsin follows the regular legislative process, it must be passed by both houses of the Wisconsin Legislature and signed by the Governor of Wisconsin—unless the Legislature has sufficient votes to override a gubernatorial veto. Due to legislative gridlock, however, it has become common for Wisconsin redistricting to be conducted by courts. The 1982, 1992, and 2002 legislative maps were each created by panels of United States federal judges.

The 105th Wisconsin Legislature convened from January 12, 2021, to March 1, 2022, in regular session. The Legislature also held two extraordinary sessions and six special sessions during the term.
The 2010 United States redistricting cycle took place following the completion of the 2010 United States census. In all fifty states, various bodies re-drew state legislative districts. States that are apportioned more than one seat in the United States House of Representatives also drew new districts for that legislative body. The resulting new districts were first implemented for the 2011 and 2012 elections.















