
A winter storm is an event in which wind coincides with varieties of precipitation that only occur at freezing temperatures, such as snow, mixed snow and rain, or freezing rain. In temperate continental and subarctic climates, these storms are not necessarily restricted to the winter season, but may occur in the late autumn and early spring as well. A snowstorm with strong winds and low visibility is called a blizzard.
The Early Winter 2006 North American storm complex was a severe winter storm that occurred on November 26, 2006, and continued into December 1. It affected much of North America in some form, producing various kinds of severe weather including a major ice storm, blizzard conditions, high winds, extreme cold, a serial derecho and some tornadoes.

The February 2007 North American blizzard was a massive winter storm that affected most of the eastern half of North America, starting on February 12, 2007, and peaking on Valentine's Day, February 14. The storm produced heavy snowfalls across the midwestern United States from Nebraska to Ohio and produced similar conditions across parts of the northeastern United States, and into Canada in Ontario, Quebec and New Brunswick. Significant sleet and freezing rain fell across the southern Ohio Valley and affected portions of the east coast of the United States, including the cities of Boston, Baltimore, Washington, D.C., New York City and Philadelphia.
The Early December 2007 North American winter storm was a major winter storm which affected the majority of the United States and portions of southern Canada from November 29 to December 5, hitting the Intermountain West and Midwestern United States, the Great Lakes region and the Northeast. The storm brought significant snows to portions of the Upper Midwest, Great Plains and Great Lakes regions of the United States and Canada on December 1 with a major winter storm for Quebec, Ontario and parts of the Northeast region on December 2 and 3 as well as the Canadian Maritimes on December 4 and 5. The system was also responsible for a major ice storm across the Midwestern states which caused disruptions to several major cities including Des Moines, Chicago, Detroit, Milwaukee and Toronto. The storm was blamed for at least 16 deaths across nine US states and one Canadian province. 10 traffic deaths had been reported, as of 2 December 2007.

The Mid-December 2007 North American winter storms were a series of two winter storms that affected much of central and eastern North America, from December 8 to December 18, 2007. The systems affected areas from Oklahoma to Newfoundland and Labrador with freezing rain, thunderstorms, sleet, snow, damaging winds, and blizzard-like conditions in various areas. The first two storms produced copious amounts of ice across the Midwestern United States and Great Plains from December 8 to December 11, knocking out power to approximately 1.5 million customers from Oklahoma north to Iowa. The second storm moved northeast, producing heavy snow across New York and New England. A third storm was responsible for a major winter storm from Kansas to the Canadian Maritimes, bringing locally record-breaking snowfalls to Ontario, an icestorm across the Appalachians, and thunderstorms and 9 tornadoes to the Southeastern United States.

The North American blizzard of 2008 was a winter storm that struck most of southern and eastern North America from March 6 to March 10, 2008. The storm was most notable for a major winter storm event from Arkansas to Quebec. It also produced severe weather across the east coast of the United States with heavy rain, damaging winds and tornadoes, causing locally significant damage. The hardest hit areas by the wintry weather were from the Ohio Valley to southern Quebec where up to a half a meter of snow fell locally including the major cities of Columbus, Ohio, Cleveland, Ohio, and Ottawa, Ontario. For many areas across portions of the central United States, Ontario and Quebec, it was the worst winter storm in the past several years. The blizzard and its aftermath caused at least 17 deaths across four US states and three Canadian provinces, while hundreds others were injured mostly in weather-related accidents and tornadoes.
Global weather activity of 2009 profiles the major worldwide storms, including blizzards, tornadoes, ice storms, tropical cyclones and other meteorogical events, from January 1, 2009, to December 31, 2009. Wintery storms are events in which the dominant varieties of precipitation are forms that only occur at cold temperatures, such as snow or sleet, or a rainstorm where ground temperatures are cold enough to allow ice to form. It may be marked by strong wind, thunder and lightning, heavy precipitation, such as ice, or wind transporting some substance through the atmosphere. Summer storms including flooding, severe thunderstorms and extratropical cyclones are also included in this list to a certain extent.
Global weather activity of 2007 profiles the major worldwide weather events, including blizzards, ice storms, tornadoes, tropical cyclones, and other weather events, from January 1, 2007, to December 31, 2007. Winter storms are events in which the dominant varieties of precipitation are formed during cold temperatures; they include snow or sleet, or a rainstorm where ground temperatures are cold enough to allow ice, including freezing rain, to form. Thehy may be marked by strong wind, thunder, lightning thunderstorms, heavy precipitation, including ice storm, wind transporting some substance through the atmosphere, including dust storms, snowstorms, and hail storms. Other major non winter events such as large dust storms, hurricanes, cyclones, tornados, gales, flooding, and rainstorms are also caused by such phenomena.
Global weather activity of 2006 profiles the major worldwide weather events, including blizzards, ice storms, tropical cyclones, tornadoes, and other weather events, from January 1, 2006, to December 31, 2006. Winter storms are events in which the dominant varieties of precipitation are forms that only occur at cold temperatures, such as snow or sleet, or a rainstorm where ground temperatures are cold enough to allow ice to form. It may be marked by strong wind, thunder and lightning, heavy precipitation, such as ice, or wind transporting some substance through the atmosphere. Other major non winter events such as large dust storms, Hurricanes, cyclones, tornadoes, gales, flooding and rainstorms are also caused by such phenomena to a lesser or greater existent.

The 2013–14 North American winter was one of the most significant for the United States, due in part to the breakdown of the polar vortex in November 2013, which allowed very cold air to travel down into the United States, leading to an extended period of very cold temperatures. The pattern continued mostly uninterrupted throughout the winter and numerous significant winter storms affected the Eastern United States, with the most notable one being a powerful winter storm that dumped ice and snow in the Southeastern United States and the Northeastern United States in mid-February. Most of the cold weather abated by the end of March, though a few winter storms did affect the Western United States towards the end of the winter.

The 2012–13 North American winter was the most active winter weather season by metric of the amount of storms rated on the Regional Snowfall Index (RSI), with a record-breaking 21 storms being rated on the scale. The season started out somewhat early, as the remnants of Hurricane Sandy brought heavy snow to the mountains of West Virginia in late October. Later, a strong nor'easter affected the weary Northeastern United States, hampering storm recovery efforts and dropping several inches of snow. The rest of the winter featured several other notable events, such as a Christmas winter storm that affected most of the Eastern United States, and the most notable event occurring in early February, when a powerful blizzard struck the Northeast and brought record snow to some areas. Overall, the majority of the continent, more specifically the central parts of the United States, experienced a persistently wintry and cold pattern that extended into the months of April and May, a theme that would be repeated the following winter on a larger and more widespread scale. During the winter, a weak El Nino was expected to influence weather conditions across the continent.

The 2010–11 North American winter was influenced by an ongoing La Niña, seeing winter storms and very cold temperatures affect a large portion of the Continental United States, even as far south as the Texas Panhandle. Notable events included a major blizzard that struck the Northeastern United States in late December with up to 2 feet (24 in) of snowfall and a significant tornado outbreak on New Year's Eve in the Southern United States. By far the most notable event was a historic blizzard that impacted areas from Oklahoma to Michigan in early February. The blizzard broke numerous snowfall records, and was one of the few winter storms to rank as a Category 5 on the Regional Snowfall Index. In addition, Oklahoma set a statewide low temperature record in February.
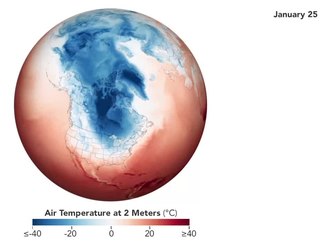
The 2018–19 North American winter was unusually cold within the Northern United States, with frigid temperatures being recorded within the middle of the season. Several notable events occurred, such as a rare snow in the Southeast in December, a strong cold wave and several major winter storms in the Midwest, and upper Northeast and much of Canada in late January and early February, record snowstorms in the Southwest in late February, deadly tornado outbreaks in the Southeast and a historic mid-April blizzard in the Midwest, but the most notable event of the winter was a record-breaking bomb cyclone that affected much of the Central United States and Canada in mid-March. Unlike previous winters, a developing weak El Niño was expected to influence weather patterns across North America. Overall, however, winter of 2018–19 had many La Niña like conditions, being mild along the mid- and lower parts of the East Coast, the West Coast, and most of the southern Plains. Overall, the meteorological winter of 2018-19 became the wettest on record for the United States.
The January 2019 North American winter storm was a long-lived winter storm, forming as a large area of low pressure off the Pacific Northwest shoreline January 16, making its way to the Northeast by January 21. Its effects included heavy rain/high elevation snow and gusty winds in California, severe weather in the south, near-blizzard conditions in Upstate New York, an ice storm in New England and minor coastal flooding in the Mid-Atlantic.

The 2019–20 North American winter was unusually warm for many parts of the United States; in many areas, neutral ENSO conditions controlled the weather patterns, resulting in strong El Niño like conditions and the sixth-warmest winter on record, and many areas in the Northeastern United States saw one of the least snowy winters in years. In fact, Baltimore and Islip saw no snow in February for the first time. Some notable events still occurred, such as a powerful blizzard that impacted the Western United States in late November, a series of cold shots in January and February, a snowstorm within the Texas Panhandle and a late-season blizzard in the High Plains.

The November 26 – December 3, 2019 North American blizzard was a major winter storm from the Rocky Mountains to the Northeast as well as a record-breaking windstorm along the West Coast. It occurred the week of American Thanksgiving, hampering travel for millions across the United States.

The 2020–21 North American winter was the most significant winter season to affect North America in several years, and the costliest on record, with a damage total of at least $33.35 billion. The season featured six storms ranking on the Regional Snowfall Index scale (RSI), with four storms ranking as at least a Category 3. Most of the winter's damage and fatalities occurred due to a historic and major cold wave in mid-February. Several other significant events occurred, including a crippling early-season ice storm in the Southern Plains, a powerful nor'easter in mid-December, another major nor'easter in early February, two major and widespread winter storms in mid-February, and a major blizzard in the Rocky Mountains in mid-March. The winter-related events were responsible for at least 358 fatalities, making it the deadliest season since 1992–93. A La Niña pattern influenced much of the winter in North America.

The December 15–17, 2020 nor'easter was a powerful nor'easter that hammered the Northeastern United States and produced widespread swaths of over 1 foot (12 in) of snow in much of the region from December 15–17, 2020, ending a 1,000+ day high-impact snowstorm drought in much of the Mid-Atlantic and coastal New England regions. The system developed out of a weak area of low-pressure that first developed over the Central United States producing some snowfall before moving eastward, and by December 16, a new, dominant area of low pressure began to develop along the Southeast coast. This low steadily deepened as it moved along and impacted the Mid-Atlantic coastline, prompting several winter-related advisories and warnings for much of the Northeast.

The January 14–17, 2022 North American winter storm brought widespread impacts and wintry precipitation across large sections of eastern North America and parts of Canada. Forming out of a shortwave trough on January 13, it first produced a swath of snowfall extending from the High Plains to the Midwestern United States. The storm eventually pivoted east and impacted much of the Southern United States from January 15–16 before shifting north into Central Canada, the Mid-Atlantic states, and the Northeastern United States. The system, named Winter Storm Izzy by The Weather Channel, was described as a "Saskatchewan Screamer".

The 2022–23 North American winter was quite warm for the eastern half of North America, with much of the Eastern United States experiencing one of their warmest and least snowy winters on record. Despite this, numerous significant events still occurred, including a severe lake-effect winter storm across the Great Lakes region in mid-November, a cold wave bringing extremely cold temperatures to the Northeast in early-February, and several tornado outbreaks throughout the winter. However, most of the winter's damage and fatalities were due to a crippling and historic winter storm that wreaked havoc across the majority of the United States and parts of Canada in late-December. Additionally, the Western United States was colder than usual in contrast to the east, with a series of atmospheric rivers through December to March bringing widespread flooding in California and record amounts of snow across the region. During the winter, five storms have been ranked on the Regional Snowfall Index (RSI), two of which have attained the “Major” category. Similar to the previous two winters, a La Niña was expected to influence weather patterns across the continent.






















