
Uridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine or UDP-GlcNAc is a nucleotide sugar and a coenzyme in metabolism. It is used by glycosyltransferases to transfer N-acetylglucosamine residues to substrates. D-Glucosamine is made naturally in the form of glucosamine-6-phosphate, and is the biochemical precursor of all nitrogen-containing sugars. To be specific, glucosamine-6-phosphate is synthesized from fructose 6-phosphate and glutamine as the first step of the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway. The end-product of this pathway is UDP-GlcNAc, which is then used for making glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, and glycolipids.
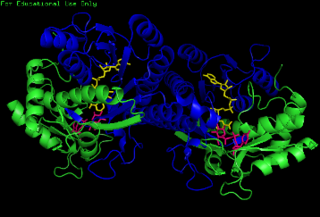
The enzyme UDP-glucose 4-epimerase, also known as UDP-galactose 4-epimerase or GALE, is a homodimeric epimerase found in bacterial, fungal, plant, and mammalian cells. This enzyme performs the final step in the Leloir pathway of galactose metabolism, catalyzing the reversible conversion of UDP-galactose to UDP-glucose. GALE tightly binds nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a co-factor required for catalytic activity.
In enzymology, a glycoprotein 3-alpha-L-fucosyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.214) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetyllactosaminide beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyl-transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a protein N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an UDP-N-acetylglucosamine—dolichyl-phosphate N-acetylglucosaminephosphotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an UDP-N-acetylglucosamine—lysosomal-enzyme N-acetylglucosaminephosphotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an UDP-N-acetylglucosamine diphosphorylase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GALNT3 gene.

Beta-1,3-galactosyl-O-glycosyl-glycoprotein beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GCNT1 gene.

Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GALNT1 gene.

Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GALNT2 gene.

Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GALNT6 gene.

UDP-N-acetylglucosamine transferase subunit ALG14 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ALG14 gene.
Alpha-1,6-mannosyl-glycoprotein 4-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:2,6-bis(N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl)-alpha-D-mannosyl-glycoprotein 4-beta-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Protein O-GlcNAc transferase also known as OGT or O-linked N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the OGT gene. OGT catalyzes the addition of the O-GlcNAc post-translational modification to proteins.
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine—undecaprenyl-phosphate N-acetylglucosaminephosphotransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine:ditrans,octacis-undecaprenyl phosphate N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminephosphotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine---decaprenyl-phosphate N-acetylglucosaminephosphotransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine:trans,octacis-decaprenyl-phosphate N-acetylglucosaminephosphotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Protein O-GlcNAcase (EC 3.2.1.169, OGA, glycoside hydrolase O-GlcNAcase, O-GlcNAcase, BtGH84, O-GlcNAc hydrolase) is an enzyme with systematic name (protein)-3-O-(N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyl)-L-serine/threonine N-acetylglucosaminyl hydrolase. OGA is encoded by the OGA gene. This enzyme catalyses the removal of the O-GlcNAc post-translational modification in the following chemical reaction:
- [protein]-3-O-(N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminyl)-L-serine + H2O ⇌ [protein]-L-serine + N-acetyl-D-glucosamine
- [protein]-3-O-(N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminyl)-L-threonine + H2O ⇌ [protein]-L-threonine + N-acetyl-D-glucosamine











