
The Republican People's Party is a Kemalist and social democratic political party in Turkey. It is the oldest political party in Turkey, founded by Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, the first president and founder of the modern Turkish Republic. The party is also cited as the founding party of modern Turkey. Its logo consists of the Six Arrows, which represent the foundational principles of Kemalism: republicanism, reformism, laicism (Laïcité/Secularism), populism, nationalism, and statism. It is currently the second largest party in Grand National Assembly with 129 MPs, behind the ruling conservative Justice and Development Party.

Elections in Turkey are held for six functions of government: presidential elections (national), parliamentary elections (national), municipality mayors (local), district mayors (local), provincial or municipal council members (local) and muhtars (local). Apart from elections, referendums are also held occasionally.

Deniz Baykal was a Turkish politician. A member of the Republican People's Party (CHP) who served as Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Foreign Affairs from 1995 to 1996. Having served in numerous government positions, Baykal led the CHP from 1992 to February 1995, from September 1995 to 1999 and again from 2000 to 2010. Between 2002 and 2010, he also served as the Leader of the Opposition by virtue of leading the second largest party in the Parliament.

The Nationalist Movement Party is a Turkish far-right, ultranationalist political party. The group is often described as neo-fascist, and has been linked to violent paramilitaries and organized crime groups. Its leader is Devlet Bahçeli.
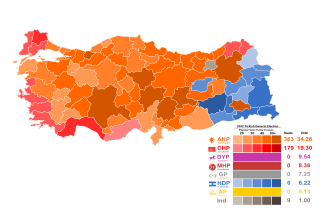
General elections were held in Turkey on 3 November 2002 following the collapse of the Democratic Left Party–Nationalist Movement Party–Motherland Party coalition led by Bülent Ecevit. All 550 members of the Grand National Assembly were up for election.

General elections were held in Turkey on 22 July 2007 to elect 550 members to the Grand National Assembly. Originally scheduled for November, the elections were brought forward after parliament failed to elect a new president to replace Ahmet Necdet Sezer. The result was a resounding victory for the incumbent Justice and Development Party (AKP), which won 46.6% of the vote and 341 seats. The party's leader Recep Tayyip Erdoğan was consequently re-elected as Prime Minister of Turkey. The opposition Republican People's Party (CHP) came second with 20.9% of the vote and took 112 seats. The Nationalist Movement Party (MHP), which had failed to surpass the 10% election threshold in the 2002 election, re-entered parliament with 14.3% of the vote and 71 MPs. The election was fought mostly on Turkey's debate over laïcité that had been perceived to be under threat from the AKP's nomination of Foreign Minister Abdullah Gül, an Islamist politician, for the Presidency. Developments in Iraq, secular and religious concerns, the intervention of the military in political issues, European Union membership negotiations, the United States and the Muslim world were other main issues.

Local elections were held in Turkey on 29 March 2009. The overall winner was the ruling party Justice and Development Party, although the party saw a decline in its vote relative to the 2007 general election. The leading opposition party, the social democratic Kemalist CHP, increased its vote share, as did a number of smaller parties including the SP, DTP and BBP, whose party leader Muhsin Yazıcıoğlu had died in a helicopter crash four days before the election. The third largest party, the Turkish nationalist MHP, enjoyed a more modest vote surge. The election was not contested by Cem Uzan's GP. The AKP failed to take certain provinces it had publicly targeted, such as Diyarbakır, İzmir and Urfa, and did not achieve its goal of exceeding 47% of the overall vote. There was localized election-related fighting in southeastern Turkey, in which five people were reported to have been killed and about a hundred injured.

General elections were held in Turkey on 12 June 2011 to elect the 550 members of Grand National Assembly. In accordance to the result of the constitutional referendum held in 2007, the elections were held four years after the previous elections in 2007 instead of five.
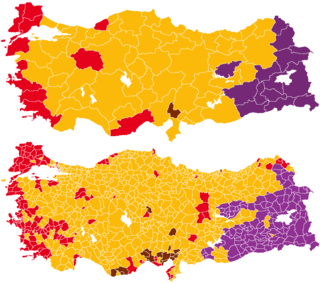
General elections were held in Turkey on 7 June 2015 to elect 550 members to the Grand National Assembly. This was the 24th general election in the history of the Turkish Republic, electing the country's 25th Parliament. The result was the first hung parliament since the 1999 general elections. Unsuccessful attempts to form a coalition government resulted in a snap general election being called for November 2015.

Local elections were held in Turkey on 30 March 2014, with some repeated on 1 June 2014. Metropolitan and district mayors as well as their municipal council members in cities, and muhtars and "elderly councils" in rural areas were elected. In light of the controversy around the elections, it was viewed as a referendum on the government of Prime Minister Recep Tayyip Erdoğan. About 50 million people were eligible to vote.
The electoral system of Turkey varies for general, presidential and local elections that take place in Turkey every five years. Turkey has been a multi-party democracy since 1950, with the first democratic election held on 14 May 1950 leading to the end of the single-party rule established in 1923. The current electoral system for electing Members of Parliament to the Grand National Assembly has a 7% election threshold.
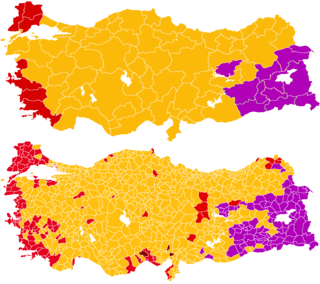
General elections were held in Turkey on 1 November 2015 to elect 550 members to the Grand National Assembly. They were the 25th general elections in the History of the Republic of Turkey and elected the country's 26th Parliament. The election resulted in the Justice and Development Party (AKP) regaining a parliamentary majority following a 'shock' victory, having lost it five months earlier in the June 2015 general elections.

The June–July 2015 Turkish Parliament Speaker Elections were held on June 30 and July 1 in order to elect the next Speaker of the Grand National Assembly of Turkey. The election took place due to the election of a new parliament in the 7 June 2015 general election. Outgoing speaker of the 24th Parliament, AKP member Cemil Çiçek, was ineligible to stand as he stood down as an MP at the general election.

The Turkish Parliament Speaker elections of 2011 were held on 4 July 2011 to elect the 25th Speaker of the Grand National Assembly. The elected speaker would preside over the 24th Parliament of Turkey, which was elected in the parliamentary election held on 12 June 2011. With the governing Justice and Development Party (AKP) holding 327 of the 550 seats in the Grand National Assembly, the election of the party's candidate Cemil Çiçek was regarded as an effective certainty.

Parliamentary elections were held in Turkey on 14 May 2023, alongside presidential elections, to elect all 600 members of the Grand National Assembly. The incoming members formed the 28th Parliament of Turkey. The elections had originally been scheduled to take place on June 18, but the government moved them forward by a month to avoid coinciding with the university exams, the Hajj pilgrimage and the start of the summer holidays. Prior to the election, the electoral threshold for a party to enter parliament was lowered from 10% to 7% by the ruling party.

The Turkish local elections of 2019 were held on Sunday 31 March 2019 throughout the 81 provinces of Turkey. A total of 30 metropolitan and 1,351 district municipal mayors, alongside 1,251 provincial and 20,500 municipal councillors were elected, in addition to numerous local non-partisan positions such as neighbourhood wardens (muhtars) and elderly people's councils.
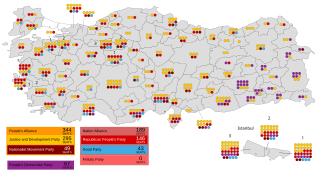
Parliamentary elections were held in Turkey on 24 June 2018 as part of general elections, with presidential elections taking place on the same day. Originally scheduled for 27 October 2019, President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan called snap elections on 18 April after months of speculation. With the passage of a series of constitutional amendments in the 2017 referendum, the number of MPs will be increased from the previous 550 to 600. These representatives will be elected by the constituents of the 87 electoral districts of Turkey by party-list proportional representation.

The Turkish Parliament Speaker election of 2018 took place on 12 July 2018 to elect the 28th Speaker of the Grand National Assembly, who will serve for the first three years of the 27th Parliament of Turkey. With 7 parties represented in the 27th Parliament, the speaker was expected to be elected in the third round, as no party or electoral bloc had the necessary two-thirds majority to elect their candidate outright.
The Republican People's Party was founded in 1919 during the Sivas Congress.
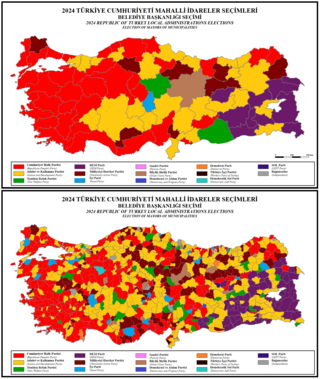
Local elections in Turkey took place on 31 March 2024 throughout the country's 81 provinces. A total of 30 metropolitan and 1,363 district municipal mayors, alongside 1,282 provincial and 21,001 municipal councillors were elected, in addition to numerous local non-partisan positions such as neighbourhood wardens (muhtars) and elderly people's councils.























