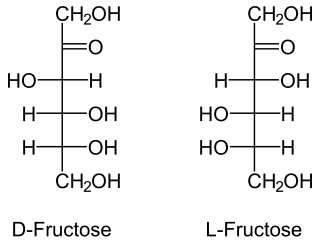
Fructosides are glycosides where the glycone group is fructose.
Galactose mutarotase is a human enzyme that converts alpha-aldose to the beta-anomer. This enzyme catalyzes the first step of the Leloir Pathway, which is involved in galactose metabolism. It belongs to family of aldose epimerases.
In enzymology, an aldose 1-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a L-fucose isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a S-methyl-5-thioribose-1-phosphate isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an ADP-sugar diphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.21) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an UDP-sugar diphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.45) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2,1-fructan:2,1-fructan 1-fructosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 6G-fructosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a beta-galactoside alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an inulosucrase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Levansucrase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a sucrose:sucrose fructosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an aldose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an aldose-1-phosphate nucleotidyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a nucleoside-triphosphate-aldose-1-phosphate nucleotidyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Alcohol dehydrogenase [NADP+] also known as aldehyde reductase or aldo-keto reductase family 1 member A1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKR1A1 gene. AKR1A1 belongs to the aldo-keto reductase (AKR) superfamily. It catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of a variety of aromatic and aliphatic aldehydes to their corresponding alcohols and catalyzes the reduction of mevaldate to mevalonic acid and of glyceraldehyde to glycerol. Mutations in the AKR1A1 gene has been found associated with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.

Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B10 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKR1B10 gene.

The aldo-keto reductase family is a family of proteins that are subdivided into 16 categories; these include a number of related monomeric NADPH-dependent oxidoreductases, such as aldehyde reductase, aldose reductase, prostaglandin F synthase, xylose reductase, rho crystallin, and many others.

Glucogallin is chemical compound formed from gallic acid and β-D-glucose. It can be found in oaks species like the North American white oak, European red oak and Amla fruit.