
Easy Cheese is the trademark for a processed cheese spread product distributed by Mondelēz International. It is also commonly referred to by generic terms such as "spray cheese", "squirt cheese" or "cheese in a can". Easy Cheese is packaged in a metal can filled with air covered with a plastic cap that reveals a straight, flexible nozzle where the cheese is extruded.

An immobilized enzyme is an enzyme, with restricted mobility, attached to an inert, insoluble material—such as calcium alginate. This can provide increased resistance to changes in conditions such as pH or temperature. It also lets enzymes be held in place throughout the reaction, following which they are easily separated from the products and may be used again - a far more efficient process and so is widely used in industry for enzyme catalysed reactions. An alternative to enzyme immobilization is whole cell immobilization. Immobilized enzymes are easily to be handled, simply separated from their products, and can be reused.
In enzymology, a GDP-4-dehydro-6-deoxy-D-mannose reductase (EC 1.1.1.281) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a GDP-mannose 6-dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.132) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a mannuronate reductase (EC 1.1.1.131) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The immobilized whole cell system is an alternative to enzyme immobilization. Unlike enzyme immobilization, where the enzyme is attached to a solid support, in immobilized whole cell systems, the target cell is immobilized. Such methods may be implemented when the enzymes required are difficult or expensive to extract, an example being intracellular enzymes. Also, if a series of enzymes are required in the reaction; whole cell immobilization may be used for convenience. This is only done on a commercial basis when the need for the product is more justified.
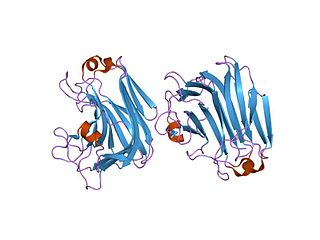
The enzyme mannuronate-specific alginate lyase catalyzes the degradation of alginate into various monosaccharide and polysaccharide products:
In enzymology, a 3-galactosyl-N-acetylglucosaminide 4-alpha-L-fucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 4-galactosyl-N-acetylglucosaminide 3-alpha-L-fucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cellulose synthase (GDP-forming) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a chitobiosyldiphosphodolichol beta-mannosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a dolichyl-phosphate beta-D-mannosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glucomannan 4-beta-mannosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glycoprotein 6-alpha-L-fucosyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.68) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a mannosyl-3-phosphoglycerate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a tRNA-queuosine beta-mannosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Calcium alginate is a water-insoluble, gelatinous, cream-coloured substance that can be created through the addition of aqueous calcium chloride to aqueous sodium alginate. Calcium alginate is also used for entrapment of enzymes and forming artificial seeds in plant tissue culture.
An alginate dressing is a natural wound dressing derived from carbohydrate sources released by clinical bacterial species, in the same manner as biofilm formation. These types of dressings are best used on wounds that have a large amount of exudate. They may be used on full-thickness burns, surgical wounds, split-thickness graft donor sites, Mohs surgery defects, refractory decubiti, and chronic ulcers. They can also be applied onto dry wounds after normal saline is first applied to the site of application.
UDP-2,3-diacetamido-2,3-dideoxyglucuronic acid 2-epimerase is an enzyme with systematic name 2,3-diacetamido-2,3-dideoxy-alpha-D-glucuronate 2-epimerase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Edible packaging refers to packaging which is edible and biodegradable.





