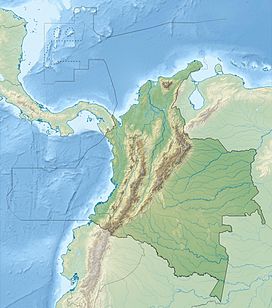
Nevado del Ruiz, also known as La Mesa de Herveo is a volcano on the border of the departments of Caldas and Tolima in Colombia, being the highest point of both. It is located about 130 km (81 mi) west of the capital city Bogotá. It is a stratovolcano composed of many layers of lava alternating with hardened volcanic ash and other pyroclastic rocks. Volcanic activity at Nevado del Ruiz began about two million years ago, during the Early Pleistocene or Late Pliocene, with three major eruptive periods. The current volcanic cone formed during the present eruptive period, which began 150,000 years ago.

Arenal Volcano is an active andesitic stratovolcano in north-western Costa Rica around 90 km (56 mi) northwest of San José, in the province of Alajuela, canton of San Carlos, and district of La Fortuna. The Arenal volcano measures at least 1,633 metres (5,358 ft) high. It is conically shaped with a crater 140 metres (460 ft) in diameter. Geologically, Arenal is considered a young volcano and it is estimated to be less than 7,500 years old. It is also known as "Pan de Azúcar", "Canaste", "Volcan Costa Rica", "Volcan Río Frío" or "Guatusos Peak".

The Poás Volcano, is an active 2,697-metre (8,848 ft) stratovolcano in central Costa Rica and is located within Poas Volcano National Park. It has erupted 40 times since 1828, with a strong eruption on April 2017—causing the evacuation of visitors and residents. The volcano and surrounding park were closed for nearly 17 months, with a 2.5 kilometer safety perimeter established around the erupting crater. On September 1, 2018, the park was reopened to the public only with limited access to the crater observation area. They have started to require a reservation on the National Park Website before visitation. Adjacent trails to Lake Botos, and the museum at the visitor center remained closed. The volcano erupted briefly twice in September 2019.

El Altar or Capac Urcu is an extinct volcano on the western side of Sangay National Park in Ecuador, 170 km (110 mi) south of Quito, with a highest point of 5,319 m (17,451 ft). Spaniards named it so because it resembled two nuns and four friars listening to a bishop around a church altar. In older English sources it is also called The Altar.

The Irazú Volcano is an active volcano in Costa Rica, situated in the Cordillera Central close to the city of Cartago.

Nevado Ojos del Salado is a dormant complex volcano in the Andes on the Argentina–Chile border. It is the highest volcano on Earth and the highest peak in Chile. The upper reaches of Ojos del Salado consist of several overlapping lava domes, lava flows and volcanic craters, with sparse ice cover. The complex extends over an area of 70–160 square kilometres (27–62 sq mi) and its highest summit reaches an altitude of 6,893 metres (22,615 ft) above sea level. Numerous other volcanoes rise around Ojos del Salado.

Laguna Verde is a salt lake in an endorheic basin, in the southwestern Altiplano in Bolivia. It is located in the Sur Lípez Province of the Potosí Department. It is close to the Chilean border, at the foot of the volcano Licancabur.

Aracar is a large conical stratovolcano in northwestern Argentina, just east of the Chilean border. It has a main summit crater about 1–1.5 kilometres (0.6–0.9 mi) in diameter which sometimes contains crater lakes, and a secondary crater. The volcano has formed, starting during the Pliocene, on top of a lava platform and an older basement. Constructed on a base with an altitude of 4,100 metres (13,500 ft), it covers a surface area of 192.4 square kilometres (74.3 sq mi) and has a volume of 148 cubic kilometres (36 cu mi). The only observed volcanic activity was a possible steam or ash plume on March 28, 1993, seen from the village of Tolar Grande about 50 km (31 mi) southeast of the volcano, but with no evidence of deformation of the volcano from satellite observations. Inca archeological sites are found on the volcano.

Cerro El Cóndor is a stratovolcano in Argentina.

Poás Volcano National Park is a national park in Costa Rica that covers an area of approximately 65 square kilometres ; the summit of Poás Volcano located within the park is at an elevation of 2,700 metres (8,900 ft). The park was established on 25 January 1971. Depending on conditions, visitors can walk all the way to the edge of the main crater, but on 13 April 2017 the park was closed to visitors due to an explosive eruption on the evening of 12 April. Still further eruptions, including on Easter, 16 April, caused the park to be closed until August 2018.

Incahuasi is a volcanic mountain in the Andes of South America. It lies on the border of the Catamarca Province of Argentina and the Atacama Region of Chile. Incahuasi has a summit elevation of 6,621 metres (21,722 ft) above sea level.

Aucanquilcha is a massive stratovolcano located in the Antofagasta Region of northern Chile, just west of the border with Bolivia and within the Alto Loa National Reserve. Part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, the stratovolcano has the form of a ridge with a maximum height of 6,176 metres (20,262 ft). The volcano is embedded in a larger cluster of volcanoes known as the Aucanquilcha cluster. This cluster of volcanoes was formed in stages over eleven million years of activity with varying magma output, including lava domes and lava flows. Aucanquilcha volcano proper is formed from four units that erupted between 1.04–0.23 million years ago. During the ice ages, both the principal Aucanquilcha complex and the other volcanoes of the cluster were subject to glaciation, resulting in the formation of moraines and cirques.

Miñiques is a massive volcanic complex containing a large number of craters, lava domes and flows, located in the Antofagasta Region of Chile. Located 21 km (13 mi) south of Volcán Chiliques and 26 km (16 mi) west of Cordón Puntas Negras, it is part of a frequently visited attraction conformed by the high plain lagoons Laguna Miscanti, Laguna Miñiques and the Cerro Miscanti volcano.

Aguas Calientes Volcano or Cerro Aguas Calientes, also called Simba, is a cone-shaped stratovolcano located 5 kilometres (3 mi) east of the Lascar volcano and 14 kilometres (8.7 mi) north of Laguna Lejía, Chile. It is located within a 500 square kilometres (190 sq mi) area where the Cordón de Puntas Negras and the Cordón Chalviri volcanic chains intersect. The volcano is constructed from andesite and dacite containing hornblende and anhydrite; its pyroclastics are all older than Lascar. It has a diameter of about 7 kilometres (4.3 mi). Some xenoliths of calc-alkaline material are found in Aguas Calientes lavas, and magma mixing has generated lavas containing andesite inclusions in dacites. One eruption of Aguas Calientes postdates the first centre of Lascar and was originally linked to the Lascar Piedras Grandes eruption, before sampling on the deposits of this eruption indicated a relationship with the Lascar volcano itself. Effusion of lava ceased after the cone was built. One summit lava flow may be of Holocene age, but no evidence of historical activity is found.

Chiliques is a stratovolcano located in the Antofagasta Region of Chile.

Volcán Putana, sometimes referred to as Jorqencal or Machuca, is a stratovolcano located In the Central Volcanic Zone (CVZ) of the Andes on the border between Bolivia and Chile and close to the Sairecabur volcanic complex. Its summit is 5,884 metres (19,304 ft) above sea level and contains a summit crater with two smaller craters nested within it. Beneath the summit, the volcano features a number of lava domes and lava flows, some of which originated in flank vents.

Cordón de Puntas Negras is a 500 km2 (193 sq mi) volcanic chain located east of the Salar de Atacama in Chile's Antofagasta Region.

Sairecabur is a volcano located on the frontier between Bolivia and Chile. It is part of the Andean Central Volcanic Zone. Sairecabur proper is 5,971 m (19,590 ft) high; other mountains in the range are 5,722 m (18,773 ft) high Curiquinca, 5,819 m (19,091 ft) high Escalante and 5,748 m (18,858 ft) high Cerro Colorado, all of which have erupted a number of lava flows. Also in close proximity to Sairecabur lie the volcanic centres Licancabur, Putana and Juriques.

The Ocetá Páramo is a páramo, which means an ecosystem above the continuous forest line yet below the permanent snowline. This particular páramo is located at altitudes between 2,950 metres (9,680 ft) and 3,950 metres (12,960 ft) in the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. It covers parts of the municipalities Monguí, Mongua and Tópaga, belonging to the Sugamuxi Province, Boyacá. The Ocetá Páramo is known for its collection of small shrubs called frailejones, as well as other Andean flora and fauna. Hiking tours from Monguí or Mongua to the páramo take a full day.

Laguna Negra is a lake in the Catamarca Province of Argentina. It lies on the Puna high plateau next to two other lakes and salt flats. The lake is less than 2 metres deep and forms a rough rectangle with a surface of 8.6 square kilometres (3.3 sq mi). Laguna Negra loses its water through evaporation, and is replenished through surface runoff and groundwater which ultimately originate to a large part from snowmelt. The waters of the lake are salty.