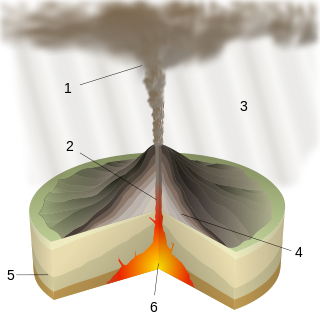
A caldera is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcanic eruption. An eruption that ejects large volumes of magma over a short period of time can cause significant detriment to the structural integrity of such a chamber, greatly diminishing its capacity to support its own roof, and any substrate or rock resting above. The ground surface then collapses into the emptied or partially emptied magma chamber, leaving a large depression at the surface. Although sometimes described as a crater, the feature is actually a type of sinkhole, as it is formed through subsidence and collapse rather than an explosion or impact. Compared to the thousands of volcanic eruptions that occur over the course of a century, the formation of a caldera is a rare event, occurring only a few times within a given window of 100 years. Only eight caldera-forming collapses are known to have occurred between 1911 and 2018, with a caldera collapse at Kīlauea, Hawaii in 2018. Volcanoes that have formed a caldera are sometimes described as "caldera volcanoes".

Nevado del Ruiz, also known as La Mesa de Herveo is a volcano on the border of the departments of Caldas and Tolima in Colombia, about 129 km (80 mi) west of the capital city Bogotá. It is a stratovolcano composed of many layers of lava alternating with hardened volcanic ash and other pyroclastic rocks. Volcanic activity at Nevado del Ruiz began about two million years ago, during the Early Pleistocene or Late Pliocene, with three major eruptive periods. The current volcanic cone formed during the present eruptive period, which began 150,000 years ago.

Mount Pinatubo is an active stratovolcano in the Zambales Mountains, located on the tripoint boundary of the Philippine provinces of Zambales, Tarlac and Pampanga, all in Central Luzon on the northern island of Luzon. Most people were unaware of its eruptive history before the pre-eruption volcanic activity in early 1991. Dense forests, which supported a population of several thousand indigenous Aetas, heavily eroded and obscured Pinatubo.

The volcanism of Italy is due chiefly to the presence, a short distance to the south, of the boundary between the Eurasian Plate and the African Plate. Italy is a volcanically active country, containing the only active volcanoes in mainland Europe. The lava erupted by Italy's volcanoes is thought to result from the subduction and melting of one plate below another.
Plinian eruptions or Vesuvian eruptions are volcanic eruptions marked by their similarity to the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, which destroyed the ancient Roman cities of Herculaneum and Pompeii. The eruption was described in a letter written by Pliny the Younger, after the death of his uncle Pliny the Elder.
The Decade Volcanoes are 16 volcanoes identified by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior (IAVCEI) as being worthy of particular study in light of their history of large, destructive eruptions and proximity to densely populated areas. The Decade Volcanoes project encourages studies and public-awareness activities at these volcanoes, with the aim of achieving a better understanding of the volcanoes and the dangers they present, and thus being able to reduce the severity of natural disasters.

The Armero tragedy occurred following the eruption of the Nevado del Ruiz stratovolcano in Tolima, Colombia, on November 13, 1985. The volcano's eruption after 69 years of dormancy caught nearby towns unprepared, even though volcanological organizations had warned the government to evacuate the area after they detected volcanic activity two months earlier.

Nemrut is a dormant volcano in Tatvan district, Bitlis province, Eastern Turkey, close to Lake Van. The volcano is named after King Nimrod who is said to have ruled this area in about 2100 BC.

Kambalny is a stratovolcano located in the southern part of the Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia. It is the southernmost active volcano of Kamchatka. It has erupted mafic rocks. It has a summit crater as well as five cinder cones on its flanks which are the source of lava flows.

Quilotoa is a water-filled crater lake and the most western volcano in the Ecuadorian Andes. The 3-kilometre (2 mi)-wide caldera was formed by the collapse of this dacite volcano following a catastrophic VEI-6 eruption about 800 years ago, which produced pyroclastic flows and lahars that reached the Pacific Ocean, and spread an airborne deposit of volcanic ash throughout the northern Andes. This last eruption followed a dormancy period of 14,000 years and is known as the 1280 Plinian eruption. The fourth eruptive phase was phreatomagmatic, indicating that a Crater lake was already present at that time. The caldera has since accumulated a 250-metre-deep (820 ft) crater lake, which has a greenish color as a result of dissolved minerals. Fumaroles are found on the lake floor and hot springs occur on the eastern flank of the volcano.

Phreatomagmatic eruptions are volcanic eruptions resulting from interaction between magma and water. They differ from exclusively magmatic eruptions and phreatic eruptions. Unlike phreatic eruptions, the products of phreatomagmatic eruptions contain juvenile (magmatic) clasts. It is common for a large explosive eruption to have magmatic and phreatomagmatic components.

The volcanism of New Zealand has been responsible for many of the country's geographical features, especially in the North Island and the country's outlying islands.

Puyehue and Cordón Caulle are two coalesced volcanic edifices that form a major mountain massif in Puyehue National Park in the Andes of Ranco Province, in the South of Chile. In volcanology this group is known as the Puyehue-Cordón Caulle Volcanic Complex (PCCVC). Four volcanoes constitute the volcanic group or complex, the Cordillera Nevada caldera, the Pliocene Mencheca volcano, Cordón Caulle fissure vents and the Puyehue stratovolcano.
Calabozos is a Holocene caldera in central Chile's Maule Region. Part of the Chilean Andes' volcanic segment, it is considered a member of the Southern Volcanic Zone (SVZ), one of the three distinct volcanic belts of South America. This most active section of the Andes runs along central Chile's western edge, and includes more than 70 of Chile's stratovolcanoes and volcanic fields. Calabozos lies in an extremely remote area of poorly glaciated mountains.

The Galeras tragedy occurred when six scientists and three tourists were killed as a result of the January 1993 eruption of the Galeras stratovolcano in Colombia. Geologist Stanley Williams and six others on the volcano survived.
Chiqllarasu Portugueza or Portuguesa is a mountain in the Andes of Peru, about 5,167 metres (16,952 ft) high. It is situated in the Ayacucho Region, Cangallo Province, Paras District. Chiqllarasu lies north-east of the mountain Saywa Q'asa, between the villages Patawasi (Patahuasi) in the northwest and Kichkawasi (Quichcahuasi) in the southeast.
Dispersal index is a parameter in volcanology. The dispersal index was defined by George P. L. Walker in 1973 as the surface area covered by an ash or tephra fall, where the thickness is equal or more than 1/100 of the thickness of the fall at the vent. An eruption with a low dispersal index leaves most of its products close to the vent, forming a cone; an eruption with a high dispersal index forms thinner sheet-like deposits which extends to larger distances from the vent. A dispersal index of 500 square kilometres (190 sq mi) or more of coarse pumice is one proposed definition of a Plinian eruption. Likewise, a dispersal index of 50,000 square kilometres (19,000 sq mi) has been proposed as a cutoff for an ultraplinian eruption. The definition of 1/100 of the near-vent thickness was partially dictated by the fact that most tephra deposits are not well preserved at larger distances.

Ubinas is an active stratovolcano in the Moquegua Region of southern Peru, approximately 60 kilometres (37 mi) east of the city of Arequipa. Part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, it rises 5,672 metres (18,609 ft) above sea level. The volcano's summit is cut by a 1.4-kilometre-wide (0.87 mi) and 150-metre-deep (490 ft) caldera, which itself contains a smaller crater. Below the summit, Ubinas has the shape of an upwards-steepening cone with a prominent notch on the southern side. The gently sloping lower part of the volcano is also known as Ubinas I and the steeper upper part as Ubinas II; they represent different stages in the volcano's geological history.

The Cascade Volcanic Arc is a chain of volcanoes stretching from southern British Columbia down to northern California. Within the arc there is a variety of stratovolcanoes like Mount Rainier and broad shield volcanoes like Medicine Lake. But calderas are very rare in the Cascades, with very few forming over the 39 million year lifespan of the arc.
Marta Lucía Calvache Velasco is a Colombian geologist and volcanologist, best known for her work on geological hazards and risk reduction in Colombia.