
Arequipa is a department and region in southwestern Peru. It is the sixth largest department in Peru, after Puno, Cuzco, Madre de Dios, Ucayali, and Loreto, its sixth most populous department, and its eleventh least densely populated department. It is bordered by the departments of Ica, Ayacucho, Apurímac and Cusco in the north, the Department of Puno in the east, the Department of Moquegua in the south, and the Pacific Ocean in the west. Its capital, also called Arequipa, is Peru's second-largest city.

Nevado Ojos del Salado is a dormant complex volcano in the Andes on the Argentina–Chile border. It is the highest volcano on Earth and the highest peak in Chile. The upper reaches of Ojos del Salado consist of several overlapping lava domes, lava flows and volcanic craters, with sparse ice cover. The complex extends over an area of 70–160 square kilometres (27–62 sq mi) and its highest summit reaches an altitude of 6,893 metres (22,615 ft) above sea level. Numerous other volcanoes rise around Ojos del Salado.

Incahuasi is a volcanic mountain in the Andes of South America. It lies on the border of the Catamarca Province of Argentina and the Atacama Region of Chile. Incahuasi has a summit elevation of 6,621 metres (21,722 ft) above sea level.

Nevado de Longaví is a volcano in the Andes of central Chile. The 3,242 m (10,636 ft) high volcano lies in the Linares Province, which is part of the Maule Region. It features a summit crater and several parasitic vents. The volcano is constructed principally from lava flows. Two collapses of the edifice have carved collapse scars into the volcano, one on the eastern slope known as Lomas Limpias and another on the southwestern slope known as Los Bueye. The volcano features a glacier and the Achibueno and Blanco rivers originate on the mountain.

Tacora is a stratovolcano located in the Andes of the Arica y Parinacota Region of Chile. Near the border with Peru, it is one of the northernmost volcanoes of Chile. It is part of the Central Volcanic Zone in Chile, one of the four volcanic belts of the Andes. The Central Volcanic Zone has several of the highest volcanoes in the world. Tacora itself is a stratovolcano with a caldera and a crater. The youngest radiometric age is 50,000 years ago and it is heavily eroded by glacial activity.

Yanteles is an isolated stratovolcano composed of five glacier-capped peaks along an 8 km-long NE-trending ridge. It is located approximately 30 km (19 mi) south of the Corcovado volcano in the Chilean X Region within the Corcovado National Park. The name Yanteles can refer only to the main summit, which is also known as Volcán Nevado.

The Purico complex is a Pleistocene volcanic complex in Chile close to Bolivia, formed by an ignimbrite, several lava domes and stratovolcanoes and one maar. It is in the Chilean segment of the Central Volcanic Zone, one of the four volcanic belts which make up the Andean Volcanic Belt. The Central Volcanic Zone spans Peru, Bolivia, Chile and Argentina and includes 44 active volcanoes as well as the Altiplano–Puna volcanic complex, a system of large calderas and ignimbrites of which Purico is a member. Licancabur to the north, La Pacana southeast and Guayaques to the east are separate volcanic systems.
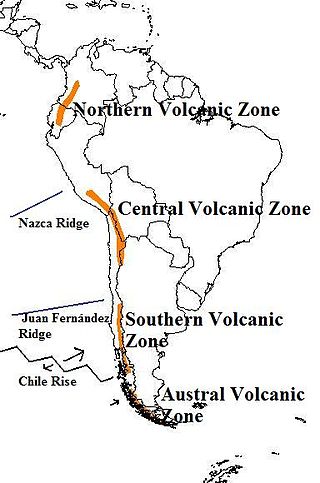
The Andean Volcanic Belt is a major volcanic belt along the Andean cordillera in Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. It is formed as a result of subduction of the Nazca plate and Antarctic plate underneath the South American plate. The belt is subdivided into four main volcanic zones which are separated by volcanic gaps. The volcanoes of the belt are diverse in terms of activity style, products, and morphology. While some differences can be explained by which volcanic zone a volcano belongs to, there are significant differences within volcanic zones and even between neighboring volcanoes. Despite being a type location for calc-alkalic and subduction volcanism, the Andean Volcanic Belt has a broad range of volcano-tectonic settings, as it has rift systems and extensional zones, transpressional faults, subduction of mid-ocean ridges and seamount chains as well as a large range of crustal thicknesses and magma ascent paths and different amounts of crustal assimilations.

Cotahuasi Canyon, near the city of Arequipa in Peru, is one of the deepest canyons in the world. With a depth of approximately 3,354 metres (11,004 ft), as defined as the difference in elevation at river level and the peak of a mountain alongside the canyon, it is more than twice as deep as the Grand Canyon. The Cotahuasi River eroded the canyon between two mountain massifs: the Coropuna and the Solimana. It extends from spurs of the snow-covered Solimana to the confluence with the Ocoña River near the village of Chaucalla.

Sollipulli is an ice-filled volcanic caldera and volcanic complex, which lies southeast of the small town of Melipeuco in the La Araucanía Region, Chile. It is part of the Southern Volcanic Zone of the Andes, one of the four volcanic belts in the Andes chain.

Hualca Hualca is an extinct volcano in Arequipa Region in the Andes of Peru. It has a height of 6,025 metres (19,767 ft). It is located at the Peruvian province of Caylloma.

Pichu Pichu is an inactive eroded volcano in the Andes of Peru, with seven summits; the highest reaches a height of 5,664 metres (18,583 ft). It lies east of the city Arequipa and together with its neighbours Misti and Chachani is part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes. Pichu Pichu was active many millions of years ago, producing ignimbrites and lava flows with andesitic composition. During the last two million years, a gigantic landslide descended the western side of the volcano and left a large scar that runs north to south. Pichu Pichu bore glaciers during the last glacial maximum, which left moraines and other glacial landforms after they retreated.

Solimana is a volcanic massif in the Andes of Peru, South America, that is approximately 6,093 metres (19,990 ft) high. It is considered an extinct stratovolcano that is part of the Central Volcanic Zone, one of the volcanic belts of the Andes. It features a caldera as well as traces of a sector collapse and subsequent erosion. The volcano is glaciated.

Coropuna is a dormant compound volcano located in the Andes mountains of southeast-central Peru. The upper reaches of Coropuna consist of several perennially snowbound conical summits, lending it the name Nevado Coropuna in Spanish. The complex extends over an area of 240 square kilometres (93 sq mi) and its highest summit reaches an altitude of 6,377 metres (20,922 ft) above sea level. This makes the Coropuna complex the third-highest of Peru. Its thick ice cap is the most extensive in Earth's tropical zone, with several outlet glaciers stretching out to lower altitudes. Below an elevation of 5,000 metres (16,000 ft), there are various vegetation belts which include trees, peat bogs, grasses and also agricultural areas and pastures.
Jotabeche is a Miocene-Pliocene caldera in the Atacama Region of Chile. It is part of the volcanic Andes, more specifically of the extreme southern end of the Central Volcanic Zone (CVZ). This sector of the Andean Volcanic Belt contains about 44 volcanic centres and numerous more minor volcanic systems, as well as some caldera and ignimbrite systems. Jotabeche is located in a now inactive segment of the CVZ, the Maricunga Belt.

Sairecabur is a volcano located on the frontier between Bolivia and Chile. It is part of the Andean Central Volcanic Zone. Sairecabur proper is 5,971 m (19,590 ft) high; other mountains in the range are 5,722 m (18,773 ft) high Curiquinca, 5,819 m (19,091 ft) high Escalante and 5,748 m (18,858 ft) high Cerro Colorado, all of which have erupted a number of lava flows. Also in close proximity to Sairecabur lie the volcanic centres Licancabur, Putana and Juriques.

Sara Sara is a 5,505-metre-high (18,061 ft) volcano lying between Lake Parinacochas and the Ocoña River in Peru. It is situated in the Parinacochas Province and the Paucar del Sara Sara Province. The volcano formed during the Pleistocene during four different stages of volcanic activity, which constructed a volcanic edifice with an oval outline consisting of lava flows and lava domes. The volcano was glaciated during the last glacial maximum; it may still feature glaciers. The last eruption was about 14,000 years ago and future eruptions are possible. The volcano was worshipped by the local population, and an Inca mummy of a 15-year old girl was found on the summit by archaeologists.

Sillajhuay is a volcano on the border between Bolivia and Chile. It is part of a volcanic chain that stretches across the border between Bolivia and Chile and forms a mountain massif that is in part covered by ice; whether this ice should be considered a glacier is debatable but it has been retreating in recent decades.

Chachani is a volcanic group in southern Peru, 22 kilometres (14 mi) northwest of the city of Arequipa. Part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, it is 6,057 metres (19,872 ft) above sea level. It consists of several lava domes and individual volcanoes such as Nocarane, along with lava shields such as the Airport Domes. Underneath Chachani lies a caldera.

Nevado Tres Cruces is a massif of volcanic origin in the Andes Mountains on the border of Argentina and Chile. It has two main summits, Tres Cruces Sur at 6,748 metres (22,139 ft) and Tres Cruces Centro at 6,629 m (21,749 ft) and a third minor summit, Tres Cruces Norte 6,030 m (19,780 ft). Tres Cruces Sur is the sixth highest mountain in the Andes.



















