
Parañaque, officially the City ofParañaque, is a first class highly urbanized city in the National Capital Region of the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 689,992 people.

The South Luzon Expressway (SLEX), signed as E2 of the Philippine expressway network and R-3 of the Metro Manila arterial road network, is a controlled-access highway that connects Metro Manila to the provinces in the Calabarzon, Mimaropa and Bicol Region on the island of Luzon in the Philippines. The expressway has a length of 49.56 km, traveling from its northern terminus at the Magallanes Interchange in Makati to its southern terminus at Santo Tomas, Batangas, connecting it to the Southern Tagalog Arterial Road. A portion of the expressway from the Magallanes Interchange to the Calamba Exit is part of Asian Highway 26 of the Asian highway network. It will be the longest expressway in the Philippines starting with the completion of Toll Road 4 surpassing the Subic–Clark–Tarlac Expressway (SCTEX) as well as providing a gateway to Visayas upon the completion of Toll Road 5.
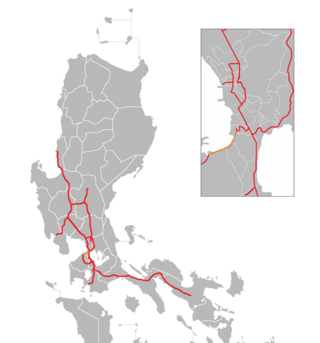
The Manila–Cavite Expressway, signed as E3 of the Philippine expressway network and R-1 of Metro Manila's arterial road network, is a 14-kilometer-long (8.7 mi) controlled-access highway linking Manila to the southern province of Cavite in the Philippines. At its north end, it feeds into and from Roxas Boulevard in the city of Parañaque in Metro Manila, also part of R-1. At the south end, it splits into two termini, both along the north coast in Kawit, Cavite. The first feeds into the intersection of Covelandia Road, Tirona Highway and Antero Soriano Highway. The second southern terminus is an exit-only to Tirona Highway in Barangay Marulas.

The Metro Manila Skyway, officially the Metro Manila Skyway System (MMSS) or simply the Skyway, is an elevated highway serving as the main expressway of Metro Manila, Philippines. It connects the North and South Luzon Expressways with access to Ninoy Aquino International Airport via the NAIA Expressway (NAIAX). It is the first fully grade-separated highway in the Philippines and one of the longest elevated highways in the world, with a total length of approximately 39.2 kilometers (24.4 mi).

Roxas Boulevard is a popular waterfront promenade in Metro Manila in the Philippines. The boulevard, which runs along the shores of Manila Bay, is well known for its sunsets and stretch of coconut trees. The divided roadway has become a trademark of Philippine tourism, famed for its yacht club, hotels, restaurants, commercial buildings and parks.

Circumferential Road 5 (C-5), informally known as the C-5 Road, is a network of roads and bridges that all together form the fifth beltway of Metro Manila in the Philippines. Spanning some 43.87 kilometers (27.26 mi), it connects the cities of Las Piñas, Parañaque, Pasay, Pasig, Quezon City, Taguig, and Valenzuela.

The Ninoy Aquino International Airport Expressway (NAIAX), signed as E6 of the Philippine expressway network, is an 12.65-kilometer (7.86 mi) elevated highway in Metro Manila, Philippines, which links the Skyway to Ninoy Aquino International Airport and Entertainment City. Traversing the cities of Pasay, and Parañaque, the NAIAX runs along Andrews Avenue, Electrical Road, and NAIA Road connecting the Skyway to Ninoy Aquino Avenue, Macapagal Boulevard, New Seaside Drive and the Manila–Cavite Expressway.
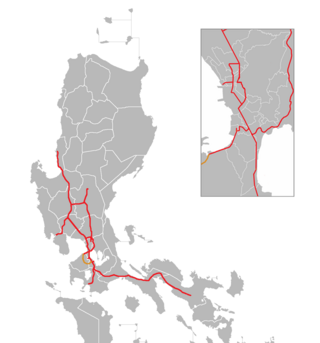
The Cavite–Laguna Expressway, signed as E3 of the Philippine expressway network, is a partially operational controlled-access toll expressway in the provinces of Cavite and Laguna, Philippines. The construction of the 44.63-kilometer-long (27.73 mi) expressway, which began in June 2017, costs an estimated ₱35.43 billion. Once completed, it will connect the Manila–Cavite Expressway in Kawit to the South Luzon Expressway in Biñan and is expected to ease the traffic congestion in the Cavite–Laguna area, particularly along the Aguinaldo Highway, Governor's Drive, and the Santa Rosa–Tagaytay Road.

Alabang–Zapote Road is a four-lane national road which travels east–west through the southern limits of Metro Manila, Philippines. It runs parallel to Dr. Santos Avenue in the north and is named for the two barangays that it links: Alabang in the city of Muntinlupa and Zapote in both the cities of Bacoor and Las Piñas.

Circumferential Road 6 (C-6), informally known as the C-6 Road, is a network of roads and bridges that all together will form the sixth and outermost beltway of Metro Manila in the Philippines once it is completed.
The Philippine expressway network, also known as the High Standard Highway Network, is a controlled-access highway network managed by the Department of Public Works and Highways (DPWH) which consists of all expressways and regional high standard highways in the Philippines.
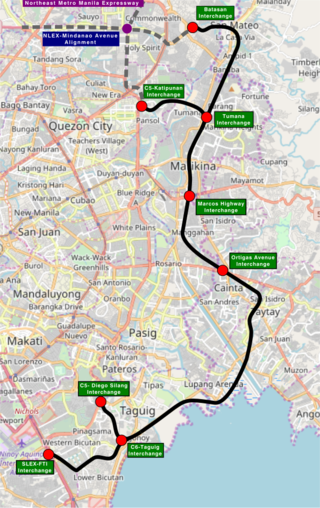
The Southeast Metro Manila Expressway (SEMME), also known as Skyway Stage 4, C-6 Expressway and formerly as Metro Manila Expressway, is an on-hold 32.664-kilometer (20.296 mi) tolled expressway running across eastern Metro Manila and western Rizal. The expressway will help decongest the existing roadways across Metro Manila, such as EDSA and Circumferential Road 5. The expressway is part of the larger Circumferential Road 6 project. Which it's expansion from original C-6 length currently passing from General Santos Avenue in Taguig up to Highway 2000 in Taytay, will expand to Cainta, Pasig, Marikina, San Mateo, and in Quezon City.

NLEX Harbor Link, signed as E5 of the Philippine expressway network, is a four- to six-lane expressway that serves as a spur of North Luzon Expressway (NLEX) linking it to the Port of Manila to the west and Quezon City to the east. It runs from Katipunan and C.P. Garcia Avenues in Quezon City to Radial Road 10 in Navotas, which in turn leads to the Port of Manila. Currently, its segment from Mindanao Avenue in Valenzuela to Navotas is operational.

National Route 62 (N62) forms part of the Philippine highway network. It runs south from Metro Manila to northeastern Cavite.

National Route 11 (N11) is an 18-kilometer (11 mi) major primary route that forms part of the Philippine highway network. It is a component and the main route of Circumferential Road 5 (C-5), connecting the cities of Taguig, Pasig and Quezon.
Expressway 2 (E2) forms part of the Philippine expressway network. Its main route runs from Makati to Santo Tomas as South Luzon Expressway and from Santo Tomas to Batangas City as STAR Tollway. It also has spurs signed as E2 as well. South Luzon Expressway's section from Makati to Calamba, apparently as well as Skyway from Makati to Muntinlupa, is also part of AH26.

Don Galo, also historically known as Dongalo, is an administrative division in southern Metro Manila, the Philippines. It is a barangay in the city of Parañaque along the north bank of the Parañaque River by its mouth in Manila Bay. It is located directly west of the village of Santo Niño, separated from it by the Estero de Tripa de Gallina stream, and between Tambo to the north and the Parañaque poblacion of La Huerta to the south. The barangay also includes the southernmost section of Bay City, including portions of the Asia World subdistrict such as Entertainment City and Marina Bay.

La Huerta is a barangay in the city of Parañaque, Metro Manila, Philippines. It comprises a section of the old poblacion of Parañaque along the south bank of the Parañaque River by its mouth in Manila Bay. The coastal village encompasses the area from Don Galo on the north, Santo Niño and Moonwalk on the east and San Dionisio on the south. A portion of Global Airport Business Park along C-5 Road Extension is also under the jurisdiction of La Huerta. It also extends west to the reclaimed area in Manila Bay and covers the northernmost section of Freedom Island in the Las Piñas–Parañaque Critical Habitat and Ecotourism Area. As of the 2020 census, it had a population of 8,592.

San Martin de Porres is an administrative division in southern Metro Manila, the Philippines. It is an elongated barangay located in the northeast corner of Parañaque adjoining the areas of Bicutan in Taguig and northern Muntinlupa. It is unique in that it is connected to the rest of Parañaque by only two bridges, one of which is a footbridge. Its western border follows the South Luzon Expressway, thus separating it from Merville, Sun Valley, Don Bosco and Marcelo Green. It neighbors Western Bicutan to the north, particularly the redevelopment area of the former Food Terminal Inc. (FTI) known as Arca South. To the east, it adjoins Taguig's barangays of Upper Bicutan, Central Bicutan, North Daang Hari and Tanyag. It neighbors South Daang Hari and Sucat, Muntinlupa to the south.





















