
Birdoswald Roman Fort was known as Banna in Roman times, reflecting the geography of the site on a triangular spur of land bounded by cliffs to the south and east commanding a broad meander of the River Irthing in Cumbria below.

Hadrian's Wall Path is a long-distance footpath in the north of England, which became the 15th National Trail in 2003. It runs for 84 miles (135 km), from Wallsend on the east coast of England to Bowness-on-Solway on the west coast. For most of its length it is close to the remains of Hadrian's Wall, the defensive wall built by the Romans on the northern border of their empire. This is now recognised as part of the "Frontiers of the Roman Empire" World Heritage Site.

Segedunum was a Roman fort at modern-day Wallsend, North Tyneside in North East England. The fort lay at the eastern end of Hadrian's Wall near the banks of the River Tyne. It was in use for approximately 300 years from around 122 AD to almost 400. Today Segedunum is the most thoroughly excavated fort along Hadrian's Wall, and is operated as Segedunum Roman Fort, Baths and Museum. It forms part of the Hadrian's Wall UNESCO World Heritage Site.

Bremenium is an ancient Roman fort (castrum) located at Rochester, Northumberland, England. The fort is part of the defensive system built along the extension of Dere Street, a Roman road running from York to Corbridge and onwards to Melrose. Significantly the fort is a long way north of Hadrian's Wall. It was one of the last forts north of Hadrian's wall to remain occupied until the 270s.

Burgh by Sands is a village and civil parish in the Cumberland unitary authority area of Cumbria, England, situated near the Solway Firth. The parish includes the village of Burgh by Sands along with Longburgh, Dykesfield, Boustead Hill, Moorhouse and Thurstonfield. It is notable as the site of the first recorded North African (Mauri) military unit in Roman Britain, garrisoning the frontier fort of Aballava on Hadrian's Wall in the 3rd century AD. It is also where Edward I of England died in 1307.

Magnis or Magna was a Roman fort near Hadrian's Wall in northern Britain. Its ruins are now known as Carvoran Roman Fort and are located near Carvoran, Northumberland, in northern England. It was built on the Stanegate frontier and Roman road, linking Coria (Corbridge) in the east to Luguvalium (Carlisle) in the west, before the building of Hadrian's Wall.

Kirkbride is a village and civil parish in northern Cumbria, England. The civil parish population at the 2011 census was 489.

Hunnum was a Roman fort on Hadrian's Wall located north of the modern-day village of Halton, Northumberland in North East England. It was the fifth fort on Hadrian's Wall and is situated about 7.5 miles west of Vindobala fort, 5.9 miles east of Chesters fort and 2.5 miles north of the Stanegate fort of Coria (Corbridge). The site of the fort is bisected by the B6318 Military Road, which runs along the route of the wall at that point.

Aesica was a Roman fort, one and a half miles north of the small town of Haltwhistle in Northumberland,. It was the ninth fort on Hadrian's Wall, between Vercovicium (Housesteads) 6.0 miles to the east and Banna (Birdoswald) 6.5 miles to the west.
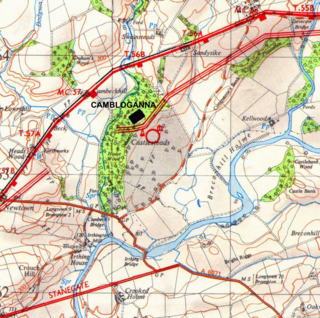
Camboglanna was a Roman fort. It was the twelfth fort on Hadrian's Wall counting from the east, between Banna (Birdoswald) almost 7 miles (11 km) to the east and Uxelodunum (Stanwix), 9 miles to the west. It was on a high bluff commanding the Cambeck Valley. It guarded an important approach to the Wall and also watched the east bank of the Cambeck against raiders from the Bewcastle area. The site was drastically levelled in 1791 when the gardens of Castlesteads House were laid over it. The name "Camboglanna" is believed to mean "Crook Bank", or "Bent Valley" because it overlooks a bend in the river Irthing; the name is Brythonic, made of cambo- "curved, bent, crooked" and glanna "steep bank, stream/river side, valley with a stream".

Uxelodunum was a Roman fort with associated civilian settlement (vicus) in modern-day Carlisle, Cumbria, England. It was the largest fort on Hadrian's Wall and is now buried beneath the suburb of Stanwix.

Aballava or Aballaba was a Roman fort on Hadrian's Wall, between Petriana (Stanwix) to the east and Coggabata (Drumburgh) to the west. It is about one and a half miles south of the Solway Firth, and its purpose was to guard the south end of two important Solway fords, the Peat Wath and the Sandwath, which were also to become favourite routes for medieval border raiders.

Maia, or Mais, in Cumbria, England was a Roman fort on Hadrian's Wall, and was the last fort at the western end of the Wall, overlooking the Solway Firth.

Hadrian's Wall is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the Emperor Hadrian. Running from Wallsend on the River Tyne in the east to Bowness-on-Solway in the west of what is now northern England, it was a stone wall with large ditches in front and behind, stretching across the whole width of the island. Soldiers were garrisoned along the line of the wall in large forts, smaller milecastles, and intervening turrets. In addition to the wall's defensive military role, its gates may have been customs posts.

Habitancum was an ancient Roman fort (castrum) located at Risingham, Northumberland, England. The fort was one of series of built along the extension of Dere Street, a Roman road running from York to Corbridge and onwards to Melrose, in Scotland.

Bewcastle Roman Fort was built to the north of Hadrian's Wall as an outpost fort possibly intended for scouting and intelligence. The remains of the fort are situated at the village of Bewcastle, Cumbria, 7 miles (11 km) to the north of the Roman fort at Birdoswald, on Hadrian's Wall.

Drumburgh is a small settlement in Cumbria, England. It is 13 kilometres (8 mi) northwest of the city of Carlisle and is on the course of Hadrian's Wall, near to Burgh by Sands. The village is sited on a gentle hill with a good view in all directions over the surrounding lowlands.

Leahill Turret is a typical example of one of the lookout towers located between the milecastles on Hadrian's Wall in Cumbria; located on the Lanercost Road near Banks, Parish of Waterhead. It is designated turret 51b and lies east of the Signal Tower at Pike Hill.

Milecastle 79 (Solway House) was one of a series of Milecastles or small fortlets built at intervals of approximately one Roman mile along Hadrian's Wall (grid reference NY23596224).

Milecastle 76 (Drumburgh) was one of a series of Milecastles or small fortlets built at intervals of approximately one Roman mile along Hadrian's Wall (grid reference NY26685987).























