Order is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families.

The emu is the second-tallest living bird after the ostrich, its ratite relative. It is endemic to Australia, where it is the largest native bird and the only extant member of the genus Dromaius. The emu's range covers most of the mainland. The Tasmanian, Kangaroo Island and King Island subspecies became extinct after the European settlement of Australia in 1788.

The sand martin, also known as the bank swallow, collared sand martin, or common sand martin, is a migratory passerine bird in the swallow family. It has a wide range in summer, embracing practically the whole of Europe and the Mediterranean countries and across the Palearctic to the Pacific Ocean. It is a Holarctic species also found in North America. It winters in eastern and southern Africa, South America, and the Indian Subcontinent.

The willie wagtail, scientific name Rhipidura leucophrys, is a passerine bird native to Australia, New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, the Bismarck Archipelago, and Eastern Indonesia. It is a common and familiar bird throughout much of its range, living in most habitats apart from thick forest. Measuring 19–21.5 cm in length, the willie wagtail is contrastingly coloured with almost entirely black upperparts and white underparts; the male and female have similar plumage.

The Folland Gnat is a British compact swept-wing subsonic fighter aircraft that was developed and produced by Folland Aircraft. Envisioned as an affordable light fighter in contrast to the rising cost and size of typical combat aircraft, it was procured as a trainer aircraft for the Royal Air Force (RAF) as well as by export customers, who used the Gnat in both combat and training capacities.

The Grand National Assembly of Turkey, usually referred to simply as the TBMM or Parliament, is the unicameral Turkish legislature. It is the sole body given the legislative prerogatives by the Turkish Constitution. It was founded in Ankara on 23 April 1920 amid the National Campaign. This constitution had founded its pre-government known as 1st Executive Ministers of Turkey in May 1920. The parliament was fundamental in the efforts of Mareşal Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, 1st President of the Republic of Turkey, and his colleagues to found a new state out of the remnants of the Ottoman Empire.

The BAE Systems Mark 36 Super Rapid Bloom Offboard Countermeasures Chaff and Decoy Launching System is an American short-range decoy launching system (DLS) that launches radar or infrared decoys from naval vessels to foil incoming anti-ship missiles. The decoys present false signals and interference to the attacking missiles' guidance and fire-control systems.

The Nematocera are a suborder of elongated flies with thin, segmented antennae and mostly aquatic larvae. This group is paraphyletic and contains all flies but species from suborder Brachycera, which includes more commonly known species such as the housefly or the common fruit fly. The equivalent clade to Nematocera is the whole Diptera, with Brachycera as a subclade. Families in Nematocera include mosquitoes, crane flies, gnats, black flies, and multiple families commonly known as midges. The Nematocera typically have fairly long, fine, finely-jointed antennae. In many species, such as most mosquitoes, the female antennae are more or less threadlike, but the males have spectacularly plumose antennae.

Fungus gnats are small, dark, short-lived gnats, of the families Sciaridae, Diadocidiidae, Ditomyiidae, Keroplatidae, Bolitophilidae, and Mycetophilidae ; they comprise six of the seven families placed in the superfamily Sciaroidea.

Keroplatidae is a family of small flies known as fungus gnats. About 950 species are described, but the true number of species is undoubtedly much higher. The long-beaked fungus gnats, formerly placed in a separate family Lygistorrhinidae, have been placed into Keroplatidae as subfamily Lygistorrhininae. They are generally forest dwellers found in the damp habitats favoured by their host fungi. They can also often be found in caves. Larvae both feed on fungi and are predatory - they can spin webs by secreting acid fluids, which they use to kill smaller invertebrates and capture spores. Some of the predatory larvae cannibalize pupa of their own species. The family notably include the genus Arachnocampa; the larvae of which are known as "glowworms" in Australia and New Zealand.

Henry Luke White was a wealthy grazier, and a keen philatelist, book collector, amateur ornithologist and oölogist of Scone, New South Wales, Australia.

Eucalyptus patens, commonly known as yarri or blackbutt, is a species of flowering plant in the family Myrtaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It has rough bark on the trunk and branches, lance-shaped leaves, creamy-white flowers and spherical to oval fruit.

Hawking is a feeding strategy in birds involving catching flying insects in the air. The term usually refers to a technique of sallying out from a perch to snatch an insect and then returning to the same or a different perch, though it also applies to birds that spend almost their entire lives on the wing. This technique is called "flycatching" and some birds known for it are several families of "flycatchers": Old World flycatchers, monarch flycatchers, and tyrant flycatchers; however, some species known as "flycatchers" use other foraging methods, such as the grey tit-flycatcher. Other birds, such as swifts, swallows, and nightjars, also take insects on the wing in continuous aerial feeding. The term "hawking" comes from the similarity of this behavior to the way hawks take prey in flight, although, whereas raptors may catch prey with their feet, hawking is the behavior of catching insects in the bill. Many birds have a combined strategy of both hawking insects and gleaning them from foliage.

The rufous-banded honeyeater is a species of bird in the family Meliphagidae. It is found in the Aru Islands, New Guinea and northern Australia. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical mangrove forests. The rufous-banded honeyeater is considered one of the most common small birds in the suburban ecosystem of Darwin, Australia, notable because its lack of introduced bird species. Ornithologist F. Salomonsen recognized two subspecies of rufous-banded honeyeater, Conopophila albogularis and Conopophila mimikae but J. Ford disagreed with this subspeciation.

The rufous-throated honeyeater is a species of bird in the family Meliphagidae. It is endemic to northern Australia.
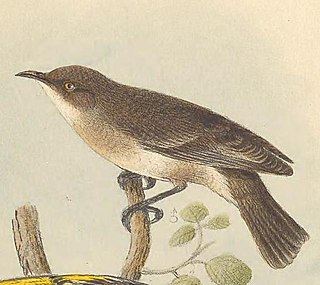
The grey honeyeater is a species of bird in the honeyeater family. It is an uncommon and little-known bird, an often overlooked endemic of remote areas in central Australia.

Sciaroidea is a superfamily in the infraorder Bibionomorpha. There are about 16 families and more than 15,000 described species in Sciaroidea. Most of its constituent families are various gnats.

Cyrtostylis reniformis, commonly known as common gnat-orchid, is a species of orchid endemic to eastern Australia. It usually has a single kidney-shaped leaf and a flowering spike with up to eight reddish flowers with a shelf-like labellum.

A gnat is any of many species of tiny flying insects in the dipterid suborder Nematocera, especially those in the families Mycetophilidae, Anisopodidae and Sciaridae. They can be both biting and non-biting. Most often they fly in large numbers, called clouds. "Gnat" is a loose descriptive category rather than a phylogenetic or other technical term, so there is no scientific consensus on what constitutes a gnat. Some entomologists consider only non-biting flies to be gnats. Certain universities and institutes also distinguish eye gnats: the Smithsonian Institution describes them as "non-biting flies, no bigger than a few grains of salt, ... attracted to fluids secreted by your eyes".

The Hillman Gnat was an experimental World War II era light armoured car developed in Britain.
























