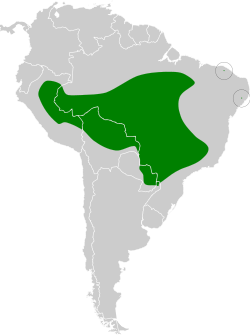
| Pipra | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Wire-tailed manakin Cristalino River, Southern Amazon, Brazil | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Pipridae |
| Genus: | Pipra Linnaeus, 1764 |
| Type species | |
| Parus aureola Linnaeus, 1758 | |