
A designer drug is a structural or functional analog of a controlled substance that has been designed to mimic the pharmacological effects of the original drug, while avoiding classification as illegal and/or detection in standard drug tests. Designer drugs include psychoactive substances that have been designated by the European Union as new psychoactive substances (NPS) as well as analogs of performance-enhancing drugs such as designer steroids. Some of these were originally synthesized by academic or industrial researchers in an effort to discover more potent derivatives with fewer side effects and were later co-opted for recreational use. Other designer drugs were prepared for the first time in clandestine laboratories. Because the efficacy and safety of these substances have not been thoroughly evaluated in animal and human trials, the use of some of these drugs may result in unexpected side effects.

Benzylpiperazine (BZP) is a recreational drug with euphoriant and stimulant properties. The effects produced by BZP are comparable to those produced by amphetamine. Adverse effects have been reported following its use including acute psychosis, renal toxicity and seizures. No deaths have been reported following a sole ingestion of BZP, although there have been at least two deaths from the combination of BZP and MDMA. Its sale is banned in several countries, including Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United States, the Republic of Ireland, the United Kingdom, Bulgaria, Romania and other parts of Europe.
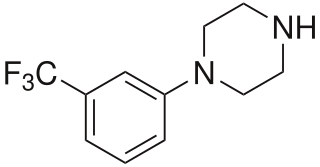
3-Trifluoromethylphenylpiperazine (TFMPP) is a recreational drug of the piperazine chemical class. Usually in combination with benzylpiperazine (BZP) and other analogues, it is sold as an alternative to the illicit drug MDMA ("Ecstasy").

Party pills, also known as "herbal highs", "pep pills" "dance pills" and "natural power", is a colloquialism for a type of recreational drug whose main ingredient was originally benzylpiperazine (BZP), but has expanded to a wide range of compounds with a variety of effects. BZP is banned in a few countries, including the USA, Republic of Ireland, Australia and New Zealand, but is available on a more or less restricted basis in many jurisdictions. A range of other piperazine derivatives have also been sold as ingredients in party pills, and many of these branded "proprietary blends" have subsequently been sold in countries around the world.

meta-Chlorophenylpiperazine (mCPP) is a psychoactive drug of the phenylpiperazine class. It was initially developed in the late-1970s and used in scientific research before being sold as a designer drug in the mid-2000s. It has been detected in pills touted as legal alternatives to illicit stimulants in New Zealand and pills sold as "ecstasy" in Europe and the United States.

para-Methoxyphenylpiperazine is a piperazine derivative with stimulant effects which has been sold as an ingredient in "Party pills", initially in New Zealand and subsequently in other countries around the world.

MBZP (1-methyl-4-benzylpiperazine) is a stimulant drug which is a derivative of benzylpiperazine. MBZP has been sold as an ingredient in legal recreational drugs known as "Party pills", initially in New Zealand and subsequently in other countries around the world.
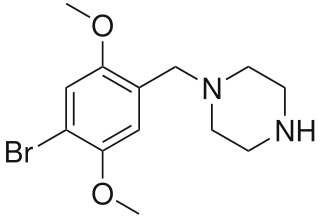
4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxy-1-benzylpiperazine (2C-B-BZP) is a psychoactive drug and research chemical of the piperazine chemical class which has been sold as a "designer drug". It produces stimulant effects similar to those of benzylpiperazine (BZP).

Mephedrone, also known as 4-methyl methcathinone (4-MMC) or 4-methyl ephedrone, is a synthetic stimulant drug of the amphetamine and cathinone classes. Slang names include bath salts, drone, M-CAT, White Magic and meow meow. It is chemically similar to the cathinone compounds found in the khat plant of eastern Africa. It comes in the form of tablets or a powder, which users can swallow, snort or inject, producing similar effects to MDMA, amphetamines and cocaine.
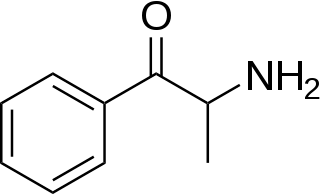
Substituted cathinones, which include some stimulants and entactogens, are derivatives of cathinone. They feature a phenethylamine core with an alkyl group attached to the alpha carbon, and a ketone group attached to the beta carbon, along with additional substitutions. Cathinone occurs naturally in the plant khat whose leaves are chewed as a recreational drug.
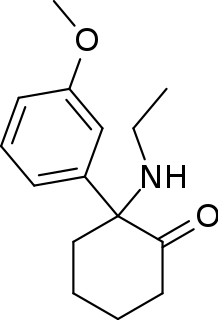
Methoxetamine, abbreviated as MXE, is a dissociative hallucinogen that has been sold as a designer drug. It differs from many dissociatives such as ketamine and phencyclidine (PCP) that were developed as pharmaceutical drugs for use as general anesthetics in that it was designed for grey market distribution.

On 2 October 2010, the Poland's State Health Inspectorate in a controversial decision, closed down and sealed off almost 1400 retail smart shops specializing in the off sales of psychoactive substances in Poland. A few weeks following the operation, a law was passed to criminalise all open sales of psychotropic and mind-altering drugs, including those not on the government list of banned psychotropic drugs in Poland. Some of the drugs previously sold at smart shops were banned earlier in March 2009 and 2010 (mephedrone).

Bath salts are a group of recreational designer drugs. The name derives from instances in which the drugs were disguised as bath salts. The white powder, granules, or crystals often resemble Epsom salts, but differ chemically. The drugs' packaging often states "not for human consumption" in an attempt to circumvent drug prohibition laws. Additionally, they may be mislabeled as plant food, powdered cleaner, and other such products.

3-(4-Hydroxymethylbenzoyl)-1-pentylindole is a synthetic cannabinoid. It is planned to be scheduled in Poland. It has been reported to the EMCDDA and Europol for the first time in 2010 under the terms of European Council Decision 2005/387/JHA of 10 May 2005 on the information exchange, risk-assessment and control of new psychoactive substances.

3-Methylmethcathinone, also known as 3-MMC and 3-mephedrone, is a designer drug from the substituted cathinone family. 3-MMC is closely related in structure to the more common illicit drug mephedrone (4-MMC), and is illegal in most countries that have banned mephedrone as it is a structural isomer of it. However, 3-MMC has still appeared on the recreational drug market as an alternative to mephedrone, and was first identified being sold in Sweden in 2012. Unlike other legal highs 3-MMC was tested and characterized in large mammals, providing much more knowledge about it than is known about other synthetic cathinones. 3-MMC is a monoamine transporter substrate that potently inhibits norepinephrine uptake and displays more pronounced dopaminergic vs. serotonergic activity.

MDMB-CHMICA (also incorrectly known as MMB-CHMINACA) is an indole-based synthetic cannabinoid that is a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor and has been sold online as a designer drug. While MDMB-CHMICA was initially sold under the name "MMB-CHMINACA", the compound corresponding to this code name (i.e. the isopropyl instead of t-butyl analogue of MDMB-CHMINACA) has been identified on the designer drug market in 2015 as AMB-CHMINACA.

Bromazolam (XLI-268) is a benzodiazepine derivative which was first synthesised in 1976, but was never marketed. It has subsequently been sold as a designer drug, first being definitively identified by the EMCDDA in Sweden in 2016. It is the bromo instead of chloro analogue of alprazolam, and has similar sedative and anxiolytic effects. Bromazolam is a non subtype selective agonist at the benzodiazepine site of GABAA receptors, with a binding affinity of 2.81nM at the α1 subtype, 0.69nM at α2 and 0.62nM at α5.

Methoxyacetylfentanyl, commonly known as MAF is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of fentanyl and has been sold online as a designer drug.

Cyclopropylfentanyl is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of fentanyl and has been sold as a designer drug. Between June and December 2017, a total of 78 cyclopropylfentanyl-related deaths with analytical confirmation in post-mortem samples were reported by various European countries. Another 115 deaths involving cyclopropylfentanyl were reported from the United States in 2017.
Operation DRYER is a joint operation between the Spanish Civil Guard, Austrian police, and Europol working to shut down labs and organizations which produce designer drugs. Authorities seized over 4.5 million euros' worth of cryptocurrency, as well as 788,606 doses of LSD; these are the largest seizures of cryptocurrency and LSD in European history. The operation was revealed to the public on June 28, 2018.