
1,4-alpha-glucan-branching enzyme, also known as brancher enzyme or glycogen-branching enzyme is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GBE1 gene.
In enzymology, a 1,4-alpha-glucan 6-alpha-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction that transfers an alpha-D-glucosyl residue in a 1,4-alpha-D-glucan to the primary hydroxyl group of glucose or 1,4-alpha-D-glucan.
In enzymology, an isomaltulose synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1,3-beta-D-glucan phosphorylase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1,3-beta-oligoglucan phosphorylase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alpha-1,3-glucan synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alpha-1,4-glucan-protein synthase (ADP-forming) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an amylosucrase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cellodextrin phosphorylase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cellulose synthase (GDP-forming) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a dextrin dextranase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 4-alpha-glucanotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes a chemical reaction that transfers a segment of a 1,4-alpha-D-glucan to a new position in an acceptor carbohydrate, which may be glucose or a 1,4-alpha-D-glucan.
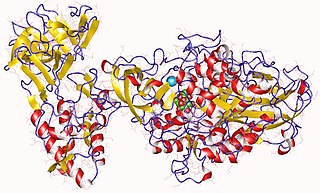
In enzymology, an alternansucrase is an enzyme that catalyzes a chemical reaction that transfers an alpha-D-glucosyl residue from sucrose alternately to the 6- and 3-positions of the non-reducing terminal residue of an alpha-D-glucan, thereby creating a glucan with alternating alpha-1,6- and alpha-1,3-bonds. The name "alternan" was coined in 1982 for the glucan based on its alternating linkage structure.
In enzymology, a NDP-glucose—starch glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a starch synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a sucrose-1,6-alpha-glucan 3(6)-alpha-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Sucrose-phosphate synthase (SPS) is a plant enzyme involved in sucrose biosynthesis. Specifically, this enzyme catalyzes the transfer of a hexosyl group from uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-glucose) to D-fructose 6-phosphate to form UDP and D-sucrose-6-phosphate. This reversible step acts as the key regulatory control point in sucrose biosynthesis, and is an excellent example of various key enzyme regulation strategies such as allosteric control and reversible phosphorylation.

In enzymology, a sucrose synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Glucansucrase is an enzyme in the glycoside hydrolase family GH70 used by lactic acid bacteria to split sucrose and use resulting glucose molecules to build long, sticky biofilm chains. These extracellular homopolysaccharides are called α-glucan polymers.
Dextranase is an enzyme with systematic name 6-α-D-glucan 6-glucanohydrolase. It catalyses the following chemical reaction






