Shadwell is a census-designated place (CDP) in Albemarle County, Virginia. It is located by the Rivanna River near Charlottesville. The site today is marked by a Virginia Historical Marker to mark the birthplace of President Thomas Jefferson. It is listed on the National Register of Historic Places along with Clifton.

The Cane River Creole National Historical Park was established in 1994 to preserve the resources and cultural landscapes of the Cane River region in Natchitoches Parish, Louisiana. Located along Cane River Lake, the park is approximately 63 acres and includes two French Creole cotton plantations, Oakland and Magnolia. Both plantations are complete in their historic settings, including landscapes, outbuildings, structures, furnishings, and artifacts; and they are the most intact French Creole cotton plantations in the United States. In total, 65 historic structures and over a million artifacts enhance the National Park Service mission as it strives to tell the story of the evolution of plantation agriculture through the perspective of the land owners, enslaved workers, overseers, skilled workers, and tenant farmers who resided along the Cane River for over two hundred years. This park is included as a site on the Louisiana African American Heritage Trail.

Yulee Sugar Mill Ruins Historic State Park is a Florida State Park located in Homosassa, off U.S. 19. It contains the ruins of a forced-labor farm owned by David Levy Yulee. Yulee was an enslaver and a delegate of the Florida Territorial Legislative Council. After Florida became a state, he was elected by the legislature in 1845 to the United States Senate, becoming the first American of Jewish heritage to serve there. After Florida seceded from the Union, Yulee served in the Confederate Congress. He is credited with having developed a network of railroads that tremendously boosted the state's economy.

Oatlands Historic House and Gardens is an estate located in Leesburg, Virginia, United States. Oatlands is operated by the National Trust for Historic Preservation and is listed on the National Register of Historic Places as a National Historic Landmark. The Oatlands property is composed of the main mansion and 415 acres of farmland and gardens. The house is judged one of the finest Federal period country estate houses in the nation.

McLeod Plantation is a former slave plantation located on James Island, South Carolina, near the intersection of Folly and Maybank roads at Wappoo Creek, which flows into the Ashley River. The plantation is considered an important Gullah heritage site, preserved in recognition of its cultural and historical significance to African-American and European-American cultures.

Magnolia Plantation is a former cotton plantation in Natchitoches Parish, Louisiana. The site was declared a National Historic Landmark in 2001, significant as one of the most intact 19th-century plantation complexes in the nation, as it is complete with a suite of slave cabins and numerous outbuildings and period technology. Included in the Cane River Creole National Historical Park, Magnolia Plantation is also a destination on the Louisiana African American Heritage Trail. It is one of two plantations in the park; the other is Oakland Plantation.

The Varner–Hogg Plantation State Historic Site is a historical site operated by the Texas Historical Commission. The site was the home of former Governor of Texas James S. Hogg and his family. The site is located outside West Columbia, in Brazoria County.

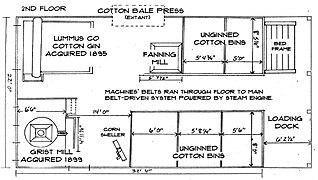
The Lenoir Cotton Mill was a 19th-century cotton mill located in the U.S. city of Lenoir City, Tennessee. One of the earliest examples of industrial architecture in Tennessee, the mill operated variously from its construction around 1830 until the 1950s. The mill was documented by the Historic American Buildings Survey and placed on the National Register of Historic Places in the 1970s. Efforts to restore the mill began in 1980, but before the restoration could be completed, the mill was destroyed by arson in 1991.

Plantation complexes were common on agricultural plantations in the Southern United States from the 17th into the 20th century. The complex included everything from the main residence down to the pens for livestock. Until the abolition of slavery, such plantations were generally self-sufficient settlements that relied on the forced labor of enslaved people.
Pearce's Mill is a former mill site east of Hamilton in Marion County, Alabama. The mill was founded along the Buttahatchee River in the 1840s, before being abandoned during the Civil War. James P. Pearce returned to the mill in 1865 and developed it into an economic center in the region. At its height in the 1870s, the complex hosted a general store with a post office, a gristmill, sawmill, flour mill, and cotton gin, in addition to the family house. Pearce's mule teams carried the mills' production to market in Tuscumbia. as improved roads and railroads drove commerce to Hamilton and other nearby towns, the store closed in 1930, and the mills ceased operation in 1959.

Waverly is a historic home and farm located near Burnt Chimney, Franklin County, Virginia. It was built beginning about 1853 for Armistead Lewis Burwell (1809-1883) and his family, who inherited it from the parents of his wife, Mary Hix (1811-1895). Descended from the First Families of Virginia, Armistead L. Burwell operated a tobacco and grain plantation of about 350 improved acres using enslaved labor, and also had a chewing tobacco factory, gristmill and sawmill by 1860. His son William A. Burwell (1836-1882) ran the factory and bought the plantation from his father in 1864, and sold it in 1868 to his younger brother John Spotswood Burwell who operated a dairy farm until after the turn of the century.

The McIntosh Sugarworks, near St. Marys, Georgia, was built in the late 1820s by John Houstoun McIntosh. They are a significant example of tabby concrete architecture and represent an industrial component of southeastern plantation agriculture. The Tabby Ruins, as they are also known, are at 3600 Charlie Smith Sr. Highway at Georgia Spur 40, six miles north of St. Marys. The entrance is approximately across the street from the entrance to the Naval Submarine Base Kings Bay, on Charlie Smith Highway, at 30.79310°N 81.57712°W.

TheCagle House is a historic house in an area known as Cagletown, Jasper, Georgia. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places on March 20, 2002. It is located on Waleska Highway 108, approximately 1+1⁄2 miles west of Georgia 5/515.

Historic Oak View, also known as the Williams-Wyatt-Poole Farm, is a 19th-century historic farmstead and national historic district located east of downtown Raleigh, North Carolina, United States. Founded as a forced-labor farm worked by black people enslaved by the land's white owners, Oak View features an early 19th-century kitchen, 1855 farmhouse, livestock barn, cotton gin barn, and tenant house dating to the early 20th century. The Farm History Center located on site provides information to visitors regarding the history of the Oak View and the general history of farming in North Carolina. Aside from the historic buildings, the site also features an orchard, a honey bee hive, a small cotton field, and the largest pecan grove in Wake County.

Motor is an unincorporated community in Clayton County, Iowa, United States. The townsite is also a nationally recognized historic district listed as a historic site on the National Register of Historic Places in 1977.
Oaklyn Plantation is a historic plantation and national historic district located near Darlington, Darlington County, South Carolina. The district encompasses 40 contributing buildings, 6 contributing sites, 2 contributing structures, and contributing object. Founded as a forced-labor farm worked by black people enslaved by the land's white owners, it was one of the major plantation establishments of the county and served as the seat of the Williamson family for more than 200 years.

The Hofwyl-Broadfield Plantation was a plantation on the Altamaha River in Glynn County, Georgia, United States. Operated as a forced-labor farm using enslaved peoples until 1865, it produced rice from 1800 until 1915, when growing rice became unprofitable. Then it was primarily a dairy farm until 1942. Since 1976, the Georgia Department of Natural Resources has managed it as Hofwyl-Broadfield Plantation State Historic Site.

Frogmore Plantation is an historic, privately owned cotton plantation complex, located near Ferriday in Concordia Parish, Louisiana. Since 1997, Frogmore Plantation is a working farm, tourist attraction featuring many structures, and educational center. Buildings on the site include a cotton gin, and a plantation manor house named Gillespie. Formerly this plantation relied on enslaved African American labor.

Birdsville Plantation, in Birdsville, Jenkins County, Georgia near Millen, is a 50 acres (20 ha) property which was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1971. It then included 10 contributing buildings. It is a National Bicentennial Farm.

The Terrell-Sadler House near Eatonton, Georgia was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2000. It is located at 122 Harmony Road.